Introduction
Tenebrio molitor (Mealworm beetles), a species belonging to the Tenebrionidae family, is well known for its larvae (Kotsou et al., 2024). These insects are widely distributed globally and have attracted considerable attention for their potential applications. Previous research has revealed several health-supporting properties associated with mealworms, such as antioxidant activity [2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH·) scavenging], anti-obesity potential (lipase inhibition), and anti-inflammatory properties (decrease in iNOS levels; Navarro del Hierro et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2016). Additionally, mealworm larvae have been utilised in Asian culture to treat liver diseases (Lee et al., 2015). Fatty acids (FAs) extracted from mealworms are rich and have various uses. They are valuable for their potential cardiovascular and brain health benefits (Pessina et al., 2020). In the cosmetic industry, they offer moisturising properties ideal for skincare products (Kim et al., 2018). Furthermore, these FAs are utilised in animal feed to enhance the nutritional content of poultry, fish, and pet food (Valdés et al., 2022). From an environmental perspective, they contribute to renewable energy through biodiesel production (Lee et al., 2022).
There has been an increasing demand for adopting sustainable and eco-conscious approaches to extract valuable compounds from natural origins (Paneerselvam et al., 2024; Psarianos et al., 2024). Mealworms have emerged as a promising source of lipids and proteins, with potential uses in the food, feed, and pharmaceutical industries. However, conventional extraction methods often involve using unsafe solvents and energy-intensive processes, raising concerns about environmental impact and sustainability. To address these challenges, researchers have been exploring using green solvents and innovative extraction technologies to recover lipids and proteins from mealworms efficiently. Green solvents, like ethyl acetate (EtOAc), ethanol (EtOH), isopropanol (IPA), and their combinations, present environmentally sound alternatives to traditional solvents, reducing environmental contamination and lowering health hazards (Usman et al., 2023; Yabré et al., 2018). Additionally, advanced extraction technologies, such as ultrasonication and homogenisation, provide efficient means of disrupting cellular structures and enhancing extraction yields while reducing energy consumption and processing time (Koubaa et al., 2020; Mokhtar et al., 2024).
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to compare various green solvents for extracting mealworm larvae and to evaluate their FA profiles, protein yield, and cytotoxicity. Therefore, the primary objective of this manuscript is to evaluate the FA profile and total protein content of mealworms using various green solvents and compare them with conventional solvents. The secondary goal is to assess total phenolic contents (TPCs) and DPPH· scavenging activity of the extracts and evaluate cytotoxicity using two liver cancer cell lines.
Materials and Methods
The mealworms (T. molitor) were raised at King Saud University Insectary in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. They were fed a wheat bran and cabbage diet until the final stage before pupation. Prior to processing, the mealworms underwent a 24-hour fasting period and were subsequently euthanised by deep-freezing at –80°C. Subsequently, the frozen larvae underwent a brief blanching process in boiling water for 5 minutes, using a larvae-to-water ratio of 1:10 (w/v). This method was employed to inhibit browning and significantly decrease microbial contamination, as investigated by Mancini et al. (2019). After blanching, the larvae were drained, oven-dried until reaching a constant weight, ground into powder using a commercial grinder (Stardust, Kalita, Yokohama, Japan), and sieved through a 2 mm screen. It is important to note that all larvae used in this process originated from the same batch to ensure consistency for comparison purposes.
EtOAc, EtOH and IPA (Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany) were chosen as green solvents as potential substitutes for the commonly used conventional solvent, n-hexane, in extracting insect powder. The extraction method followed the modified method outlined by Choi et al. (2017). In summary, 3 grams of insect powder were dispersed separately in 30 mL of each solvent and shaken at 8.944×g for 3 hours at 25°C. After the initial extraction, the mixtures were filtered using Whatman No. 1 filter paper (Whatman, Maidstone, UK) to separate the residues. The solvents were rotary evaporated (Heidolph, Schwabach, Germany) at 45°C.
Two hundred milligrams of each mealworm extract were added to 1 mL hexane. Then 0.2 mL of methanolic NaOH (1 M) was added and mixed for 20 seconds at 50°C in a shaking water bath (SB-12L, Benchmark Scientific, Pohang, Korea). After cooling, 0.2 mL of methanolic HCl (1 M) was added and vortexed for 10 seconds, followed by another 10 seconds of heating at 50°C. The upper phase (~500 μL) was transferred into a fresh tube, and the extraction was repeated one more time with 250 μL of 100% hexane, pooling the upper phases. The pooled fatty acid methyl ester were dissolved in 500 μL of hexane in GC vials.
gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses were conducted using a GC-MS 7890B GC system from Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA). The chromatographic column, a DB-5 MS capillary column from Agilent Technologies (30 m length×0.25 mm internal diameter, phase thickness 0.25 μm), was used with helium as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1 mL/min, inlet temperature 250°C with split mode ratio (50), and oven temperature ranging from 50°C to 250°C with a total analysis time of 73 min. 0.9 μL was injected via an autosampler injection. The MS detector was set as follows: Acquisition scan type, mass ranging from 40 to 500 g/mol, scan speed 1.56, 2 min solvent delay, and 230°C MS source temperature. The products were identified using the integrated software of the National Institute of Standards and Technology Mass Spectrometry (NIST MS) database.
The insect powder (10 g) was mixed with distilled water at 1:15 (w/v) in a 500 mL media bottle. Then, EtOAc, EtOH and IPA were added to the mixture at 1:1. The resulting solution was homogenised for 5 minutes (IKA®, Staufen, Germany). Subsequently, ultrasonication was carried out using an Ultrasonic Cleaner (Wisd, Daihan Scientific, Wonju, Korea). Throughout the ultrasonication process, the temperature was kept at 25°C. The ultrasonication was performed for 30 minutes. After ultrasonication, 0.9% ammonium sulfate was introduced into the mixture and mechanically stirred for 20 minutes under the same conditions. The mixture was kept undisturbed for 2 hours at 4°C to facilitate protein precipitation before being centrifuged at 5,000×g for 15 minutes at 4°C (Centrifuge 5418 R, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). Subsequently, the organic solvent fraction was cautiously separated and collected. The obtained protein extracts were further washed with their cold respected solvent, and finally, each mixture was centrifuged, and the supernatant was collected and dried in an oven at 60°C for 3 h. The protein content of the samples was determined using the Bradford assay, as described by Bradford (1976). Bovine serum albumin (BSA) served as the protein standard, with concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 0.9 mg/mL. The total protein content was calculated using the standard curve equation y=0.5849x+0.5943, where r2=0.9779.
The TPC was calculated using the Folin-Ciocalteu (FC) method (Al-Zharani and Abutaha, 2023). Two microliters of the sample with 20 μL of FC reagent were mixed in 96-well plates and left for 5 minutes, and then 80 μL of a 7.5% Na2CO3 solution was added. The mixture was then kept in darkness for 60 minutes. Next, the absorbance was measured at 760 nm using a plate reader (ChroMate, Awareness Technology, Palm City, FL, USA). Finally, the calibration curve of gallic acid was used to calculate the TPC, which was expressed as mg GAE/g [milligrams of gallic acid equivalents (GAE)] per gram of the sample.
The DPPH· scavenging was investigated using a DPPH· assay based on a previously described protocol (Al-Zharani and Abutaha, 2023). In summary, each extract (10 μL) was mixed with DPPH· solution (100 mM) in MeOH (190 μL). The reaction mixture was then left to incubate in the dark for 30 minutes at 25°C in a 96-well plate. Subsequently, the absorbance changes were measured using a microplate reader at 515 nm. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate, with ascorbic acid serving as the positive control and DMSO as the negative control. The IC50 value was determined using OriginPro 8.5. The DPPH· radical scavenging activity was estimated using the following formula:
Human liver (HepG2 and Huh7) cancer cell lines were acquired from the German cell culture Collection (DSMA, Hamburg, Germany). The cells were then maintained in T-25 flasks (NEST, Wuxi, China) using Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (high glucose) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen, Norwood, MA, USA) and 1% antibiotic of penicillin-streptomycin (Invitrogen). Cells were raised in a 5% CO2 at 37°C. The cells were washed with phosphate buffer saline at 80% confluence. The cells were trypsinised using 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (Gibco, London, UK), and 3 mL of medium was added. They were transferred to 15 mL centrifuge tubes and centrifuged for 3 minutes at 558×g. The cells were pelleted by centrifugation, the supernatant was carefully removed, fresh medium was used for cell suspension, and the cells were then counted using a hemocytometer.
Cell viability was assessed using the colourimetric 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. A 24-well culture plate was used to culture the HepG2 and Huh7 cell lines (25,000 cells/well) and left to incubate for 24 h. The cells were treated in triplicate with various concentrations ranging from 200 to 1,000 μg/mL, following an incubation period of 24 hours. The MTT assay was carried out as described by Al-Zharani and Abutaha (2023). Following treatment, the medium was discarded from each well, and 100 μL of MTT solution (Invitrogen) was introduced. Each well was then incubated in the dark at 37°C for 4 h. Post incubation, the MTT solution was replaced with 1,000 μL of 0.01% HCl–IPA solution. The cells were then placed on a shaker for 5 minutes. Absorbance at 570 nm was measured using a plate reader.
Result
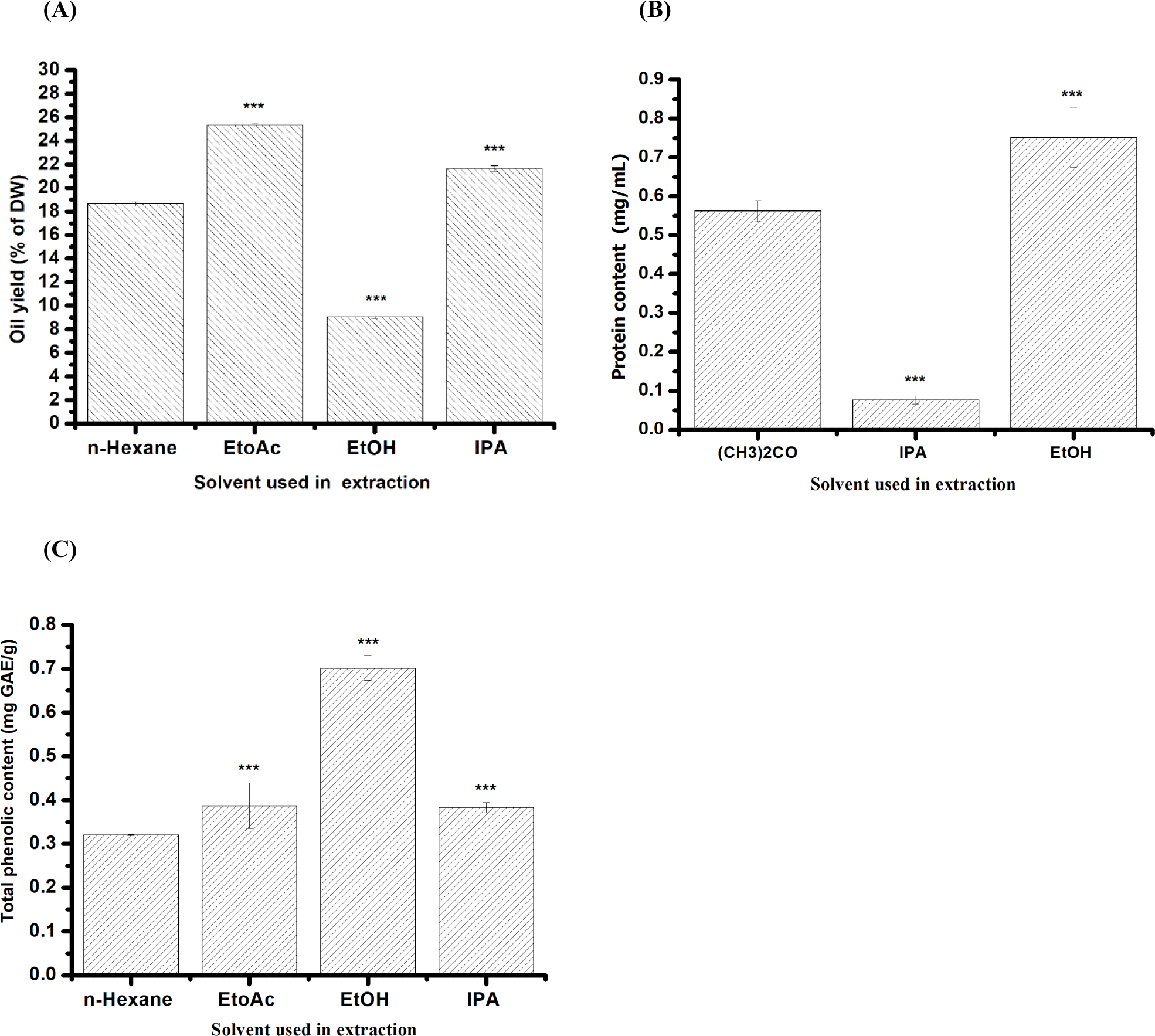
The oil extraction yields from mealworms were compared using different solvents, including EtOAc, EtOH, IPA, and conventional n-hexane extraction methods. Based on the results in Fig. 1, the mealworms exhibited a yield of 18.6±0.02% using n-hexane. In contrast, the yields obtained using green solvents were 25.33±0.01% for EtOAc, 21.66±0.02% for IPA, and 9.06±0.001% for EtOH. Notably, using green solvents such as EtOAc and IPA for mealworm extraction resulted in significantly higher yields than n-hexane. Our findings suggest that EtOAc and IPA are promising alternative solvents for oil extraction from mealworm larvae (Fig. 1A).
The mealworm FA profile obtained with green extraction and conventional methods is summarised in Table 1. Oleic acid (C18:1) serves as the marker FA of EtOAc (35.1±0.09%) and IPA (32.22±0.00%), followed by linoleic acid (C18:2), which records concentrations of 24.7±0.25% and 27.93±0.08% in EtOAc and IPA, respectively. In contrast, linoleic acid (C18:2) was the marker for EtOH and hexane, which recorded concentrations of 36.86±0.31% and 29.78±0.14%. The results also showed that the oils were notably rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (∑MUFA), with a total of 41.3% and 39.55% in EtOAc and IPA, respectively. Meanwhile, the hexane extract was characterised by high levels of saturated fatty acids (∑SFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (∑PUFA), at 36.8% and 30.23%, respectively. Methyl stearate (C20:0) was the third most abundant FA and present in hexane-extracted oils (24.6±0.14%). However, EtOH and IPA improved the extraction of ∑MSFA in mealworm oil, while the percentages of PUFA were reduced. On the other hand, the ∑PUFA/SFA ratio for the EtOAc, EtOH, IPA, and n-hexane extracts was found to be 0.7, 1.23, 0.88, and 0.82, respectively (Table 1).
This study assessed how different solvents affect the release of proteins from mealworms. BSA served as a standard to create a standard curve. The protein concentration in mealworm larvae was determined using an equation derived from the standard curve (Y=0.5849x+0.5948, r2=0.9777). The findings revealed that among the tested solvents, EtOH yielded the highest protein concentration extracted from mealworm larvae at 0.75±0.01 mg/mL, followed by (CH3)2CO at 0.56±0.02 mg/mL and IPA at 0.07±0.001 mg/mL (Fig. 1B).
A comparison of green and conventional extraction showed that the EtOH extract obtained had significantly higher TPC (0.70±0.02 mg GAE/g oil) than the ones extracted by other solvent n-hexane (0.32±0.05 mg GAE/g oil), EtOAc (0.38 mg GAE/g oil) and IPA (0.38±0.01 mg GAE/g oil). As a result, the green-based solvent proposed in this study facilitated the extraction of the highest polyphenol content in mealworm oil, as depicted in Fig. 1C.
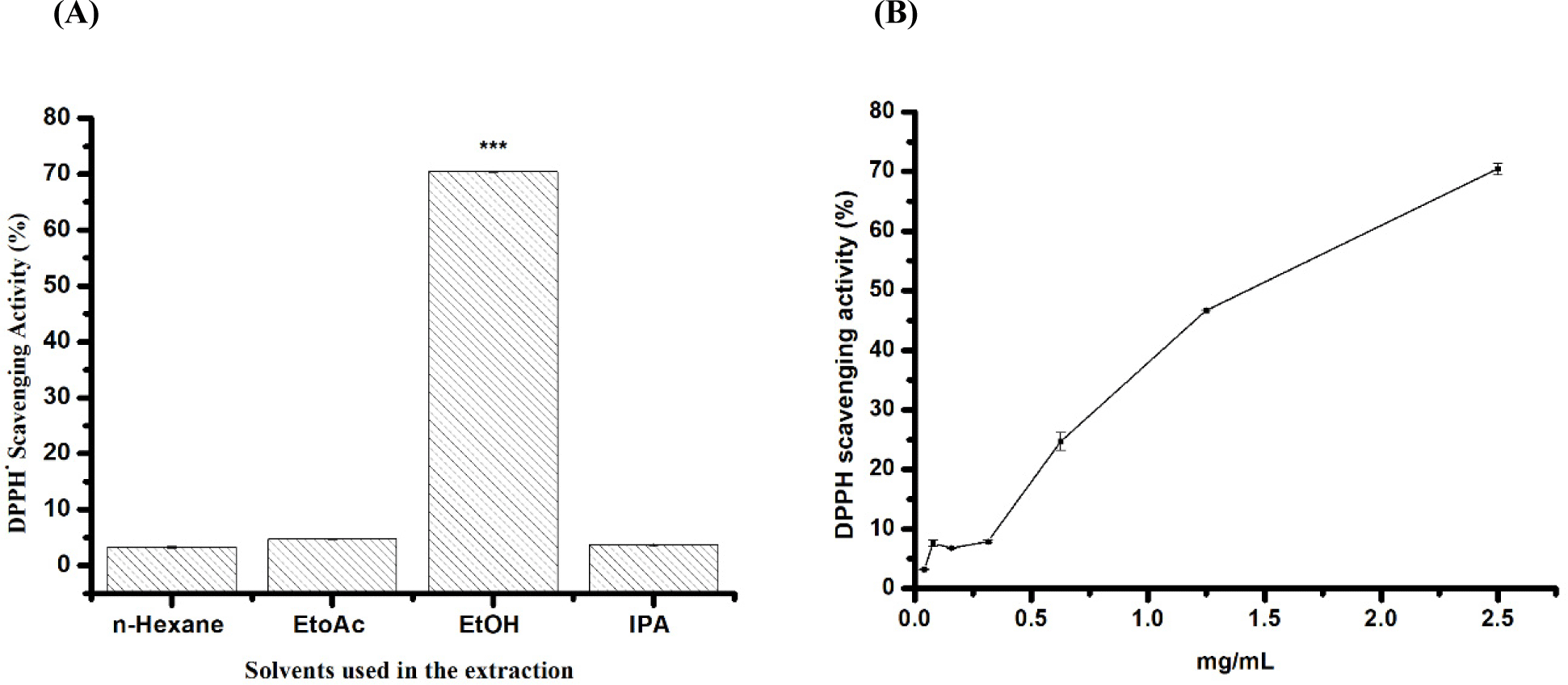
This study explored the antioxidant potentials of mealworm extracts at 5 mg/mL obtained using conventional and green solvents. Mealworm oils extracted conventionally with n-hexane exhibited weak radical scavenging activity (3.2±0.17%) (Figs. 2A and B). In contrast, extracts obtained using EtOH, EtOAc, and IPA showed higher DPPH. radical scavenging activity, with values of 70±0.02%, 4.73±0.11%, and 3.7±0.26%, respectively. EtOH demonstrated significant antiradical activity, which was higher than that of all the extracts tested. Therefore, a range of concentrations was used to calculate the IC50 value, which was found to be 1.41 mg/mL (Figs. 2A and B).
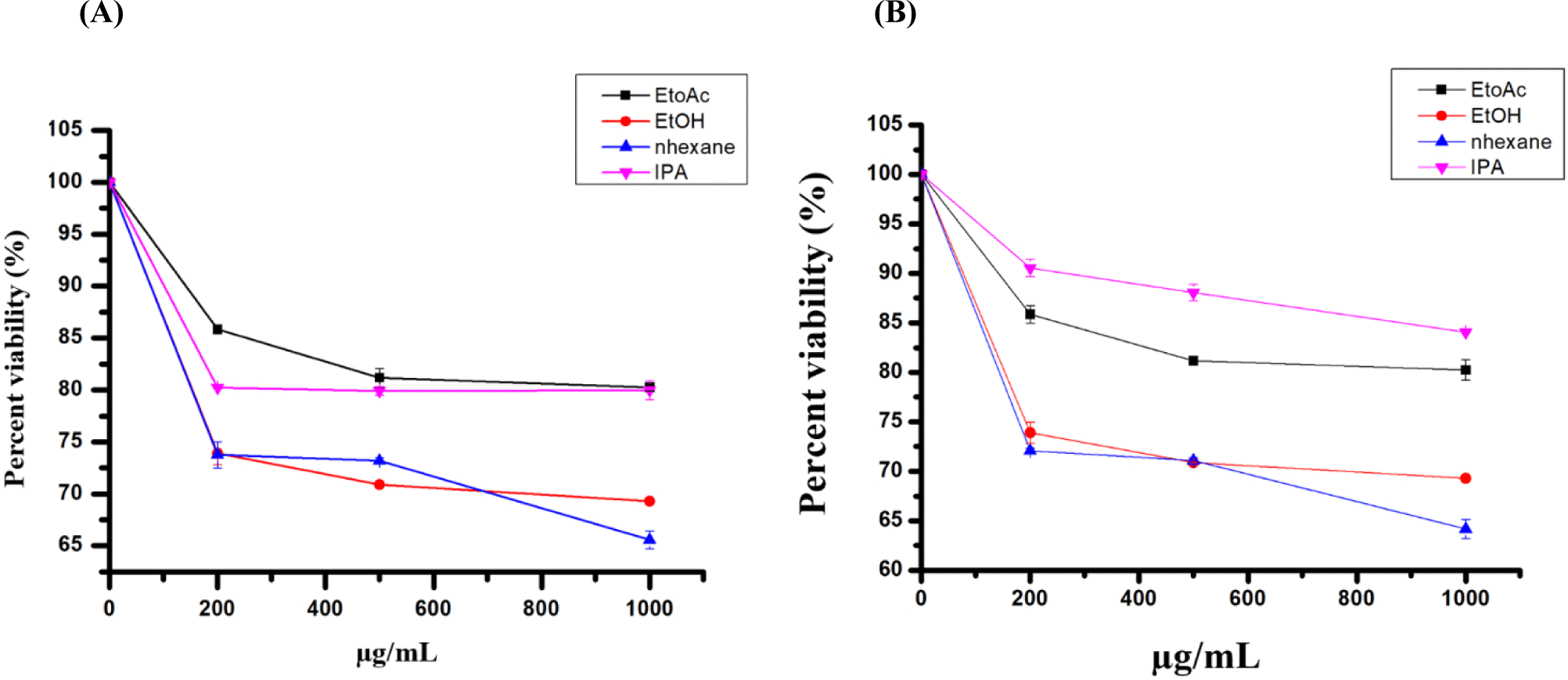
The study investigated the cytotoxic effects of conventional and green extracted FA on HepG2 and Huh7 cells using the MTT test after 48 hours of incubation with various concentrations. The extracts displayed varying levels of toxicity against the tested cell lines. At the highest concentration, the percentage viability of HepG2 cells treated with n-hexane, EtOH, EtOAc, and IPA extracts were 64.1±0.25%, 69.2±0.01%, 80.2±0.03%, and 84.2±0.03%, respectively. Similarly, for Huh7 cells, the percentage viability with the same extracts was 62.5±0.01%, 75.8±0.2%, 90.8.1±0.1%, and 96.4±0.001%. The n-hexane extract showed higher toxicity to the tested cell lines than the other extracts (Figs. 3A and B).
Discussion
Solvents used in extraction processes are mostly synthesised from non-renewable sources (Chemat et al., 2012). Hexane, the most used solvent for oil extraction, is cost-effective and efficient but poses significant risks due to its volatility, flammability, petroleum-based origin, and detrimental effects on the environment and human health (Chemat et al., 2019). In response, there has been a concerted effort to identify safer, green, bio-based alternatives such as EtOH, IPA, EtOAc, and D-limonene, which can be sourced from agricultural biomass (Chemat et al., 2012). These green solvents are endorsed by various guidelines, including those from AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and the Green Chemistry Institute-Pharmaceutical Roundtable, which evaluate solvents based on safety, environmental impact, occupational health, cost, and technical constraints (Henderson et al., 2011; Joshi and Adhikari, 2019; Prat et al., 2013; Prat et al., 2014).
In addition, the extraction of bioactive compounds is significantly influenced by the choice of solvent, which plays a crucial role in deciding the types and proportions of compounds extracted. This selection maximises the yield and potency of bioactive extracts and enhances the efficiency of development processes. Factors such as solvent polarity, penetration power, the ability of the solvent to protect extracted compounds from oxidation, chemical profiles, and synergistic effects all contribute to these differences (Gil-Martín et al., 2022; Pateiro et al., 2018; Sasidharan et al., 2011).
In the present study, EtOH was the best green solvent for precipitating proteins, extracting polyphenols, and calculating the percentage of PUFA/SFA. It also showed the best DPPH· scavenging activity. Overall, the polar nature, hydrogen bonding ability, denaturation capability, disruption of protein-protein interactions, and precipitation potential make EtOH a more efficient choice (Mohammad-Beigi et al., 2016; Yang et al., 2022; Yoshizawa et al., 2014). Considering that EtOH and EtOAc are more sustainable and efficient than n-hexane, they may serve as suitable alternatives for precipitating proteins, extracting polyphenols, DPPH· scavenging activity (EtOH), and oil extraction yield (EtOAc). Additionally, the ignition temperature EtOH (425°C) and EtOAc (426°C) pose fewer handling risks and are recognised as nontoxic compared to n-hexane (225°C). The boiling points of EtOH (78.2°C) and EtOAc (77.1°C) are only slightly higher than that of n-hexane (69.0°C; Smallwood, 1997), indicating that solvent evaporation does not require significantly higher temperatures when employing EtOH, EtOAc, or n-hexane.
Our results indicated that EtOAc (25.33±0.01%) are the best solvent for extracting mealworm oil. These results are in close agreement with Laroche and colleagues, who investigated the six methods of defatting on the oil extraction yield of Acheta domesticus and T. molitor. Their study revealed that EtOH consistently increased the oil extraction yield regardless of the insect type or method of extraction (Laroche et al., 2019). Table 1 illustrates that a comparison of FA compositions uncovered variations between oils extracted using n-hexane and those extracted using a green method, particularly in the percentages of extracted FAs. FA profile results align with the observations of Jajić et al. (2020), who analysed the mealworm larvae nutritional composition. They noted the presence of unsaturated FAs, notably oleic acid (C18:1) at 40.83%, followed by linoleic acid (C18:2) at 29.80% and linolenic acid (C18:3) at 1.08%. These findings are similar to the finding of Mlček et al. (2019), who reported similar trends, observing significant levels of palmitic (18.6%) and oleic acid (36.9%), although linoleic acid content was notably higher at 30.9%.
Ultrasound or pressurised liquid extraction (PLE) by EtOH or EtOH: H2O extraction was reported by del Hierro et al. (2020). PLE using EtOH (50.91%) and EtOH: H2O (45.21%) revealed that the major compound present was linoleic acid. The second major compound identified was palmitic acid, present in EtOH extracts at 17.44% and in EtOH: H2O extracts at 15.49%. Similarly, PLE by EtOH or EtOH: H2O extract revealed that the major compounds present were linoleic acid (55.20%) and palmitic acid (17.4%), respectively. In another investigation involving black soldier Fly (BSF), the FA profiles of oils extracted through traditional Soxhlet extraction using n-hexane and green extraction with 2-methyloxolane (2-MeO) were relatively similar. The predominant FA was lauric acid (42.29%), followed by linoleic acid (13.91%), palmitic acid (13.83%), oleic acid (11.43%), and myristic acid (9.36%), listed in decreasing order of abundance. These results indicated no significant difference between conventional and green solvent extraction methods.
A dietary intake with a low PUFA/SFA ratio (below 0.45) is associated with increased blood cholesterol levels. The extracted oils from this study exhibited high PUFA/SFA ratios across all extracts. These findings suggest that mealworms extracted with EtOH possess well-balanced and desirable FA profiles, which could have positive implications for human dietary consumption. Furthermore, oils rich in PUFA are often sought after for their potential use in skincare products within the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries, as discussed by Ramadan et al. (2003).
There is a need for more sustainable processes in chemical extraction, particularly in protein recovery, due to the drawbacks of classical solvents. However, finding green solvents suitable for protein recovery has been challenging, as proteins are often not soluble in typical green solvents like water or supercritical fluids such as CO2 (Bubalo et al., 2018; Chemat et al., 2019). Combining of biodegradable solvents with innovative technologies like microwave or ultrasound can enhance the purification process. Replacing classical solvents with biodegradable ones can lead to greener processes due to their efficient extraction capabilities and environmental friendliness (Bubalo et al., 2018; Kumar et al., 2021).
Polyphenols are known for enhancing potential health benefits such as antioxidant, antihypertensive, immunomodulatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, and antiviral activities (Rathod et al., 2023). As given in Fig. 1C, mealworms extracted with EtOH displayed significant phenolic contents (0.7 mg GAE/g). The amount of TPC depends on the solvent polarity and various factors such as diet and the extraction method used (Baek et al., 2019). Comparing green and conventional extraction methods revealed that mealworms extracted using EtOH exhibited higher TPC than those extracted using other organic solvents, including n-hexane. Therefore, the EtOH solvent utilised in this study facilitated the extraction of maximum polyphenol content from mealworms. As per the findings of Ravi et al. (2019) the polyphenol content in BSF oil extracted using MeTHF was higher than that extracted using n-hexane. In a recent study, an investigation was carried out to quantify the TPC present in extracts derived from T. molitor and A. domesticus using various extraction techniques and solvents of different polarities. The study revealed that the amounts varied significantly depending on the extraction solvent used. Results revealed that aqueous EtOH extract was the preferred solvent for extracting phenolic compounds (del Hierro et al., 2020). Phenols play a significant role in enhancing the sensory and nutritional quality of oils. They also offer protection against lipid oxidation by quenching radical reactions. Oils enriched with phenolic compounds may have health-enhancing potential, especially regarding antioxidant properties, antimicrobial effects, immune system support, growth performance, and overall animal health (Mahfuz et al., 2021).
Remarkably, mealworms extracted with EtOH exhibited notably higher radical scavenging activity (IC50=1.5 mg/mL) than those extracted using conventional methods or other environmentally friendly solvents (Fig. 2). Consistent with the findings by Ravi et al. (2019) employing a polar solvent like MeTHF enhanced the antioxidant capacity of BSF oil compared to that extracted using n-hexane. The higher DPPH· scavenging capacity can be attributed to their distinct phenolic compositions. Our study found that mealworms extracted with EtOH were particularly abundant in phenolic acids, which are known for their antioxidant properties and efficacy in scavenging intracellular ROS. However, various other compounds present in mealworms contribute significantly to their antioxidant activity. Both oils and FAs have been recognised for their potent antioxidant properties and impact on antioxidant activities (Çakmak et al., 2012).
The cytotoxicity of green and conventional extracted oils on HepG2 and Huh7 cells was examined using the MTT test. The results from the 48-hour incubation period revealed that n-hexane and EtOH extracts exhibited cytotoxic effects compared to the other extracts when tested against HepG2 and Huh7 cells (Fig. 3). At 1,000 μg/mL, green and conventional-extracted oils reduced cell viability, reaching 65.5% and 69.2% for n-hexane and EtOH, respectively. Our findings align with previously published research, although our study demonstrates relatively weak activity. Specifically, it was reported that the Soxhlet-extracted mealworm using petroleum ether inhibited the growth of HepG2 (IC50: 0.98%) and Caco-2 (IC50: 0.37%) cells. The apoptotic mechanism was associated with the activation of caspases -8, -9, and -3, correlating with the action of its FAs (Wu et al., 2020). Another study has also reported the cytotoxic effects of mealworm crude extracts on hepatic and colon cancer cells (Lee et al., 2015). Di Nunzio and colleagues suggested that certain FAs, such as linoleic acid and α-linolenic acid, are associated with growth inhibition in HepG2 cells (Di Nunzio et al., 2011).
Conclusion
Our findings revealed the possibility of using green solvents rather than n-hexane to extract mealworms. These green solvents also led to a better FA composition, particularly rich in MUFA. Additionally, EtOH showed higher protein extraction capability, the highest DPPH· scavenging activity and TPC. Furthermore, the cytotoxicity assessment revealed varying toxicity levels among the extracts, with the hexane extract displaying higher toxicity than others. These results highlight the capability of green solvents to enhance the extraction efficiency and bioactivity of mealworm-derived products. Further research is necessary before green solvents can be employed in mealworm extraction processes.













