Introduction
Animal meat is a rich source of essential amino acids (such as histidine, lysine, leucine, and threonine, which cannot be synthesized by the human body), as well as minerals and vitamins that are important sources of energy for humans (Karwowska et al., 2021). Although, beef, pork, and chicken are the predominantly consumed animal meats, the consumption of mutton and goat meat, which were previously domesticated for milk production, has consistently increased, particularly in regions such as Asia, the Middle East, and Africa (Pandey and Upadhyay, 2022; Teixeira et al., 2020). The black goat (Capra hircus) is a domesticated goat belonging to the bovine family, characterized by its small size and black fur (Dong et al., 2015). Goat meat is characterized by relatively low fat, low calories, and low cholesterol compared to other meats (Lalhriatpuii and Singh, 2021). Also, goat meat is known to be a relatively acceptable meat with few cultural and religious restrictions, so it has great potential to be widely consumed in various cultures (Sujarwanta et al., 2024). In particular, goat meat is gaining attention as a suitable meat for health-conscious consumers, as it is a high-protein food that provides a rich source of essential amino acids and various micronutrients, such as iron, zinc, and vitamins (Cordeiro et al., 2022). However, goat meat has a high proportion of unsaturated fatty acids, which makes it more susceptible to spoilage when exposed to oxygen, heat, or light (Forte et al., 2024).
Meat products are susceptible to protein degradation and lipid oxidation caused by microbial contamination resulting from factors such as high fat and moisture content, inadequate handling during processing, and insufficient heat treatment (Boeira et al., 2020). Destruction of the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins caused by various factors such as heat, oxygen, and pH can lead to protein denaturation, thereby deteriorating food quality (Barbhuiya et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021b). Furthermore, fat generates hydroperoxides through oxygen and heat, which are then decomposed into secondary byproducts such as aldehydes and ketones, significantly reducing the shelf life of meat products (Ahmad et al., 2023). Therefore, the differential chemical composition and fatty acid profile of the species-specific meat may cause differences in the shelf life (Dave and Ghaly, 2011; Karakök et al., 2010).
Emulsified sausages refer to ground meat products in which the raw meat is finely mixed with salt, fat, ice water, and other ingredients, followed by emulsification and heating (Lee et al., 2020a). In emulsification, salt-soluble protein; a crucial factor, forms a film on the outer surface of the emulsified fat globules, creating a gel matrix with an even dispersion of fat and myofibrillar tissue (Jung et al., 2022). Thus, the non-water-miscible solid fat gets dispersed into small globules, forming a uniform oil-in-water emulsion with the protein dissolved in the liquid phase (Zhang et al., 2022b). Fat not only contributes to the flavor and texture of meat products, but also influences their taste and quality (Domínguez et al., 2019). However, uneven emulsion structures and fats are composed of unstable structures that readily react with oxygen, making them susceptible to oxidation leading to quality deterioration and reduced shelf life (Wongnen et al., 2022).
Recently, the food industry has been increasingly proposing challenges for the development of products and technologies aimed at increasing the production and acceptance of goat-derived products (Guerra et al., 2011). Therefore, with the anticipated increase in consumption of alternative livestock such as sheep and goat meat, as well as meat products, there is a need to develop measures that facilitate their acceptance and consumption (Mazhangara et al., 2019; Teixeira et al., 2020). Accordingly, research on various products utilizing goat meat, such as sausages (Park et al., 2020), patties (Khan et al., 2020), nuggets (Banerjee et al., 2020), fermented sausages (Ko et al., 2021), and mortadella (Guerra et al., 2011) is actively being conducted.
In this study, to address the challenges associated with goat meat, emulsified sausages made from goat meat, as well as commonly used meats such as beef, pork, and chicken (all using the same cuts), were compared. The purpose of this study is to demonstrate that goat meat can be used as a raw material for meat products without significant differences compared to other livestock species. To this end, we performed an analysis of the quality and storage characteristics of emulsified sausages among different livestock species.
Materials and Methods
The black goat; M. biceps femoris (Gaon, Gangjin, Korea), beef; M. biceps femoris (Daon, Yesan, Korea), pork; M. biceps femoris (I-homemeat, Seoul, Korea), and chicken drumsticks (Hamoni-mart, Yesan, Korea) used in this study were purchased 24 h after slaughter and utilized for the experiments. The raw meat (with excessive connective tissue removed) and pork back fat were ground separately using a grinder (PA-82, Mainca, Barcelona, Spain) equipped with a 3 mm plate. The sausage manufacturing process consisted of the following steps. First, after adding sugar (1%) and salt (1.2%) to the raw meat (60%), the mixture was mixed for 1 min using a bowl cutter (K-30, Talsa, Valencia, Spain) to extract salt-soluble proteins. Next, the back fat (20%) and half of the ice water (20%) were added to the mixture and mixed for 1 min. Finally, the remaining half of the ice water was added, and the mixture was mixed for 1 min to produce the final emulsion. It was ensured that the temperature of the emulsion did not exceed 10°C during all the steps. The prepared emulsion was filled into natural casings using a filling machine and then heated at 80°C for 40 min using a chamber, followed by cooling at 20°C for 30 min. The manufactured sausages were stored for 5 wk at 4°C in vacuum packs and were used in the experiment. The sausages were cooked all at once, and the samples were separated by week. For each respective week, the samples were brought to room temperature at room temperature for 30 min before being used in the experiments. And a total of three batches were prepared for each species, and 700 g per batch (each 100 g×7) was produced for each species and used for the experiment.
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC, 2016a; AOAC, 2016b; AOAC, 2016c; AOAC, 2016d) analysis was used to measure and compare the proximate compositions of the samples (950.46, 942.05, 991.36, 920.153). The proximate composition used a sample immediately after manufacturing.
Color was measured at the center of the sample cross-section after cooking. The CIE L*, CIE a*, and CIE b* were measured using a colorimeter (CR-10, Minolta, Tokyo, Japan). The colorimeter was equipped with a pulsed xenon lamp, a 2° standard observer, a light source D65, and an 8 mm aperture. The hue angle was calculated using the following equation:
Water holding capacity (WHC) was measured using the method of Lee et al. (2020b). Five grams of the sample wrapped in filter paper (Whatman No. 1, GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) was placed in a 50 mL conical tube and centrifuged at 4°C and 246×g for 10 min using a centrifuge (Supra R22, Hanil Science, Gimpo, Korea). The WHC was determined by measuring the weight of the sample before and after centrifugation using the following formula:
The cooking yield was measured using same weight samples as much as possible to maintain uniformity in the degree of heat exposure to the samples. After cooking at 80°C for 40 min using a chamber (10.10ESI/SK, Alto Shaam, Menomonee Falls, WI, USA), it was allowed to cool at 20°C for 30 min (Lee and Kim, 2023). The sample weight was measured before and after cooking, and the cooking yield was calculated by incorporating these measurements into the following formula:
The pH values of the cooked samples were measured using a glass electrode pH meter (Model S220, Mettler-Toledo, Schwerzenbach, Switzerland). After mixing the sample and distilled water in a ratio of 1:4, it was homogenized for 30 s under the condition of 10,000 rpm using an ultraturrax (HMZ-20DN, Poonglim Tech, Seongnam, Korea). Before measurement, the pH meter was calibrated with buffer solutions of pH 4.01, 7.00, and 10.00, respectively (Suntex Instruments, Taipei, Taiwan).
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) levels were measured using the distillation method (Lee et al., 2024). First, 5 g from each cooked sample was homogenized with 50 mL of distilled water and 200 μL of 0.3% butylated hydroxytoluene and transferred to a distillation flask. The homogenate was dis-tilled with 47.5 mL distilled water, 2.5 mL 4 N HCl, and 1 mL antifoaming agent, and 20 mL of the distillate was collected. Next, 5 mL of 0.02 M 2-thiobarbituric acid in 90% acetic acid was added to each screw cap tube containing 5 mL of the distillate and mixed. The screw cap tubes were heated at 100°C for 35 min using a water bath (JSWB-30T, JSR, Gongju, Korea) and then cooled with running water for 10 min. The absorbance was measured at 538 nm using a multimode microplate reader (SpectraMax iD3, Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA). The amount of malondialdehyde (MDA) was calculated using a standard curve of 1,1,3,3-tetraethoxypropane, and the TBARS value was reported as mg MDA per kg of sample.
Volatile basic nitrogen (VBN) was measured using the method of Kim and Kim (2024). The VBN content of the cooked samples was measured using the microdiffusion method. After mixing 10 g of the sample with 30 mL of deionized water, the mixture was homogenized at 5,614×g for 1 min using a homogenizer (AM-5, Nihonseiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan). The homogenate was placed in a cylinder and up to 100 mL of distilled water was added. Thereafter, the homogenate was filtered through a filter paper (Whatman No. 1, GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA). Next, 1 mL of the filtrate was put into the outer chamber of the Conway dish, and 1 mL of 0.01 N H3BO3 and 100 μL of the Conway indicator were added to the inner chamber. Then, after adding 1 mL of 50% K2CO3 to the outer chamber, the Vaseline-coated lid was closed and the mixture in the inner chamber was reacted at 40°C for 90 min. The amount of VBN was titrated by mixing 0.02 N H2SO4 until the reacted solution in the inner chamber changed from green to red. The VBN content was expressed using the following formula:
Where ‘A’ is the sample weight (g); ‘B1’ is the titration amount of the sample (mL); ‘B2’ is the titration of blank (mL); ‘a’ is the standardization index of 0.02 N sulfuric acid; and ‘b’ is the dilution factor.
The total number of microorganisms on the basis of the storage period was measured using the following method. After mixing 25 g of the cooked sample with 225 mL 0.1% buffered peptone water (BPW), the mixture was homogenized for 1 min using a stomacher (WH4000-2751-9, 3M, Saint Paul, MN, USA). Thereafter, 1 mL of the filtrate was collected and diluted in 9 mL of 0.1% BPW and the process was repeated as many times as necessary. The diluted filtrate was plated on tryptic soy agar and cultured in an incubator (WSC-2610, ATTO, Tokyo, Japan) at 37°C for 24 h, and the number of colonies produced was measured and expressed as Log colony forming unit (Log CFU/g).
In this study, analyses of proximate composition, color, WHC, and cooking yield (4 treatments×5 replication), and pH, TBARS, VBN, and total bacterial counts (TBC; 4 treatments×5 storage periods×5 replication) were performed. One-way analysis of variance, following the general linear model (GLM) procedure of SAS software (Version 9.4 Windows, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA), was conducted to perform the analysis of variance of the experimental results. Additionally, the significance of the data was analyzed using Tukey’s studentized range test (p<0.05). The fixed effects for analysis of physicochemical and storage properties included the treatment types (goat, beef, pork, and chicken), and storage periods (0, 1, 3, 5 wk). The data in this experiment was presented as mean±SD. The correlation between meat, moisture, protein, fat, pH, TBARS, VBN, and TBC was analyzed using Python (google, colaboratory). This was performed using libraries such as Pandas for loading and data preparation, Matplotlib for data visualization, and Seaborn for heatmap and data summary.
Results and Discussion
The proximate compositions of the emulsified sausages according to animal species are shown in Table 1 (Table 2). The goat sausage (GS) and pork sausage (PS) samples exhibited significantly higher moisture content than the other samples (p<0.05). In contrast, the beef sausage (BS) and chicken sausage (CS) samples exhibited significantly higher fat content than that by the other samples (p<0.05). Beef is the meat of livestock with well-developed intramuscular fat; thus, the higher fat content in the BS samples may be due to the inherently higher fat content compared to that from the other livestock (Mohammed et al., 2020). On the other hand, in the case of goats, most of the fat is accumulated in the internal organs, resulting in relatively lowfat content in the carcass (van Wyk et al., 2022). Zhang et al. (2022b) reported a negative correlation between fat and moisture content, which is consistent with the findings of this study. The protein content was significantly lower in the CS samples than that in the other samples (p<0.05). Chen et al. (2016) reported that the protein content in chicken drumsticks is approximately 19%, which is lower than that of black goats (approximately 21%), pork (approximately 21%), and beef (approximately 22%; Cheng et al., 2020; Choi et al., 2023; Wójciak et al., 2021). The variation in the protein content of the sausages according to animal species is presumed to be derived from differences in the proximate composition of the raw meat. The GS sample exhibited a lower crude ash content than that by the other samples. The typical ash content of goat meat ranges from approximately 0.93%–1.63%, and a similar value of approximately 1.62% was observed in the present study (Lalhriatpuii and Singh, 2021). Based on the general compositional analysis, variations in the proximate composition were observed depending on the animal species, suggesting potential differences in shelf life and quality. Therefore, biochemical characteristics and storage stability analyses of emulsified sausages from different animal species were performed.
The color, WHC, and cooking yield of emulsified sausages according to animal species are shown in Table 3 (Table 2). CIE L* was significantly different among the samples (p<0.05). The CIE a* was significantly higher in the GS and BS samples than that in the other samples (p<0.05). This is because chicken meat contains a high level of white muscle fibers; ‘type IIB’, whereas goat and beef contain a significant amount of red muscle fibers (Cheng et al., 2022). Livestock species exhibit varying levels of myoglobin content in the muscles. Ruedt et al. (2023) reported myoglobin content of 2.6–2.9 mg/g for goats, 4–10 mg/g for cattle, 0.3–3 mg/g for pigs, and 0.1–0.6 mg/g for chickens depending on the species. Similarly, in this study, higher CIE a* was observed in the order BS>GS>PS>CS, suggesting that the myoglobin content inherent to the original raw meat influenced the results. CIE b* was significantly higher in the CS sample than that in the other samples (p<0.05). This may be due to the feed that chickens typically consume. The color of chicken meat, particularly the yellow color, is influenced by carotenoids found in the feed (such as corn and alfalfa), and these carotenoids accumulate in the meat and fat, giving them a yellow tint (Wei et al., 2023). Generally, meat CIE b* positively correlates with CIE L* and negatively correlates with CIE a* (Luciano et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2021a). Therefore, in this study, the high CIE L* and low CIE a* of the CS samples influenced the CIE b*. The hue angle value was the highest in the CS sample followed by PS, GS, and the least in BS samples (p<0.05). The hue angle changes from 0° (red) to 90° as it approaches yellow color (Bernardez-Morales et al., 2023). Therefore, it was established that the hue angle value of CS, which exhibited higher CIE b* compared to the other samples, was high, whereas the hue angle values of the GS and BS samples, characterized by higher CIE a*, were low. Ultimately, GS showed values numerically close to those of BS in CIE a*, CIE b*, and hue angle. Goat meat provides color values within an acceptable range for meat products. However, it cannot be ruled out that the correlation between color and other factors may vary depending on the rearing environment and feed composition. Therefore, it is suggested that future analyses should be conducted under experimental conditions that eliminate the effects of feed.
The WHC of the emulsified sausages did not differ significantly among the GS, BS, and PS samples; however, the CS sample exhibited the lowest WHC (p<0.05). Xu et al. (2020) reported that as the proportion of fast-glycolytic fibers such as MyHC-IIB increases, the protein solubility decreases, leading to a decrease in the meat WHC. Therefore, the WHC of chickens, which contain a high proportion of type IIB muscle fibers, was low. The WHC measurement results showed that the GS group exhibited values similar to those of the BS and PS groups, suggesting that the use of goat meat can yield similar results in meat product manufacturing.
The CS sample exhibited the highest cooking yield, whereas the GS, BS, and PS samples demonstrated cooking yields similar to results of WHC measurement. The GS sample showed a high cooking yield, which was attributed to its high content of connective tissues (Bakhsh et al., 2019). Black goat meat and chicken legs contain more connective tissues than other animal species, and the connective tissues, which are composed of proteins, can interact with water to contribute to the formation of free water (Lee and Kim, 2021; Voytsekhivska et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022). However, free water is very unstably bound by surface tension, so it is easily released to the surface of the meat by small impact (Geng et al., 2022). As a result, the cooking yield of the CS sample was high, while the WHC was low. GS and CS samples showed significantly higher cooking yield values than those in BS and PS samples. However, as the amount of connective tissue increases, there is a possibility that the texture of meat products may become tougher or less desirable. Therefore, it is believed that the impact of a high proportion of connective tissue on consumer acceptability should also be taken into consideration.
The pH not only affects quality characteristics such as the WHC and cooking yield of meat products, but it also has a close relationship with microbial growth indicators (Clinquart et al., 2022; Nisar et al., 2020). Low pH (acidic conditions) stabilizes the oxidation state of Fe2°C, thereby inhibiting the rate at which myoglobin is oxidized to metmyoglobin (Hoa et al., 2021). Conversely, in high pH (alkaline conditions), the oxidation of myoglobin is facilitated, leading to an increase in the formation of metmyoglobin, and excessive alkalinity can also decrease the structural stability of myoglobin, resulting in color changes or deterioration (Hoa et al., 2021). Fig. 1 shows the pH of emulsified sausages based on animal species and storage period. The pH of all samples, except for the PS sample, showed an increasing trend with increasing storage period. This may be due to the accumulation of alkaline substances produced as microorganisms grow and the microbial decomposition of amino acids into alkaline compounds like ammonia, both of which increase the pH (Anal, 2019; Zhang et al., 2023). Throughout all storage periods, the pH values were significantly higher in GS and CS samples than that in the other samples (p<0.05). The normal pH of raw black goat meat is 5.5–6.2 (Gawat et al., 2022), and according to Zhang et al. (2022a), the pH of raw chicken leg meat is approximately 6.94. This is at a higher level compared to the normal pH range of other meats (5.4–5.7), and may have affected the final sausage pH. Therefore, it can be presumed that the pH of the meat itself can affect the quality and storage characteristics of the meat products, and thus, an analysis of the quality and storage characteristics of emulsified sausages according to the livestock species is deemed necessary.
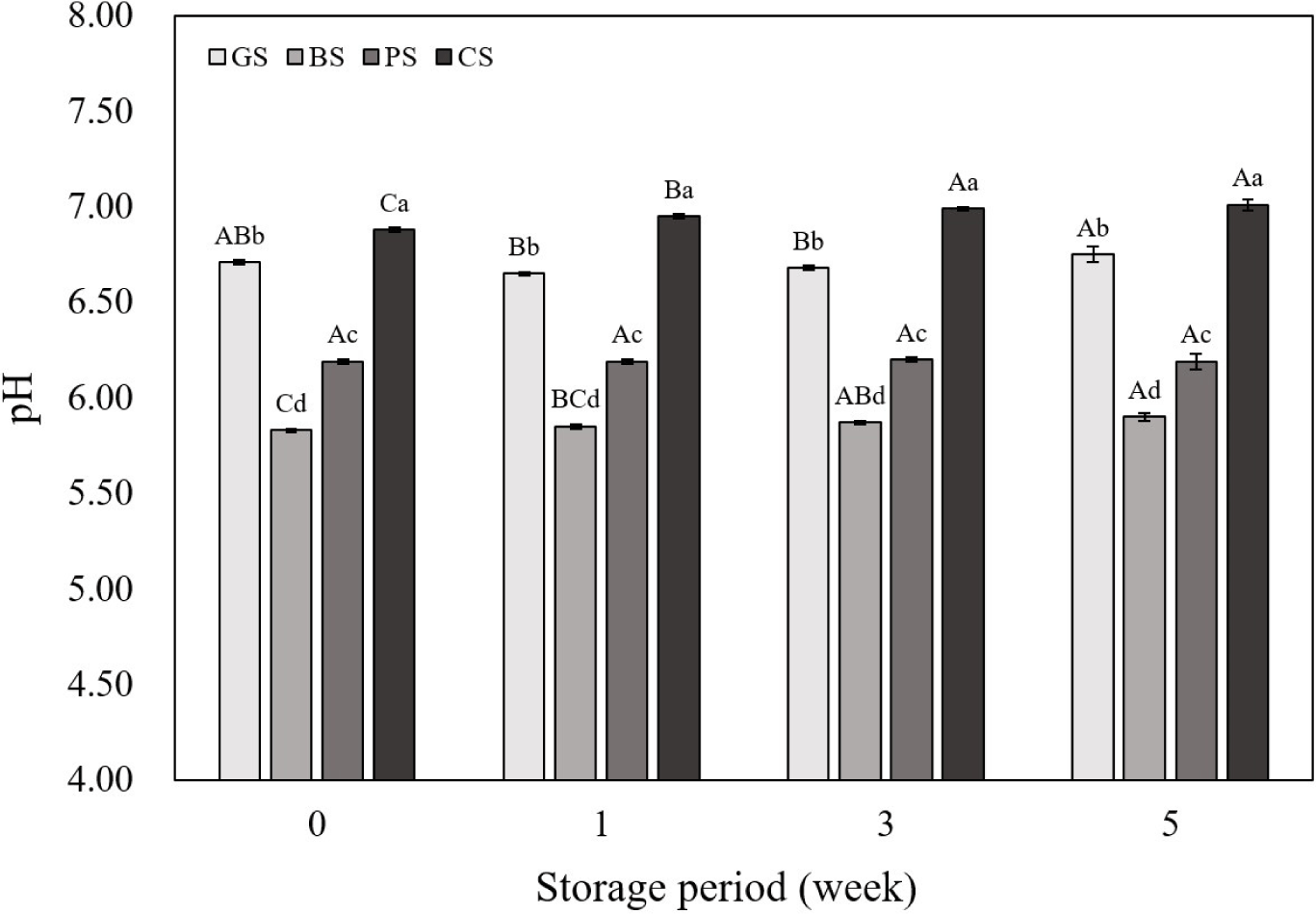
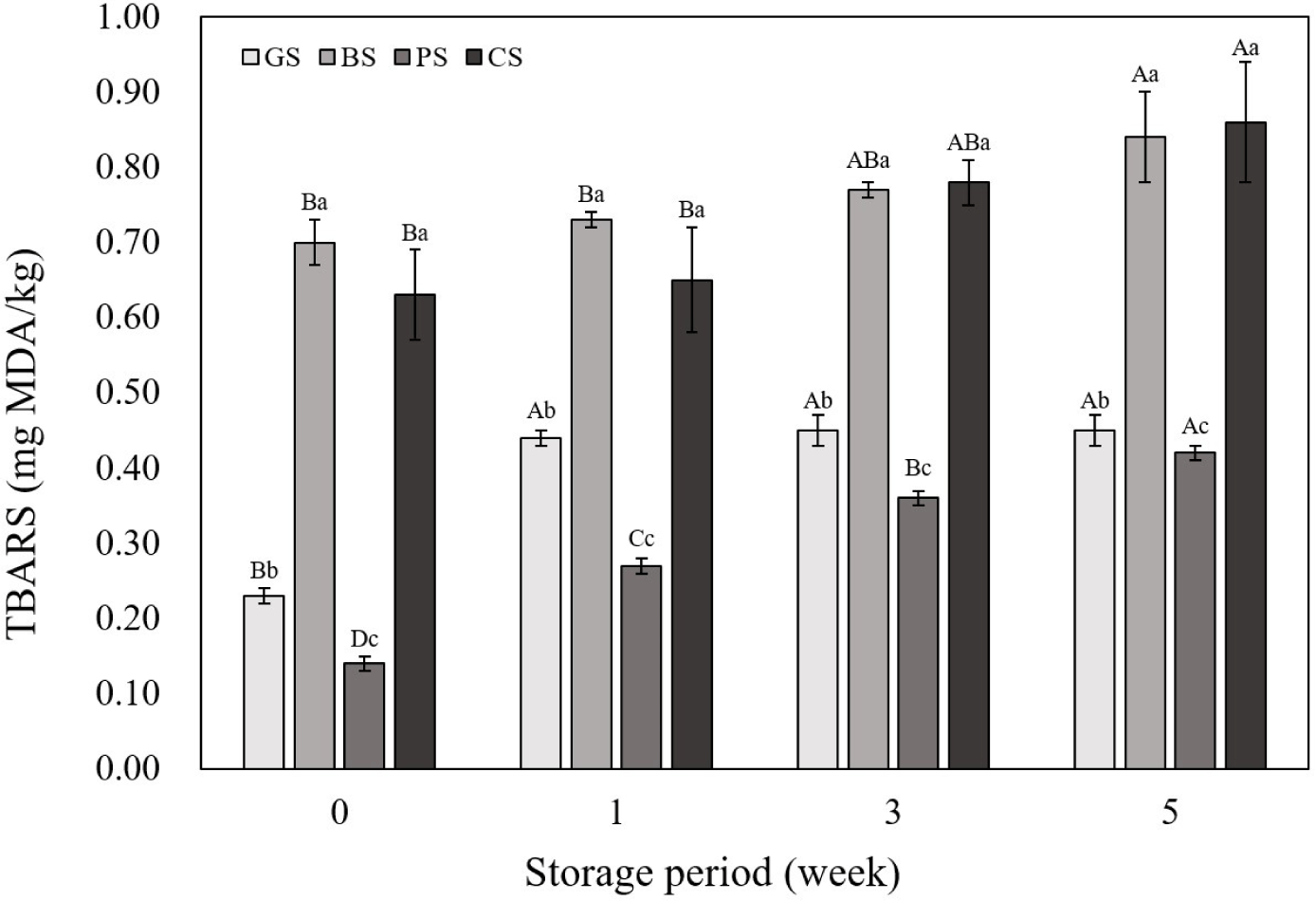
Fig. 2 shows the TBARS results of the emulsified sausages according to the livestock species. Both the BS and CS samples showed significantly higher TBARS values than those of the other samples at all time points (p<0.05). Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) contain multiple double bonds in their structure, making them highly sensitive to oxidation, and a direct correlation between PUFA content and TBARS values has been reported (Jerónimo et al., 2020; Santos et al., 2021). Meat products exhibit varying levels of PUFAs depending on the species, with black goat containing approximately 7.52%, chicken 23.29%, beef containing 3.73%, and pork containing 9.14% PUFAs (Choi et al., 2023; Muzolf-Panek and Kaczmarek, 2021). In the case of goat and PSs, the proportion of PUFA is somewhat higher compared to beef; however, the total fat content in the meat itself is low, which is judged to have contributed to this result. Furthermore, the proximate composition analysis of the emulsified sausages revealed that the fat content was significantly higher in BS and CS samples than in the other samples. The correlation coefficient indicated a significant positive correlation between the fat content of the emulsified sausages and TBARS (Fig. 3; r2=0.95). In this study, we determined that these results were due to differences in fatty acid composition and fat content between livestock species. Similarly, in a study on lipid oxidation, Pérez-Andrés et al. (2020) reported that TBARS values in beef and chicken were higher than those in sheep and pork. The TBARS values showed an increasing trend with increasing storage period for all livestock species. Lipid oxidation is a major cause of quality deterioration in meat prod-ucts and requires careful control because it causes undesirable changes in odor, taste, texture, and color (Barbhuiya et al., 2021). In this study, sausages manufactured using black goat meat showed TBARS values similar to those of commonly manufactured PSs at the 5th wk of storage.
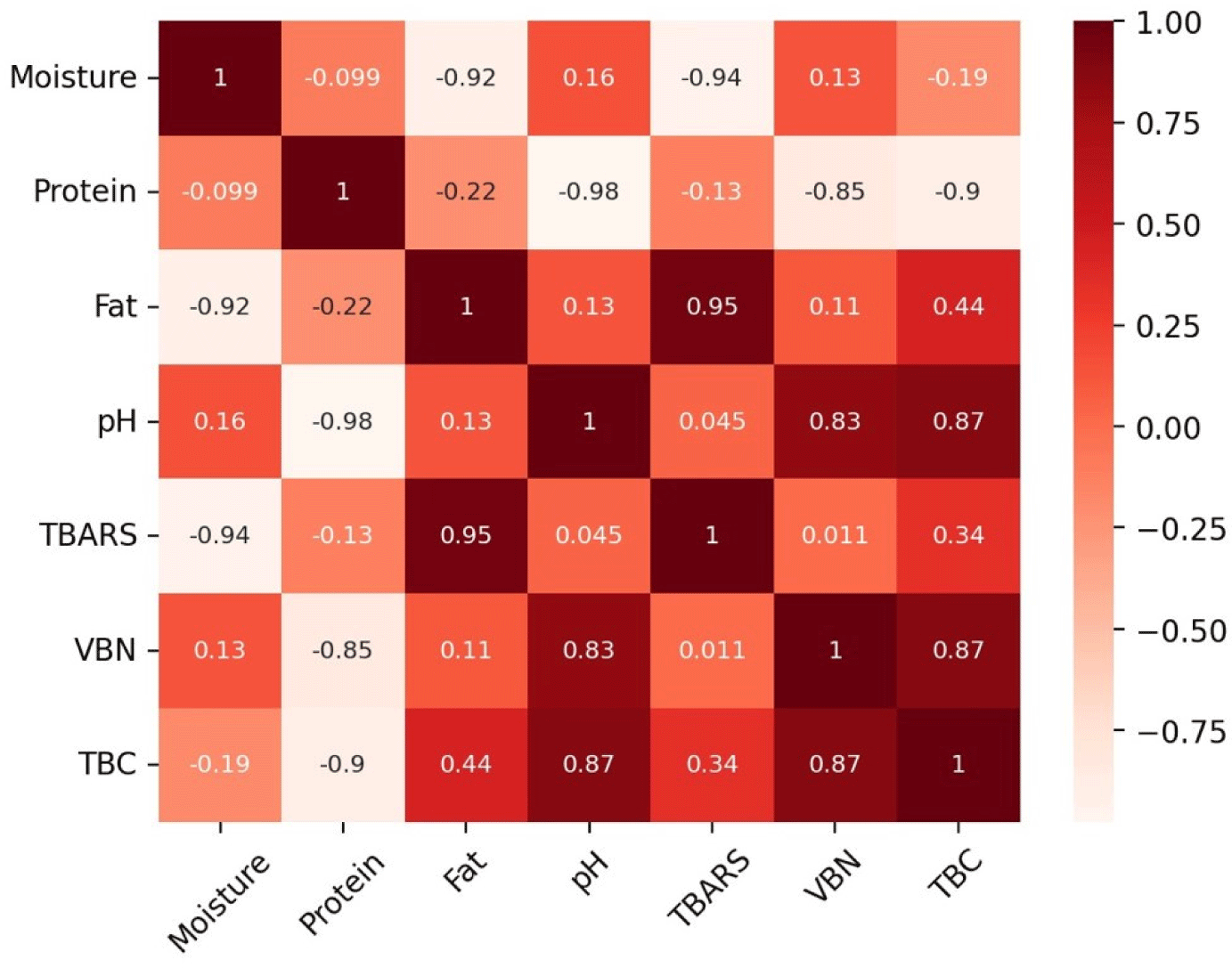
The VBN values of the emulsified sausages according to the livestock species are shown in Fig. 4. The initial VBN values at wk 0 and 1 were not significantly different between the livestock species. However, in the 3rd and 4th wk of storage, the GS and CS samples showed higher VBN levels than those in the BS and PS samples. Each livestock species has a different amino acid composition, and amino acids such as arginine and histidine are known to have a significant effect on the VBN content of meat (Hwang et al., 2022). Compared to goats and chickens, cows and pigs have lower arginine contents (Guo et al., 2019; Khalid et al., 2022; Mohammed et al., 2020; Yim et al., 2019). Additionally, a high pH promotes the growth of microorganisms, which increases protein decomposition and ultimately increases the VBN value (Kim et al., 2020). In this study, the pH of emulsified sausages showed a positive correlation with VBN (Fig. 3; r2=0.83), and the pH measurement results of emulsified sausages showed that the GS and CS group had higher pH values than those in the other groups. Therefore, the differences in VBN values among the livestock species in this study were due to differences in pH and amino acid composition. As the storage period increased for all livestock species, the VBN values increased. This is attributed to the formation and accumulation of alkaline compounds, such as NH3 and amines, produced by proteins degraded by endogenous proteases (Song et al., 2024). The destruction of nutrients due to protein decomposition in meat products can cause loss of flavor and discoloration, which can negatively impact sensory characteristics (Pellissery et al., 2020). The results of VBN analysis showed that emphasis should be laid on the aspect of protein deterioration before commercialization of black goat meat and chicken leg meat, which exhibited higher VBN levels than the other groups.
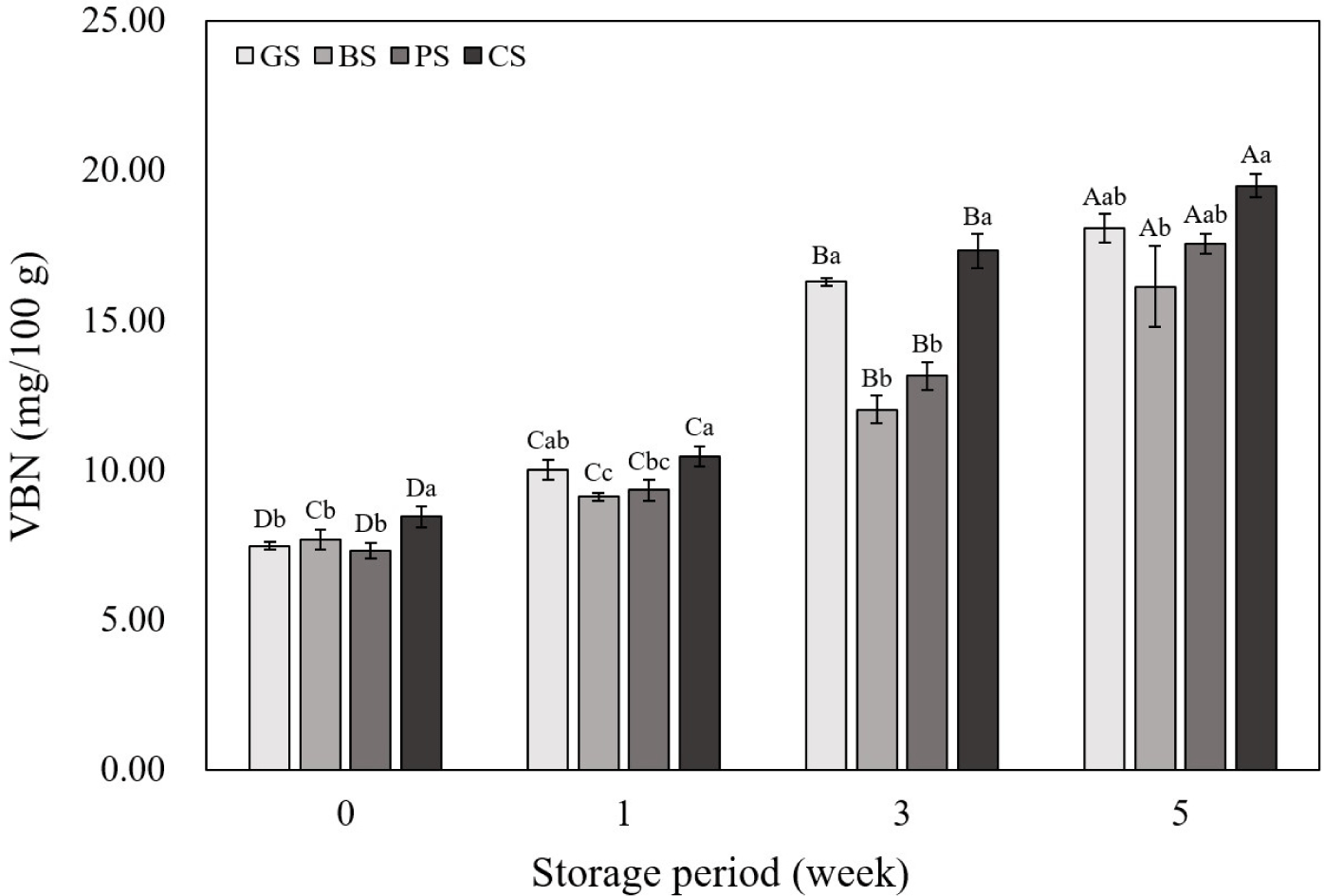
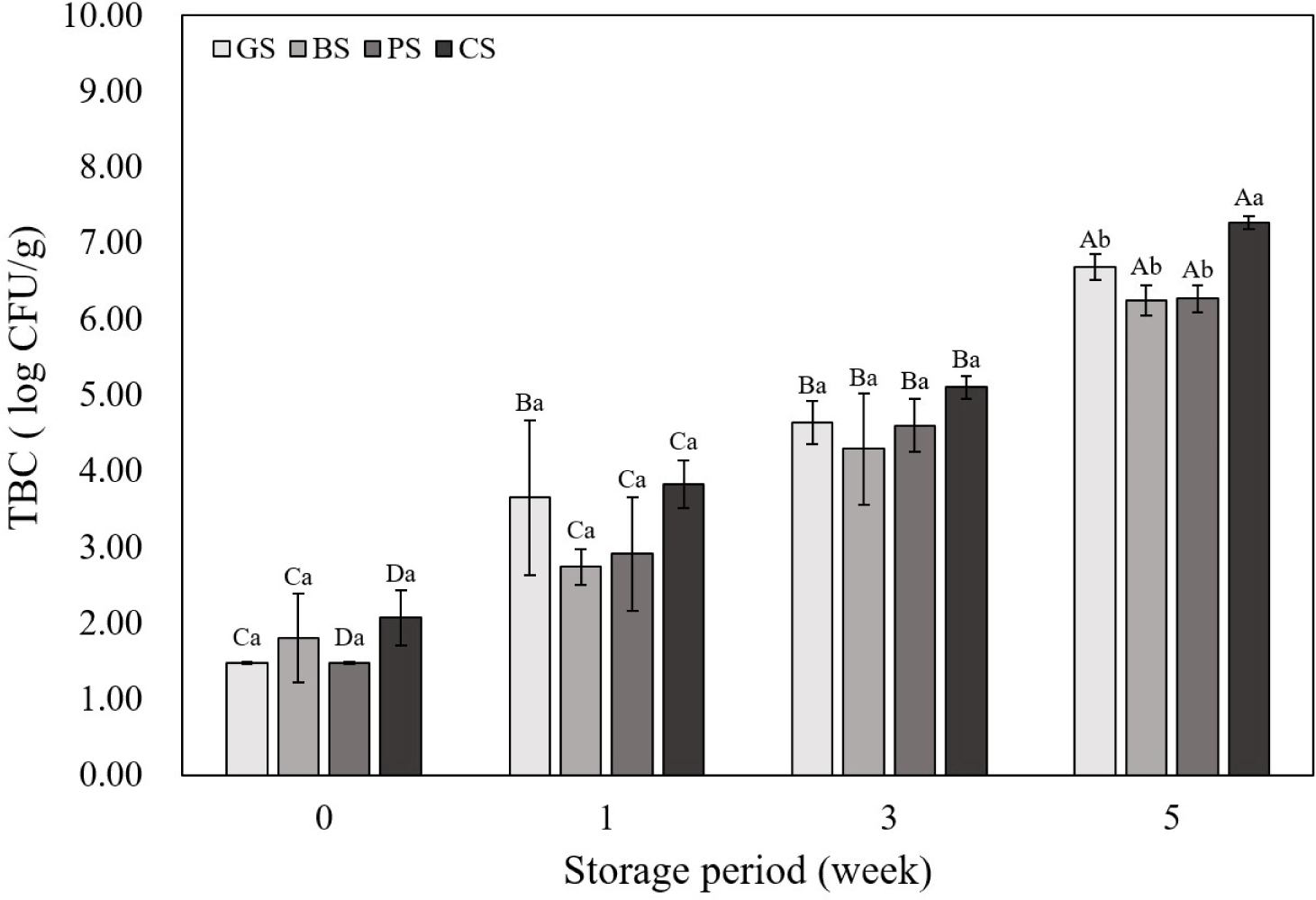
Fig. 5 shows the TBC of emulsified sausages according to the livestock species. There was no significant difference in the number of colonies between livestock species until the 3rd wk, but in the 5th wk, the CS sample showed significantly higher TBC than in the other samples (p<0.05). In this study, the pH of the CS group was the highest at all storage periods; the high pH of meat creates a favorable environment for the growth of microorganisms, which can increase the number of microorganisms (Pellissery et al., 2020). The correlation coefficient showed that the pH of emulsified sausages was positively correlated with TBC (Fig. 3; r2=0.87), and it was determined that the CS sample with a high pH showed the highest TBC at all storage periods. Mohammed et al. (2020) supported this finding by reporting that the microbial count (Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella) was higher in chicken meat than in beef, lamb, and camel meat. The TBC of all the samples tended to increase as the storage period increased, and the GS, BS, and PS samples maintained less than 7 Log CFU/mg until the 5th wk of storage. Microbial growth serves as a standard for determining whether meat is spoiled, and if the TBC exceeds 7 Log CFU/mg, meat and meat products are considered spoiled (Hwang and Hong, 2020). Sausages manufactured using black goat meat showed a similar level of microbial growth as beef and PSs up to the 5th wk of storage, suggesting that black goat meat is suitable for meat products.
Conclusion
In this study, the physicochemical and storage characteristics of emulsified sausages manufactured from black goat, beef, pork, and chicken leg meat were analyzed.
Proximate composition measurements showed that the GS and PS samples had high moisture content, and the BS and CS samples had high fat content. The highest protein content was observed in the following order: BS>PS>GS>CS. As the proximate composition was different for each livestock species, it was determined that there may be differences in storage and quality depending on the composition. The GS showed CIE a*, CIE b*, and hue angle values similar to those of the BS. In addition, black GS showed a higher WHC value than the other sausages and similarly showed a high cooking yield. Black goat meat and CS had higher pH values than the other samples, and the pH of the raw meat, depending on the livestock species, affected the emulsified sausage. Beef and CSs showed higher TBARS values than the other samples during all storage periods. This was influenced by fat content, which showed a high positive correlation with TBARS (r2=0.95). VBN and TBC analyses showed that black goat and CSs showed higher protein deterioration and faster microbial growth than the other samples. These results were related to pH, which positively correlated with VBN (r2=0.83) and TBC (r2=0.87).
The results of this study suggest that the commercialization of black goat meat holds significant potential. However, special care is needed to prevent protein deterioration, and further research should be conducted.
Research on the sensory characteristics of black GS, particularly its flavor and aroma, plays a crucial role in product development, and higher sensory satisfaction can enhance its market acceptance. Black goat has a distinctive odor that may cause aversion in some consumers, but as studies on reducing this characteristic smell progress, consumer accessibility to black goat products is likely to expand. In fact, our previous study (Choi et al., 2024) demonstrated that various treatments aimed at odor reduction positively impacted the acceptability of black goat meat, and such research can contribute to improving consumer perception and generating positive demand in the market.













