Introduction
Korean cattle have a long history and tradition. Four major breeds include Korean brown cattle (Hanwoo), Korean black cattle (KBC), Jeju black cattle (JBC), and Korean brindle cattle (Chikso; Lee et al., 2014). The well-known Hanwoo cattle breed boasts the largest population in South Korea. In contrast, the populations of the other three breeds are relatively minor. Specifically, JBC are exclusively found on Jeju Island (Han et al., 2011). Among these, Hanwoo is renowned for its superior meat quality, which is characterized by its marbling and rich flavor, making it highly popular among consumers (Jo et al., 2012). KBC refers to black cattle raised in regions outside Jeju Island and exhibit distinct characteristics from JBC. Although comparative studies between KBC and other native Korean cattle breeds are limited, recent research has reported that JBC showed enhanced flavor and umami due to its higher oleic acid content and flavor-related compounds than KBC (Hoa et al., 2024). According to historical records, JBC was renowned for being presented as a tribute to the king. The unique taste and quality of JBC enriched the royal table, serving as a historical testament to the breed’s excellence during the Joseon Dynasty. This tradition continues to elevate the value and reputation of JBC today.
Beef is an important animal food source that provides essential nutrients, including essential amino acids, unsaturated fatty acids, minerals, and various vitamins (Ahmad et al., 2018). The nutritional value of meat has garnered significant attention in recent years. Fatty acid composition is a crucial indicator of beef quality, influencing flavor, juiciness, tenderness, and overall taste, which in turn greatly affects consumer preferences (Davis et al., 2022). Numerous studies have shown that diets rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) have significant health benefits, such as reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and premature death.
The accumulation of fatty acids is regulated by various biological processes (BPs) such as fatty acid synthesis, transport, degradation, and beta-oxidation (Ahmad et al., 2018). Several studies have previously been conducted to identify candidate variants and genes related to fatty acid composition in cattle (Wang et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2022). Furthermore, many studies have explored the genetic basis of fatty acids in muscles using multi-omics approaches, including transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic analyses. For example, transcriptome analysis of bovine longissimus dorsi and skeletal muscle revealed that differentially expressed genes (DEGs) are involved in various pathways, such as fatty acid degradation and beta-oxidation, as well as PPAR and AMPK signaling pathways (Fernyhough et al., 2007; Underwood et al., 2008). In addition to the role of fatty acids, the amino acid composition of beef is a fundamental determinant of its quality, sensory attributes, and nutritional efficacy. Amino acids such as glutamic acid and alanine are pivotal in imparting umami and sweet flavors, while serine, glycine, and methionine modulate taste profiles, influencing sweetness and bitterness perceptions (Kirimura et al., 1969; Lindemann, 1996; Nelson et al., 2002; Shallenberger and Acree, 1967). Beyond their organoleptic contributions, amino acids are indispensable for human health, facilitating vital processes such as protein synthesis and enzymatic functions and serving as precursors for bioactive compounds (Chakrabarti et al., 2018). Consequently, the amino acid profile augments beef’s palatability and nutritional value, thereby shaping consumer preferences and influencing the marketability of various beef breeds.
Recently, a series of comparative studies have been performed to evaluate the meat quality of native Korean cattle breeds. Notably, investigations have focused on the carcass and meat quality and the sensory attributes of Hanwoo and Chikso (Hoa et al., 2023a; Hoa et al., 2023b; Lee et al., 2023; Utama et al., 2018). In summary, comparative studies on the meat quality of Korean cattle breeds suggest that Hanwoo is notable for its high intramuscular fat content, tender meat quality, and significantly elevated levels of umami-related amino acids. However, the perception of umami can also be affected by cooking methods, specific meat cuts, and individual taste preferences.
Despite these findings, there remains a gap in understanding the specific genetic factors that contribute to the distinct meat quality and flavor of different Korean cattle breeds. Therefore, a comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of candidate genes for different beef cuts using high-throughput RNA sequencing can help elucidate potential gene expression regulation related to fatty acid composition.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the free amino acids, constituent amino acids, and fatty acids of Hanwoo, JBC, and KBC and to investigate their meat quality characteristics. Particularly, we compared the expression levels of flavor-related genes among the breeds through RNA transcriptome analysis. JBC, with its high oleic acid content, possesses a unique flavor, which may be closely related to the expression of specific genes. This research aims to elucidate how genetic differences among cattle breeds affect the taste and nutritional components of the meat, providing crucial foundational data for developing genetic selection programs aimed at improving meat quality. Additionally, this study provides important insights to preserve the unique characteristics of Korean indigenous cattle and enhance their competitiveness in the global market.
Materials and Methods
The longissimus lumborum was utilized in this study. For the analysis, samples were collected from five JBC, five Hanwoo cattle, and five KBC, all obtained from a local meat supplier in Jeju, 24 h post-slaughter. All experimental animals were raised on various farms across Jeju Island. The animals were all castrated males, with slaughter ages of 34.4±0.9 months for KBC (487.0±12.9 kg carcass weight), 40.1±7.9 months for JBC (438.8±70.9 kg carcass weight), and 31±1.4 months for Hanwoo (453.3±30.7 kg carcass weight). All animals were fed commercially available feed. The cattle used in this study were all graded as the highest quality (1++) according to the standards of the Korean Institute for Animal Products Quality Evaluation (KAPE). The detailed beef grading criteria of Korea are presented in Table 1.
1) Evaluates the distribution of intramuscular fat with higher scores indicating greater marbling. Higher grades are given to beef with higher marbling, and marbling scores of 7, 8, or 9 correspond to grade 1++.
2) Evaluates the color of the meat, with overly pale or overly dark colors being undesirable. Grades 3 to 5 are considered ideal for high-quality beef.
3) Assesses the color of fat within the muscle and the surrounding fat. Grades 1 to 4 are rated highest for fat quality and are categorized as 1++.
The proximate analysis of the longissimus lumborum samples was conducted using Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) methods specific for moisture, protein, fat, ash, and carbohydrate content determination (AOAC, 2019).
The temperature at 24 h postmortem and pH of the longissimus lumborum were measured using a spear-type pH meter (206-pH2, Testo, Titisee-Neustadt, Germany). The meat color was measured using a Minolta chromameter (CR-300, Konica Minolta, Osaka, Japan) after exposing the meat surface to air for 30 min. The average of three measurements was recorded, and the results were expressed as CIE L*, CIE a*, and CIE b* values.
The longissimus lumborum was cut into a rectangular shape (2 cm×4 cm×6 cm), tightly wrapped in a polyethylene bag, and heated to 85°C in a water bath (KMC-1205W1, Vision, New York, NY, USA). Once the core temperature reached 75°C, the samples were cooled in cold water for 20 min. After removing surface moisture, cooking loss was calculated as the percentage difference between the initial and final weights relative to the initial weight.
Longissimus lumborum pieces, 3 cm in thickness, were sealed in polyethylene bags and heated to 85°C in a water bath (KMC-1205W1, Vision). Once the core temperature reached 80°C, the samples were cooled in cold water for 20 min. After cooling, a 13 mm-diameter steel borer (Cork borer No. 6, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used to collect cylindrical samples. These samples were then sliced into 1 cm-thick sections perpendicular to the muscle fibers and subjected to shearing using a texture analyzer (Texture Analyzer CT3, Brookfield, New York, NY, USA). Defined as the peak force exerted by the machine to shear the sample, the shear force, indicating the toughness of the meat, was measured in Newtons (N). The conditions for shear force measurement with the CT3 Texture Analyzer were a target displacement of 20 mm, a trigger load of 10 g, and a test speed of 1 mm/s. The measurement was carried out in a single cycle with a TA-52 probe and a TA-SBA fixture.
A texture analyzer (CT3, Brookfield) was used to perform texture profile analysis (TPA), which included the measurement of hardness, adhesiveness, resilience, cohesiveness, springiness, gumminess, and chewiness. This test simulates the chewing process with a two-cycle compression (Barbut, 2015). Longissimus lumborum samples were cut into 3 cm-thick pieces, tightly wrapped in polyethylene bags, and cooked in a water bath at 85°C. Once the core temperature reached 75°C, the samples were cooled in cold water for 20 min. After cooling, six subsamples, each measuring 2.5 cm×2.5 cm×2.5 cm, were prepared for TPA. The probe moved at 2.0 mm/s (pre-test), 1.0 mm/s (test), and 4.5 mm/s (post-test). It compressed the samples to 75% of their thickness, retracted to the initial contact point, paused for 2 s, and then initiated the second compression cycle.
For the analysis of free amino acids, 200 mg of longissimus lumborum sample was homogenized in 10 mL of 70% ethanol and sonicated for 30 minutes. After sonication, the mixture was centrifuged at 15,000×g for 15 minutes. The supernatant was carefully collected and filtered through a 0.45-μm aqueous syringe filter to remove any particulates. A 20 μL aliquot of the filtered extract was then mixed with 20 μL of an internal standard solution containing 50 μM of norvaline (Sigma-Aldrich). The resulting mixture was injected into the gas chromatography system with flame ionization detection (GC-FID) for analysis. The column used was a ZB-AAA (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA), measuring 10 meters by 0.25 mm. Nitrogen (N2) was used as the carrier gas with a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min. The injector temperature was set to 250°C, and the detector temperature to 320°C, with a split ratio of 5:1. Identification and quantification of the free amino acids were performed by comparing the retention times and peak areas with those of a standard amino acid solution (Phenomenex).
For the constituent amino acid analysis, 200 mg of longissimus lumborum sample was hydrolyzed with 30 mL of 6 N HCl at 110°C for 24 h and filtered through a 0.45-μm aqueous syringe filter. A mixture of 20 μL of the hydrolyzed sample and 20 μL of diluent was then analyzed using GC-FID. The column used was a ZB-AAA (Phenomenex), measuring 10 meters by 0.25 mm. The carrier gas was N2 at a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, with the injector set to 250°C, the detector set to 320°C, and a split ratio of 5:1. The identification and quantification of amino acids were achieved by comparing the retention times and peak areas with those of a standard amino acid solution (Phenomenex).
The fatty acid composition was analyzed by GC-FID. The GC column used was an SPR®-2560 (Sigma-Aldrich), measuring 100 m in length, with an internal diameter of 0.25 mm and a film thickness of 0.2 μm. For the analysis, 25 mg of longissimus lumborum sample was extracted and methylated by adding 14% BF3 in methanol, then diluted with 1 mL of isooctane. The GC operating conditions included an N2 gas flow rate of 0.8 mL/min, an injector temperature of 240°C, a detector temperature of 285°C, and a split ratio of 100:1. Fatty acid peaks were identified by comparing retention times with those of a standard fatty acid mixture (Supelco 37 Component FAME Mix, Sigma-Aldrich) under the same conditions.
A completely randomized design was adopted to analyze the main effect of the experimental factor. The significance of the model was determined using analysis of variance (ANOVA), and Duncan’s multiple range test was performed when the main factors were significant (p<0.05). All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS software v.9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA; SAS, 2023).
The longissimus lumborum samples were stored in a –80°C ultra-low temperature freezer until RNA extraction. RNA extraction and library construction were outsourced to Macrogen (Seoul, Korea).
The quality of the raw data was assessed for total bases, read count, GC (%), AT (%), Q20 (%), and Q30 (%) using the FastQC program (version 0.12.0; https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/). Subsequently, low-quality reads were filtered out using the Trimmomatic program (version 0.39). The trimmed reads were then re-evaluated with the FastQC program to ensure quality. Next, the trimmed data were aligned to the cattle reference genome using HISAT2 software (version 2.2.1). For this alignment, the reference genome assembly used was Bos taurus (GCA_002263795.4) from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The resulting SAM format data files were converted to BAM files using SAMtools software (version 1.17). The number of reads mapping to each gene or gene group was quantified using the featureCounts software (subread-2.0.6) on the BAM files. For featureCounts, the reference annotation file used was NCBI’s B. taurus (GCF_002263795.3). The calculated gene read counts were then utilized for DEG analysis using R software and associated packages. DEGs were identified based on criteria of false discovery rate (FDR<0.05) and p-value (<0.05).
Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of DEGs were performed using the DAVID web tool (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/). The functional enrichment of the gene list was also assessed using DAVID, and functions and pathways related to cultivar biological differences were identified. In DAVID, the Sus scrofa species was used as the basis for GO and KEGG databases. After that, GO terms and KEGG pathways with FDR<0.05 were identified. In addition, the DEG results were analyzed using the ClueGO (v2.5.10) tool in the Cytoscape 3.10.1 environment to identify major groups with p-value<0.05 in the correlated pathways and functional networks.
Results and Discussion
Table 2 compares the proximate composition and meat quality attributes among JBC, Hanwoo cattle, and KBC. The differences in parameters of the proximate composition among the groups were not statistically significant. For pH, temperature, meat color, and cooking loss, these parameters also showed no significant differences among the groups. According to previous research, the elevated intramuscular lipid content observed in Aberdeen Angus, Highland, and Jersey breeds may partially account for their enhanced flavor profiles, while the reduced intramuscular fat content in Limousin cattle might contribute to their comparatively subdued beef flavor (Gagaoua et al., 2016). Variations in lipid content, intramuscular collagen, and fiber type are considered significant factors influencing the sensory quality of beef (Chriki et al., 2012; Chriki et al., 2013). However, it is essential to note that these differences are inconsistently associated with muscle type, animal breed, and the breed’s primary production function, whether dairy or meat-oriented.
Regarding meat color, several studies indicate that Bos indicus breeds exhibit darker meat color and higher pH values, particularly when pasture-fed than B. taurus (Cafe et al., 2011; Gama et al., 2013). Furthermore, the increased fat deposition observed in the meat of B. taurus cattle contributes to a lighter muscle coloration than that of B. indicus cattle. However, research on the relationship between meat color and specific commercial meat cattle breeds is limited. Moreover, these results should consider individual nutritional status and production systems. In our study, when selecting samples, we ensured that all samples were of the same grade according to the evaluation criteria of KAPE, which likely explains the lack of significant differences in the meat quality attributes.
In the case of shear force (Table 3), the value was significantly higher in JBC (8,591.98±1,128.72) compared to the other groups (p<0.05). This difference can be attributed to the fact that breeds differ in muscle growth potential and muscle characteristics, which affect meat texture. Although previously extending the aging period of beef appears to mitigate differences in sensory quality across breeds, in our study, since samples were used 24 h post-mortem, the differences in tenderness among breeds due to aging are considered to have a minimal impact on the shear force results. Notably, after one week of aging, fast-growing breeds such as Pirenaica and Rubia Gallega exhibited superior tenderness scores compared to the double-muscled Spanish breed (Asturiana de los Valles), the dual-purpose breed (Brown Swiss), and rustic breeds (Avilena-Negra Iberica, Morucha, and Retinta). However, these differences in tenderness were no longer statistically significant following 21 days of aging (Campo et al., 1999). Additionally, greater collagen content of tissue has been observed in the longissimus muscle of Angus steers compared to Limousin steers (Chambaz et al., 2003), and in Limousin steers compared to double-muscled Belgian Blue cattle (Raes et al., 2003). This implies that differences in collagen content among breeds can affect meat tenderness. Furthermore, the shear force is positively correlated with intramuscular collagen content, the degree of cross-linked collagen development, and the amount of insoluble collagen, all of which increase with age (Bruce and Roy, 2019). Additionally, it was previously reported that type IIX muscle fibers positively correlated with increased shear force (Cho et al., 2024). Although this study did not investigate the muscle fiber characteristics of cattle groups’ muscle samples, our result of shear force aligns with Cho et al. (2024), which found that the longissimus lumborum of JBC exhibits higher shear force than Hanwoo cattle. Moreover, JBC, which was slaughtered at a relatively older age compared to Hanwoo and KBC in this study, is suggested to have higher collagen content, more cross-linked collagen, and a more significant amount of insoluble collagen than other breeds. These factors are considered to explain the high shear force observed in JBC in this study.
TPA is extensively used to assess the texture of meat and meat products, encompassing parameters such as hardness, springiness, adhesiveness, cohesiveness, gumminess, chewiness, and resilience (Novaković and Tomašević, 2017). This study performed TPA to test the cooked texture attributes of meat from three cattle breeds (Table 3). Excluding resilience, no statistical differences were observed in the texture parameters among the groups. As mentioned above, the resilience values of JBC and Hanwoo were significantly higher when compared to KBC (p<0.01). Generally, among the TPA parameters, hardness and shear force are accepted as indicators for estimating meat tenderness (Caine et al., 2003). While both TPA and shear force evaluate aspects related to the tenderness of meat texture, they do so through different mechanisms: TPA through compression and Warner-Bratzler shear force through shearing. These differences in measurement can lead to variations in results, especially concerning aspects of texture not directly related to tenderness (Novaković and Tomašević, 2017). For this reason, both measurements were presented in this study to provide a more comprehensive evaluation. In our study, the differences in shear force among breeds, but not in hardness, are considered to be due to methodological differences.
The analysis of the free amino acid contents in the longissimus lumborum of different cattle groups is exhibited in Table 4. Compared to KBC, the two other cattle groups (JBC and Hanwoo cattle) exhibited significantly higher levels of glutamic acid, glycine, and phenylalanine, whereas KBC had a significantly higher arginine content compared to the other cattle breeds. For alanine, Hanwoo had a significantly higher content than KBC. In the case of serine and threonine, Hanwoo showed significantly higher serine values than the other two cattle breeds and had a significantly higher threonine content than JBC.
In analysis of the constituent amino acids contents (Table 5), lysine, valine, arginine, isoleucine, and phenylalanine were observed to be significantly lower in JBC than in the other cattle breeds. On the other hand, KBC had significantly lower levels of glutamic acid compared to JBC and Hanwoo. According to previous research, an analysis of amino acids in the longissimus dorsi muscle of Hanwoo and JBC under identical rearing conditions showed that Hanwoo had a higher glutamic acid content than JBC (Lee et al., 2019). Our study does not provide feeding information; therefore, this study suggests that the differences in amino acid profiles are likely due to distinct metabolic pathways and dietary factors among the cattle groups. Higher levels of specific amino acids, such as arginine and glutamic acid, could have significant implications for the nutritional and flavor profiles of the longissimus lumborum (Chen and Liu, 2004; Khan et al., 2015). For instance, arginine is known for its role in protein synthesis and metabolic processes (Wu et al., 2009), and glutamic acid is a key contributor to the umami taste, enhancing the meat’s flavor (Kurihara, 2015).
In our study, the analysis of the constituent amino acids in longissimus lumborum revealed significant differences among the cattle groups. JBC showed a lower content of arginine, which is involved in protein synthesis and metabolic processes, compared to other cattle groups. Meanwhile, JBC and Hanwoo exhibited significantly higher levels of glutamic acid, which can influence umami and meat flavor, compared to KBC. These findings have significant implications for both the nutritional value and sensory attributes of meat, providing valuable information for consumers, producers, and the meat industry. Future research could further explore the factors contributing to these differences and their potential impacts on meat quality and health benefits.
The analysis of the composition of fatty acids in the longissimus lumborum of different cattle groups revealed significant differences in the proportions of several fatty acids (Table 6). Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) was present at significantly higher levels in Hanwoo than in JBC and KBC. In terms of palmitic acid (C16:0), Hanwoo exhibits the highest concentrations, followed by KBC and JBC. Although Hanwoo also shows a higher concentration of margaric acid (C17:0) than the other two groups, margaric acid accounted for a relatively low proportion of the total fatty acids, ranging from 0.58% to 0.96% in all cattle groups. For eicosenoic acid (C20:1, n-9), a MUFA, both JBC and Hanwoo display elevated levels compared to KBC. Additionally, linolenic acid (C18:3, n-3) was found in the highest concentrations in KBC, followed by Hanwoo and JBC. Oleic acid and linoleic acid are key fatty acids commonly found in beef, as identified in previous studies (Dryden and Maechello, 1970; Enser et al., 1996). Oleic acid has been reported to contribute significantly to the desirable flavor and savory taste of meat (Dryden and Maechello, 1970). These sensory attributes are highly valued by meat consumers, indicating that a high oleic acid content can enhance the overall palatability of beef. However, in this study, there were no significant differences in these two fatty acids among the cattle groups. Conversely, it was reported that saturated fatty acids (SFA) and MUFA were positively associated with eating quality traits, while PUFA negatively correlated with eating quality (Cameron and Enser, 1991). Although the levels of certain SFA such as pentadecanoic acid, palmitic acid, and margaric acid were significantly higher in Hanwoo, and KBC had the lowest levels of the unsaturated fatty acid eicosenoic acid, there were no differences in the overall ratios of total SFA, MUFA, and PUFA among the cattle groups in this study. Overall, the distinct fatty acid compositions among the cattle groups are likely influenced by genetic factors, diet, and environmental conditions. These factors, in turn, can significantly impact the nutritional and sensory qualities of the meat. Therefore, additional in-depth research on fatty acid composition is necessary to understand its impact on meat quality and health benefits.
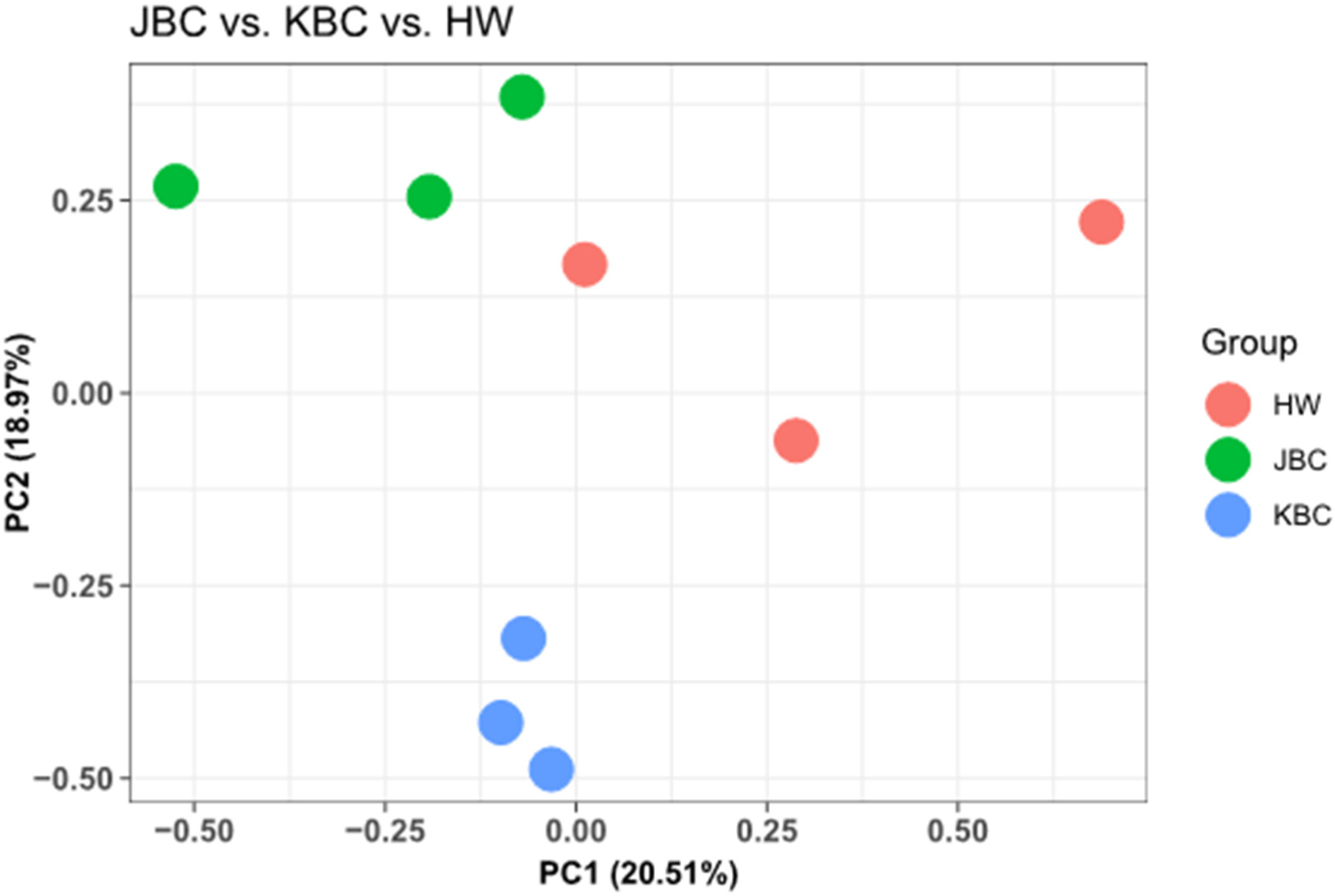
The transcriptomes of the longissimus lumborum of a total of nine cattle (3 cattle per group) were identified. An average of about 12.1 Gb of raw reads were generated from a total of 9 samples, and the averages of the GC and AT contents of the generated transcripts were 49.3% and 50.6% (ranges were 48.2%–50.8% and 49.3%–51.8%, respectively). The Q20 and Q30 percentages were 98.6%–99.0% and 95.7%–96.9%, respectively. The raw data statistics of the paired-end data of all cattle breeds analyzed in this study are provided in Supplementary Table S1. The generated sequences were mapped to the reference genome, and 97.8%–98.3% of the total sequences were mapped to each sample. Principal component analysis (PCA) is a widely used statistical technique for dimensionality reduction in genomic studies. It transforms high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional form while retaining most of the variance present in the original data (Lever et al., 2017).
This study performed PCA to analyze sequencing data, aiming to identify major sources of variance and visualize the relationships among cattle groups. The results confirmed clear differences among cattle groups. Principal component 1 (PC1) and principal component 2 (PC2) together explained 39.48% of the total variance, accounting for 20.51% and 18.97%, respectively. This indicates that these two components capture the most critical variations within the data. Fig. 1 summarizes the high-dimensional sequencing data, revealing distinct clusters and separations among the cattle groups. By elucidating the primary sources of variance within the dataset, PCA facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the underlying biological and experimental factors. This foundational insight paves the way for more in-depth investigations and robust interpretations of the observed data variability. This study conducted an analysis of differential gene expression between different cattle breeds, specifically comparing JBC with Hanwoo and KBC. Volcano plots were constructed to visualize the significant changes in gene expression levels, highlighting the genes that are most significantly up- or downregulated in each comparison (Fig. 2). Volcano plots are a key tool in genomics for visualizing differential expression data. They plot significance (p-value and FDR) against fold-change, allowing for the identification of genes that show both statistical significance and biologically meaningful changes in expression.
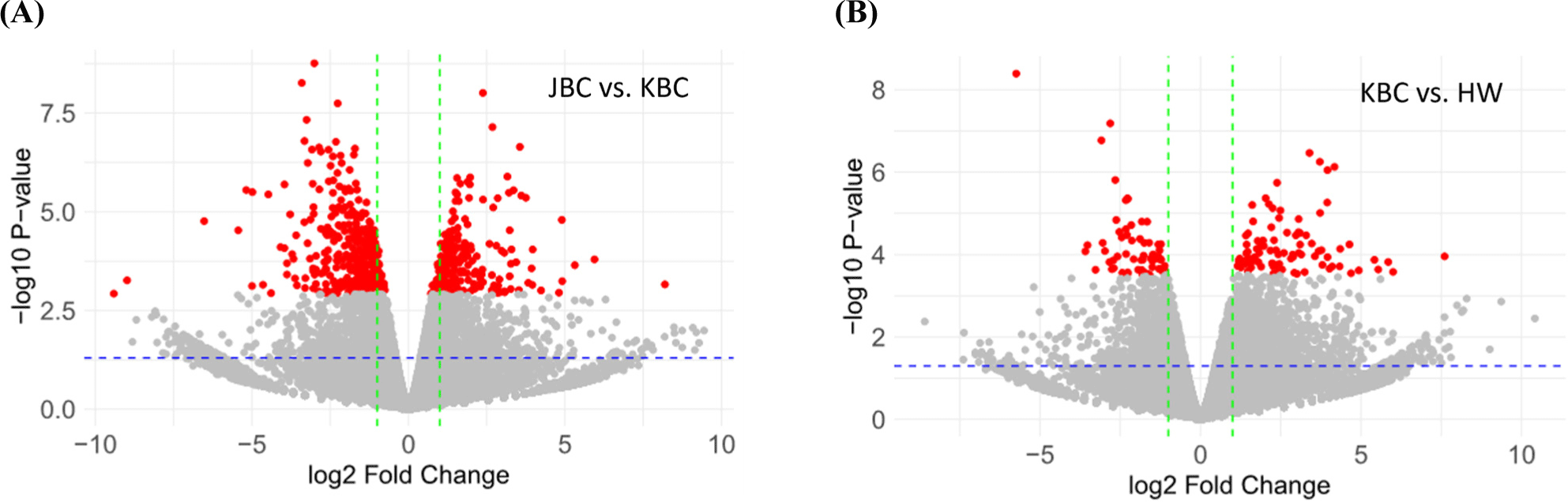
By constructing volcano plots to compare the gene expression profiles of JBC with Hanwoo and KBC, this study aimed to uncover critical genetic differences that may underpin phenotypic variations (Chen et al., 2016; Love et al., 2014; Soneson and Delorenzi, 2013). The volcano plots (Figs. 2A and B) revealed distinct patterns of differential gene expression. In the comparison between JBC and KBC, the volcano plot showed several genes that were significantly upregulated and downregulated in JBC compared to Hanwoo. Notable genes that exhibit high fold-changes and low p-values and FDR are highlighted (red dots), indicating their potential role in distinguishing the two breeds. Conversely, in the volcano plot analysis comparing JBC and Hanwoo, no genes satisfied the thresholds for both FDR and p-value.
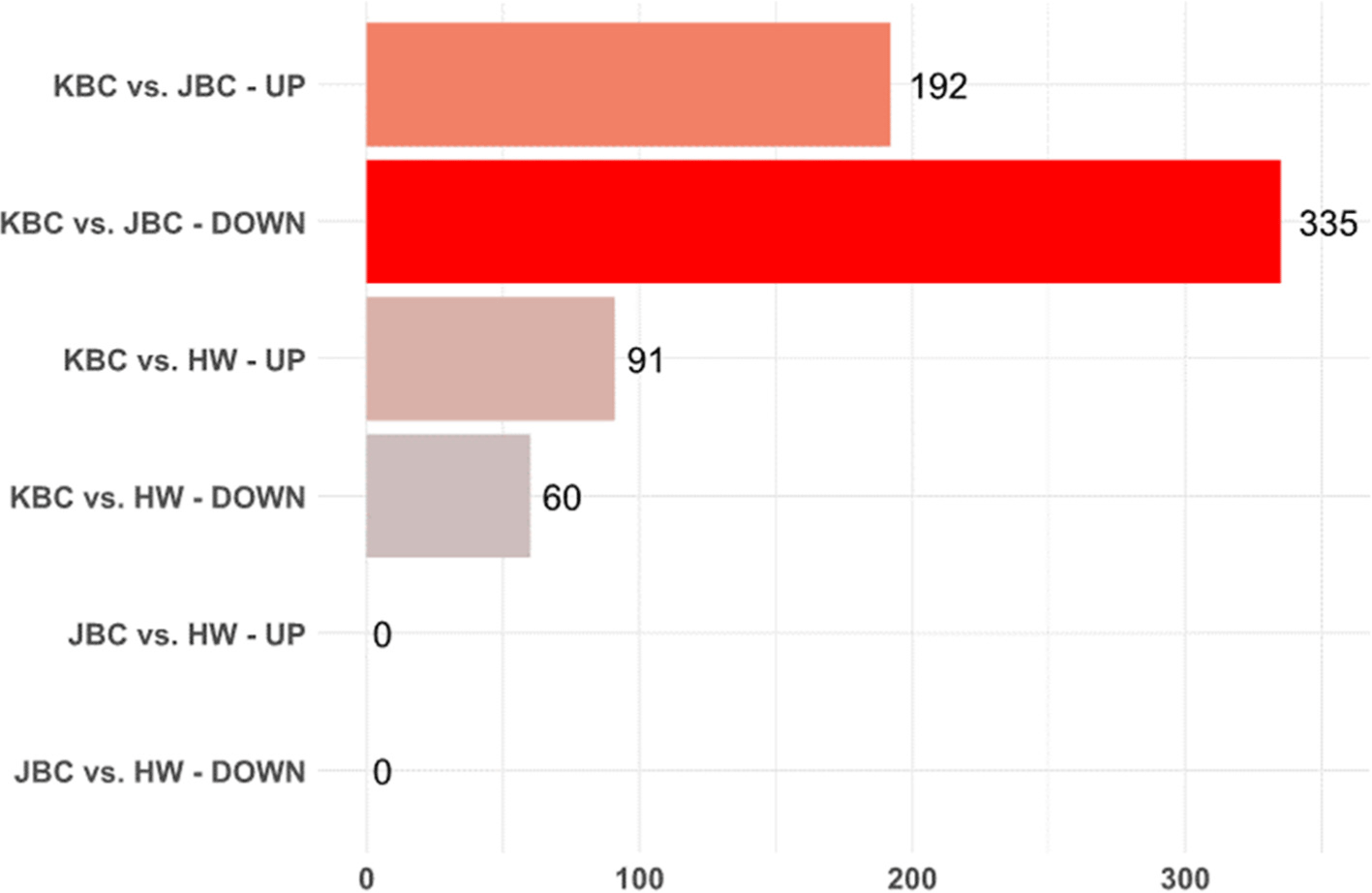
In the transcriptome analysis performed to identify the DEGs between JBC and KBC, 192 and 335 genes were upregulated and downregulated, respectively, based on an FDR<0.05 (Fig. 3). Among the 527 DEGs, the top 10 upregulated and top 10 downregulated genes were selected based on the highest absolute values of Log 2 fold change. Genes with unknown or uncharacterized functions were excluded from this analysis. The top 10 upregulated genes included A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase With Thrombospondin Motifs 8 (ADAMTS8), SH3 Domain Binding Kinase Family Member 3 (SBK3), Monoacylglycerol O-Acyltransferase 1 (MOGAT1), Histone H1.6 (H1-6), Heat Shock Protein Family A (Hsp70) member 6 (HSPA6), Natriuretic Peptide C (NPPC), Carbohydrate Sulfotransferase 8 (CHST8), Leucine Rich Repeat Containing 15 (LRRC15), and Regulator of G-protein Signaling 16 (RGS16) were selected. The top 10 downregulated genes were Glutamate Transporter 1 Domain Containing 1 (GLT1D1), ADP Ribosylation Factor Like GTPase 5C (ARL5C), WD Repeat Domain 72 (WDR72), Angiopoietin Like 8 (ANGPTL8), BPI Fold Containing Family B Member 5 (BPIFB5), Family With Sequence Similarity 205 Member C (FAM205C), NOP2/Sun RNA Methyltransferase Family Member 7 (NSUN7), DIRAS Family GTPase 3 (DIRAS3), Ectodysplasin A2 Receptor (EDA2R), and Solute Carrier Family 38 Member 4 (SLC38A4) were identified. Among these genes, MOGAT1 is involved in lipid metabolism, specifically the synthesis of diacylglycerol from monoacylglycerol, and it also plays a critical role in energy storage and lipid homeostasis (Lee and Kim, 2017; Yen et al., 2002). ANGPTL8 is important in lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis and regulates triglyceride levels and insulin sensitivity (Luo and Peng, 2018; Zhang, 2012). SLC38A4 is considered to be involved in metabolic processes as an amino acid transporter, playing a role in the uptake and regulation of amino acids in various tissues (Mackenzie and Erickson, 2004). The identified genes may contribute to phenotypic differences between JBC and KBC, such as growth rate, fat deposition, or adaptability to environmental conditions. The differential expression of genes exhibiting these biological functions may contribute to variations in meat quality, as well as the composition of amino acids and fatty acids. These findings suggest that genetic differences could underlie the meat quality traits observed among different cattle breeds. Further research is warranted to explore these associations and to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which these genes influence meat quality and composition.
The heatmap in Fig. 4A shows gene expression patterns between JBC and KBC, highlighting distinct clusters of samples and genes. This clustering suggests co-regulated genes or genes with related functions that are differentially expressed between these breeds. Genes with higher expression in JBC are grouped, indicating upregulation, while those with lower expression form separate clusters, reflecting downregulation. The distinct grouping of JBC and KBC samples underscores the genetic and phenotypic differences between the breeds, supporting the differential expression analysis. The color gradient in the heatmap visualizes gene expression levels, with brighter colors for higher expression and darker for lower, enhancing understanding of expression dynamics.
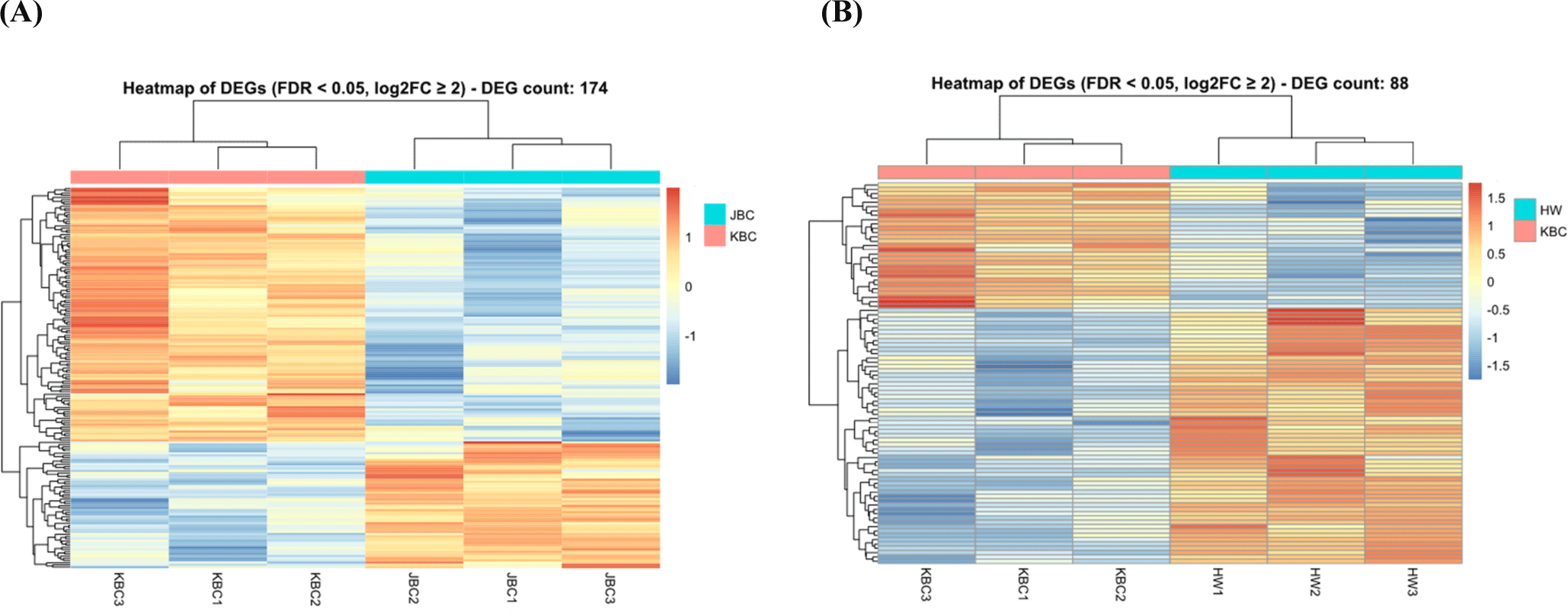
Fig. 4B presents the heatmap of DEGs between Hanwoo and KBC. Rows correspond to genes and columns to samples, with the color scale indicating normalized expression levels—red for high and blue for low. Hierarchical clustering dendrograms show sample and gene groupings based on expression pattern similarities, revealing distinct profiles between HW and KBC. This color intensity aids in identifying genes significantly upregulated or downregulated, illustrating genetic and phenotypic differences between the breeds.
The functional analysis results of the identified 594 DEGs (JBC vs. KBC) were classified into three groups: BP, cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF). The DEGs were confirmed to be related to 129 BPs, 40 CCs, and 23 MFs through the DAVID website (p<0.05). The detailed annotation results are shown in Fig. 5A. Functional annotations discovered for CC included collagen trimer (GO:0000005581, FDR<0.5).
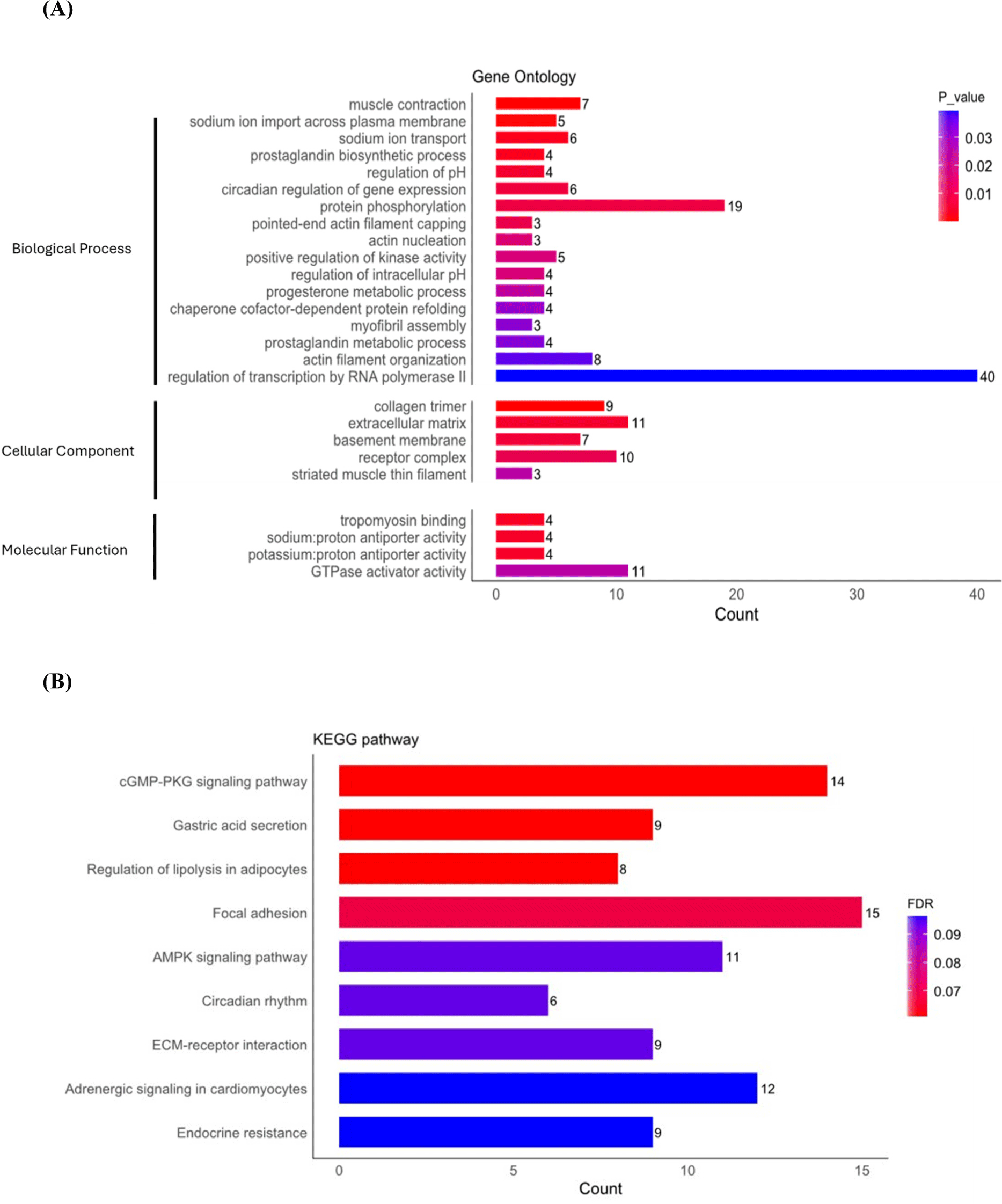
KEGG pathway analysis was performed to explore the molecular interaction network and the biological functions of DEGs (Fig. 5B). The nine KEGG pathways (FDR<0.1) encompass cGMP-PKG signaling pathway (bta04022), gastric acid secretion (bta04971), regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes (bta04923), focal adhesion (bta04510), AMPK signaling pathway (bta04152), circadian rhythm (bta04710), ECM-receptor interaction (bta04512), adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes (bta04261), and endocrine resistance (bta01522), pathways. Notably, both the AMPK signaling pathway and the regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes exhibit interconnected roles in orchestrating energy metabolism and lipid composition within muscle tissues. Their synergistic actions are pivotal for the development of high-quality meat, characterized by desirable attributes such as marbling, tenderness, and a favorable fatty acid profile. Conversely, in the GO and KEGG pathway analyses based on FDR criteria for JBC and HW, no significant terms or pathways were identified. Consequently, terms and pathways were selected based on p-values (Supplementary Fig. S1). The number of terms and pathways identified for JBC vs. HW was relatively fewer compared to those identified for JBC vs. KBC. This suggests that the variability in DEGs for JBC vs. HW is relatively smaller than that for JBC vs. KBC.
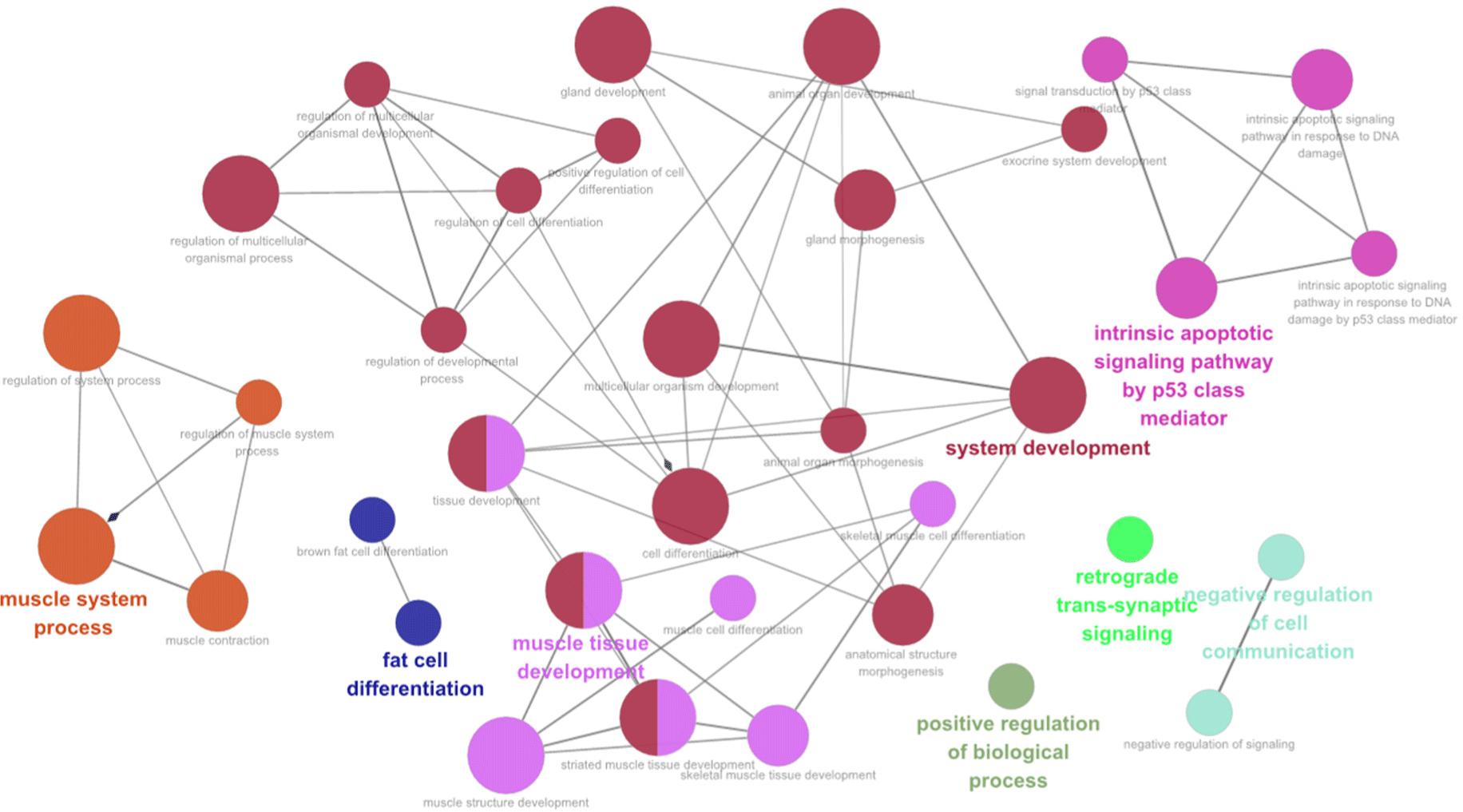
The network analysis revealed significant differences in GO terms and KEGG pathway interactions between JBC and KBC. The analysis identified substantial network in muscle system processes, fat cell differentiation, system development, muscle tissue development, intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathways mediated by the p53 class, and the positive regulation of BPs (Fig. 6). Furthermore, the network analysis elucidated the interrelationships between the identified terms and pathways. Additionally, a network analysis was conducted between KBC and Hanwoo. The network relationships observed in this comparison differed from those identified in the analysis between JBC and KBC. Significant functional terms and pathways, including cytokine receptor activity, release of sequestered calcium ion into the cytosol, regulation of G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway, and regulation of inflammatory response, were identified (Supplementary Fig. S2). While further research is necessary to elucidate the biological characteristics and meat quality factors influencing between KBC and Hanwoo breeds, it is evident that this network analysis has limitations in fully representing the network relationships involving fatty acids, amino acids, and other meat quality-related factors between these two breeds.
Conclusion
This study conducted a comparative analysis of Hanwoo, KBC, and JBC cattle, identifying significant differences in meat quality, fatty acid and amino acid compositions, and transcriptome profiles. Although there were no differences in most meat quality parameters, JBC exhibited increased toughness, while KBC demonstrated lowered resilience. Within the constituent amino acids, glutamic acid, associated with umami, was measured at the highest proportion, with JBC and Hanwoo having higher levels than KBC. KBC had higher levels of aspartic acid, the second highest proportion among the constituent amino acids. DEGs related to lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis, such as MOGAT1, ANGPTL8, and SLC38A4. Network analysis highlighted differences in GO terms and KEGG pathways between JBC and KBC, indicating the significance of genetic factors in meat quality. However, the network analysis between KBC and Hanwoo showed different patterns, suggesting limitations in fully capturing the relationships involving meat quality factors. While this study acknowledges certain limitations in experimental design related to the rearing methods and feeding practices of the test animals, it nonetheless underscores the promising potential of genetic selection and breeding programs to enhance meat quality. It advocates further research into the genetic mechanisms that influence these traits.













