Introduction
Stress resulting from density is a significant concern livestock farming. Despite ongoing regulations regarding density, there are persistent cases of noncompliance with the standards for the appropriate number of livestock per area. Overcrowding is often linked to increased farm profitability (De Vries et al., 2016), however, the stress it induces not only leads to various diseases but also causes changes in gut microbiome, which can compromise the quality of livestock products (Peixoto et al., 2021). For example, overcrowding stress has been shown to decrease macrophage activity and increase Salmonella Enteritidis invasion in broiler chickens (Gomes et al., 2014). Similarly, overcrowding in dairy cows has been linked to reduced milk production and deteriorating health (Jensen et al., 2019). Additionally, it elevates stress hormones such as dehydroepiandrosterone and cortisol (Fustini et al., 2017).
Stress stimulates the brain and impacts the intestines, either directly or indirectly. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is activated when stressed, such as in cases of overcrowding. This activation releases cortisol and other glucocorticoid stress hormones, generating oxygen and nitrogen radicals (Chen et al., 2015). Nitric oxide is synthesized from L-arginine by nitric oxide synthase (NOS), and neuronal NOS (nNOS) is known to colocalizes with the HPA axis (Mogor et al., 2021). nNOS is transcriptionally controlled by glucocorticoids and plays a significant role in stress response (Chen et al., 2015). Chronic stress promotes increased nNOS expression in the brain (Zhou et al., 2011). Furthermore, nNOS has recently been shown to modulate the sensitivity to social stress through cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Yin et al., 2021). Stress-induced activation of the HPA axis also regulates the physiological functions of the digestive system, such as smooth muscle relaxation in the gastrointestinal tract, blood flow regulation, and alterations in neurotransmitter secretion (Mogor et al., 2021).
The gut microbiota is linked to stress response and the HPA axis (Warren et al., 2024). A germ-free mouse model study showed that stress activated a hyperactive HPA axis, including elevated adrenocorticotropic hormone and corticosterone levels, and normal nervous system function was restored after fecal microbiota transplantation from healthy mice (Cenit et al., 2017). Additionally, numerous studies on the consumption of probiotic supplements have shown improvements in stress and emotional responses through changes in the gut microbiota (Allen et al., 2016; Boehme et al., 2023; Culpepper et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020). Importantly, the addition of probiotic feed containing Bifidobacterium may counteract the adverse effects of overcrowding stress, potentially enhancing gut health and improving the quality of livestock food products. However, the intricate interaction between the stress response and gut microbiota remains largely unexplored.
This research utilized the nNOS-HiBiT knock-in mouse model designed by Han et al. (2021). The HiBiT system detects luciferase intensity, allowing for the accurate quantification of nNOS expression with high sensitivity. In previous work, nNOS was identified as a biomarker of stress-activated bowel motility in a stress-induced neonatal maternal separation mouse model using nNOS-HiBiT knock-in mice (Han et al., 2021). We employed nNOS-HiBiT knock-in mice to investigate the effects of crowding stress on the gut microbiota, aiming to provide insights into the brain-gut-microbiome axis by focusing on the differential expression of nNOS and the resulting microbial alterations in the ileum, cecum, and colon. The primary objective of this study is to elucidate the relationship between overcrowding stress and gut microbiota changes, thereby informing strategies to enhance livestock health and productivity.
Materials and Methods
Thirty-six male C57BL/6J mice (6 wk old), each harboring a 33-base pair HiBiT sequence knock-in in the nNOS gene were used. Genetically modified mice were generated as described previously (Han et al., 2021).
Mice were genotyped by snipping their tails. A piece shorter than 2 mm was quickly cut from the tail tip using sharp surgical scissors, and hemostasis was achieved by applying slight pressure to the incision site. Genotyping was performed using a MightyAmpTM Genotyping Kit (Takara Bio, Seoul, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. In brief, the mouse tail was incubated in extraction buffer with Proteinase K for 5 min at 60°C, heated at 98°C for 2 min, and then centrifuged. The resulting supernatant was used as the template for polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Amplification of the nNOS-HiBiT gene was conducted using C1000 TouchTM Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) under condition 98°C for 2 min; 40 cycles of 98°C for 10 s, 60°C for 15 s, 68°C for 1 min/kb. The PCR solution containing 5X Loading Dye was analyzed by electrophoresis.
The animal experiment in this study were approved by Institution Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Seoul National University (Approval No. SNU-200803-1).
All the mice were kept in a specific pathogen-free animal room at a temperature of 23±1°C and humidity of 55±5%. The lights were turned on and off in a light-dark cycle with 12-h intervals.
The mice were randomly divided into three groups as follows: the MPC2 group (n=6; two mice per cage), the MPC10 group (n=10; ten mice per cage), and the MPC20 group (n=20; twenty mice per cage) with cages measuring 391 mm×199 mm×160 mm (Sealsafe Plus GM500, Tecniplast, West Chester, PA, USA). MPC2 was regarded as the control group, while MPC10 and MPC20 were considered as the stress-induced groups. Stress was induced for two weeks, during which time the cage bedding was changed for MPC2 but not for MPC10 and MPC20. All the mice had ad libitum access to a standard laboratory chow diet and water.
The mice were euthanized at the end of the 14-d experiment in accordance with the ethical guidelines. For corticosterone quantification, blood was collected via cardiac puncture into BD Microtainer® Blood Collection Tube and centrifuged at 12,000×g for 3 min to obtain serum. The hypothalamus, ileum, cecum, and colon samples were collected for nNOS quantification. Additionally, a portion of intestinal tissue from MPC2 and MPC20 was used for 16s rRNA sequencing. All samples were immediately frozen at –80°C and stored until further analysis.
The total protein in each hypothalamus, ileum, cecum, and colon sample was quantified using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Takara Bio). Proteins were extracted from the samples using RIPA Lysis and Extraction buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and homogenized with a bead homogenizer (BeadBugTM 6, Bechmark Scientific, Sayreville, NJ, USA). The 10-fold diluted samples were mixed with 1 mL of a working solution composed of BCA reagents A and B, and the absorbance was measured at 562 nm in triplicate using a spectrophotometer (Spectrostar Nano, BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany).
The amount of HiBiT-tagged nNOS proteins was quantified using the Nano-Glo® HiBiT Lytic Detection System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The homogenized samples were incubated with the Nano-Glo® HiBiT Lytic Reagent in a 1:1 ratio for 10 min. HiBiT binds tightly to LgBiT protein derived from the reagent solution and generates luminescence, measured in triplicate using a GloMax® 96 Microplate Luminometer (Promega).
Serum corticosterone concentration was determined using a Mouse/Rat Corticosterone ELISA Kit (Arigo Biolaboratories, Hsinchu, Taiwan). Briefly, 10 μL of serum was added in duplicate into the antibody-coated microplate and incubated for 2 h at room temperature (RT) with 100 μL of Incubation Buffer and 50 μL of HRP-conjugated Corticosterone. After four times of washing step, 200 μL of TMB substrate was added and incubated for 30 min at RT in the dark. The absorbance was measured at 450 nm.
Each 1 mg of mouse ileum, cecum, and colon sample was placed in 1 mL of UltraPureTM DNase/RNase-Free Distilled Water (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) for 10 min and heated to 95°C for 5 min using a heating block. Lysis was achieved by performing two cycles of bead-beating at maximum speed for 90 s using BeadBugTM 6 (Bechmark Scientific). According to the manufacturer’s instructions, DNA extraction was continued using the ZymoBIOMICSTM DNA Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). After estimating quality and quantity, extracted DNA was diluted to a 5 ng/μL concentration and stored at –20°C until further processing.
Library preparation was conducted using a two-step PCR protocol according to Illumina’s 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation Guide. Amplicon PCR was performed as follows for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA gene with V3-V4 universal primers: initial denaturation 94°C for 3 min; 25 cycles of 95°C for 30 s, 55°C for 30 s, 72°C for 30 s; and a final extension at 72°C for 3 min. The resulting product was purified using AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). Index PCR was performed as follows using 16s rRNA V3-V4 amplicons and Nextera® XT Index primers (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA): initial denaturation 95°C for 3 min; 8 cycles of 95°C for 30 s, 55°C for 30 s, 72°C for 30 s; and a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. Indexed libraries were cleaned using AMPure XP beads. The concentration of libraries was quantified using Quant-iTTM PicoGreenTM dsDNA Assay Kit (Invitrogen). Equal amounts of libraries were pooled and sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq system (Macrogen, Seoul, Korea).
Illumina adapters and primers were trimmed using the Trimmomatic software (version 0.38; Bolger et al., 2014). Paired-end reads were analyzed on the Nephele platform (version 2.31.2; Weber et al., 2017), employing the DADA2 pipeline (version 1.28; Callahan et al., 2016) with default parameters. This pipeline facilitates sequence denoising, chimera removal, and amplicon sequence variants assignment. Taxonomic classification was performed using the RDP method against the SILVA (version 138.1) database (Quast et al., 2012). Samples with low depths were excluded from the subsequent analyses.
Microbial composition and diversity were analyzed using MicrobiomeAnalyst 2.0 (Lu et al., 2023). Taxonomic differences between microbial communities in the groups were explored using heat tree analysis, visualizing those with a Wilcoxon p-value≤0.05. Alpha diversity was estimated using ecological indices (Chao1, Shannon, and Fisher’s alpha) and assessed using the Mann-Whitney U test. Beta diversity was evaluated using principal coordinate analysis based on Bray-Curtis dissimilarity, and statistical significance among the groups was determined using permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA). Dendrograms were constructed from feature-level calculations using unweighted UniFrac distances. The correlation between nNOS and corticosterone was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients, and between nNOS and microbial taxa using Spearman’s correlation coefficients. A multiple linear regression analysis was conducted using MaAsLin2 (Mallick et al., 2021), with nNOS and corticosterone included as covariates. p-values were adjusted using the false discovery rate, and those less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism software. Data are presented as mean±SD. Continuous variables between the MPC2 and MPC20 groups were compared using unpaired t-tests or Mann-Whitney U tests, whereas differences among three or more groups were assessed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05 significant.
Results
Mice carrying a HiBiT knock-in sequence within nNOS were generated and confirmed by genotyping (Supplementary Fig. S1), and were subsequently included in the experiment. The nNOS-HiBiT knock-in mice were randomly divided into three groups: MPC2, MPC10, and MPC20. nNOS expression in the hypothalamus exhibited an elevation with increasing density and was significantly increased in MPC20 compared to MPC2 (Fig. 1A). Serum corticosterone levels were also significantly higher in the MPC20 mice than in the MPC2 mice (Fig. 1B). Overexpression of hypothalamic nNOS and corticosterone indicated that overcrowding condition in MPC20 induced considerable stress. Additionally, variations were observed in the expression of nNOS in the ileum, cecum, and colon (Fig. 1C). In the ileum, nNOS levels were significantly higher in MPC20 than in MPC2. There was no significant difference in the nNOS levels in the cecum, but a decreasing trend was observed in the colon (p=0.06).
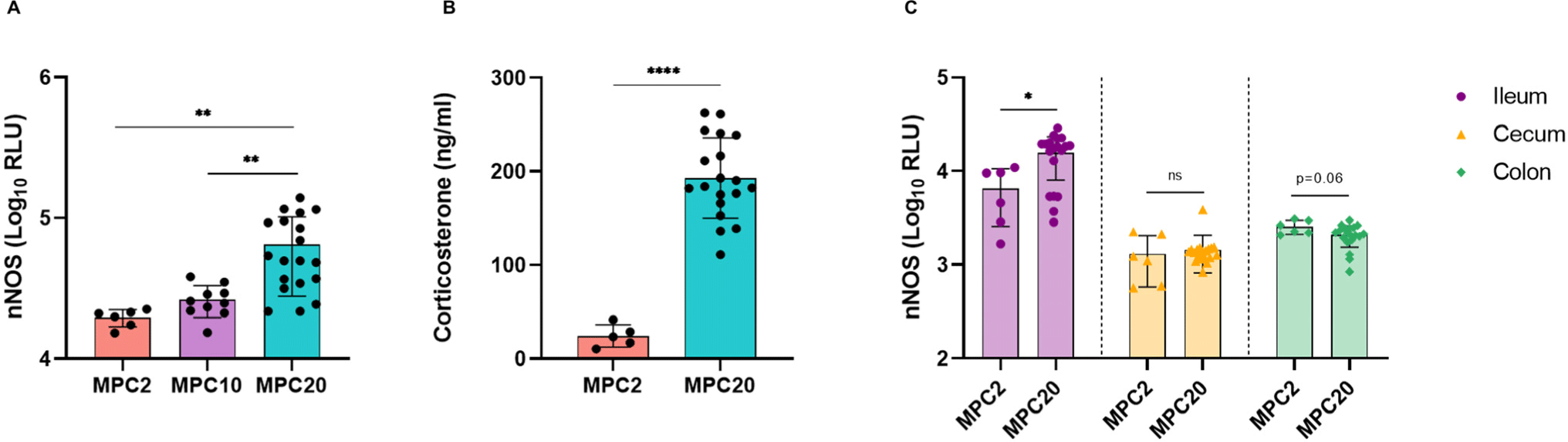
Microbial community profiling was performed on the MPC2 and MPC20. MPC20 exhibited higher alpha diversity, as estimated by the Chao1, Shannon, and Fisher’s alpha indices, compared to MPC2 (Figs. 2A, B, and C). The colon of MPC20 mice showed a significant increase in all alpha diversity indices. The alpha diversity of gut microbiota has been reported to either increase or decrease in stressful situations (Ma et al., 2023). In the beta diversity analysis, MPC2 and MPC20 clustered differently in the ileum, cecum, and colon, with PERMANOVA confirming significant differences (Figs. 2D, E, and F). Clustering based on phylogenetic diversity revealed a clear distinction between the two groups in the dendrogram (Figs. 2G, H, and I). Overcrowding stress induces considerable changes in the gut microbial community profile.
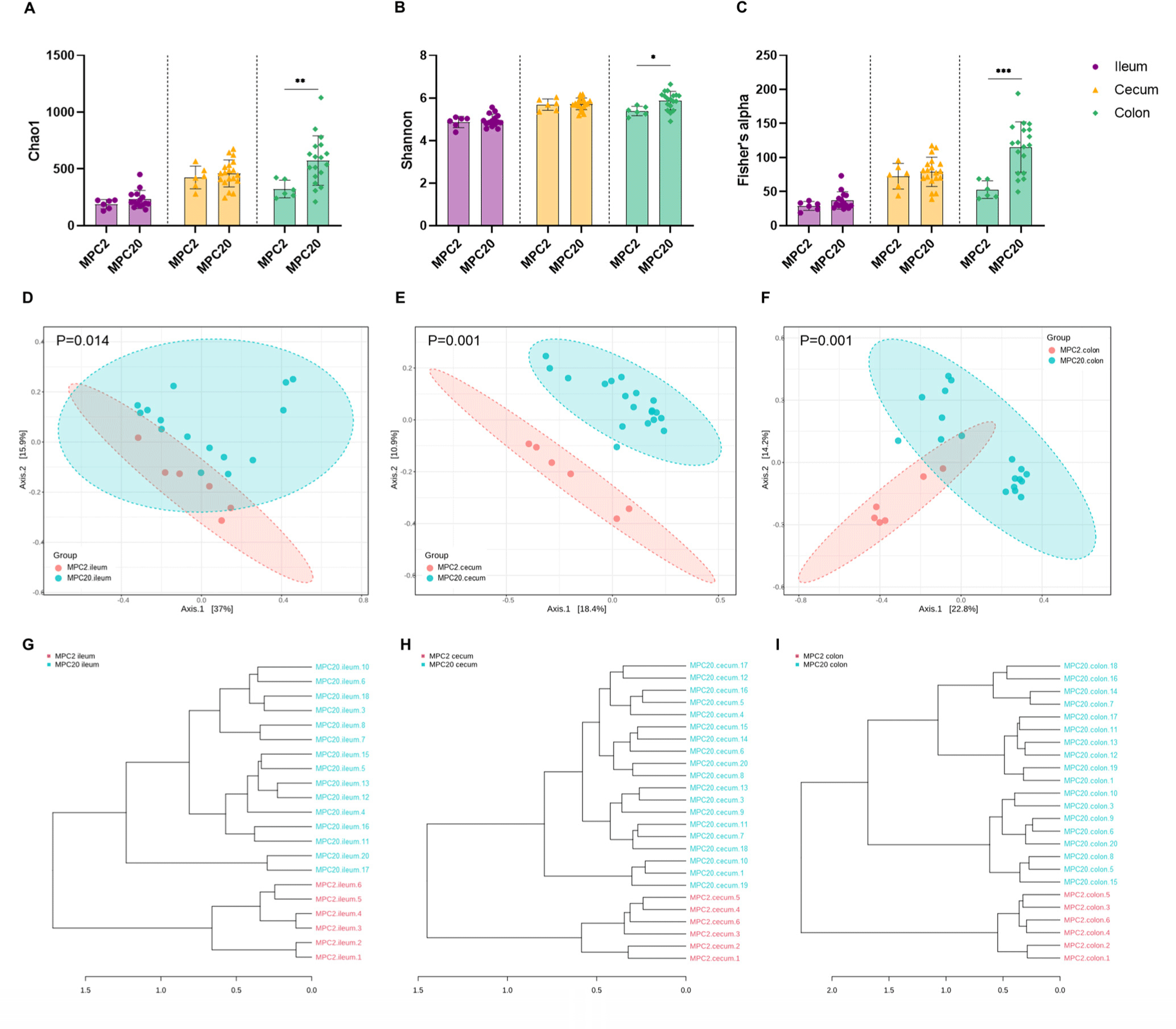
Regarding the microbial composition at the phylum level, MPC20 showed a higher relative abundance (RA) of Proteobacteria than MPC2 in the ileum, cecum, and colon. Camphylobacterota showed higher RAs in the ileum and colon of MPC20 than MPC2. In contrast, the MPC20 RAs of Actinobacteriota and Verrucomicrobiota were lower than those in MPC2 (Fig. 3A). Genus-level heat tree analysis revealed significantly lower RAs in MPC20 for Bifidobacterium (Actinobacteriota), Akkermansia (Verrucomicrobiota), Ligilactobacillus, Faecalibaculum (Bacillota). In contrast, levels of Helicobacter (Campylobacterota), Parasutterella, Muribaculum (Proteobacteria), Oscillibacter, Anaerotruncus, and Roseburia (Bacillota) RAs were significantly elevated in the MPC20 group (Fig. 3B and Supplementary Fig. S2). Regardless of the intestinal region, the RAs of Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia were significantly lower in MPC20 (Figs. 3C and D). Meanwhile, Helicobacter populations significantly increased in the ileum and colon, and Parasutterella abundance significantly increased in the cecum of MPC20 (Figs. 3E and F).
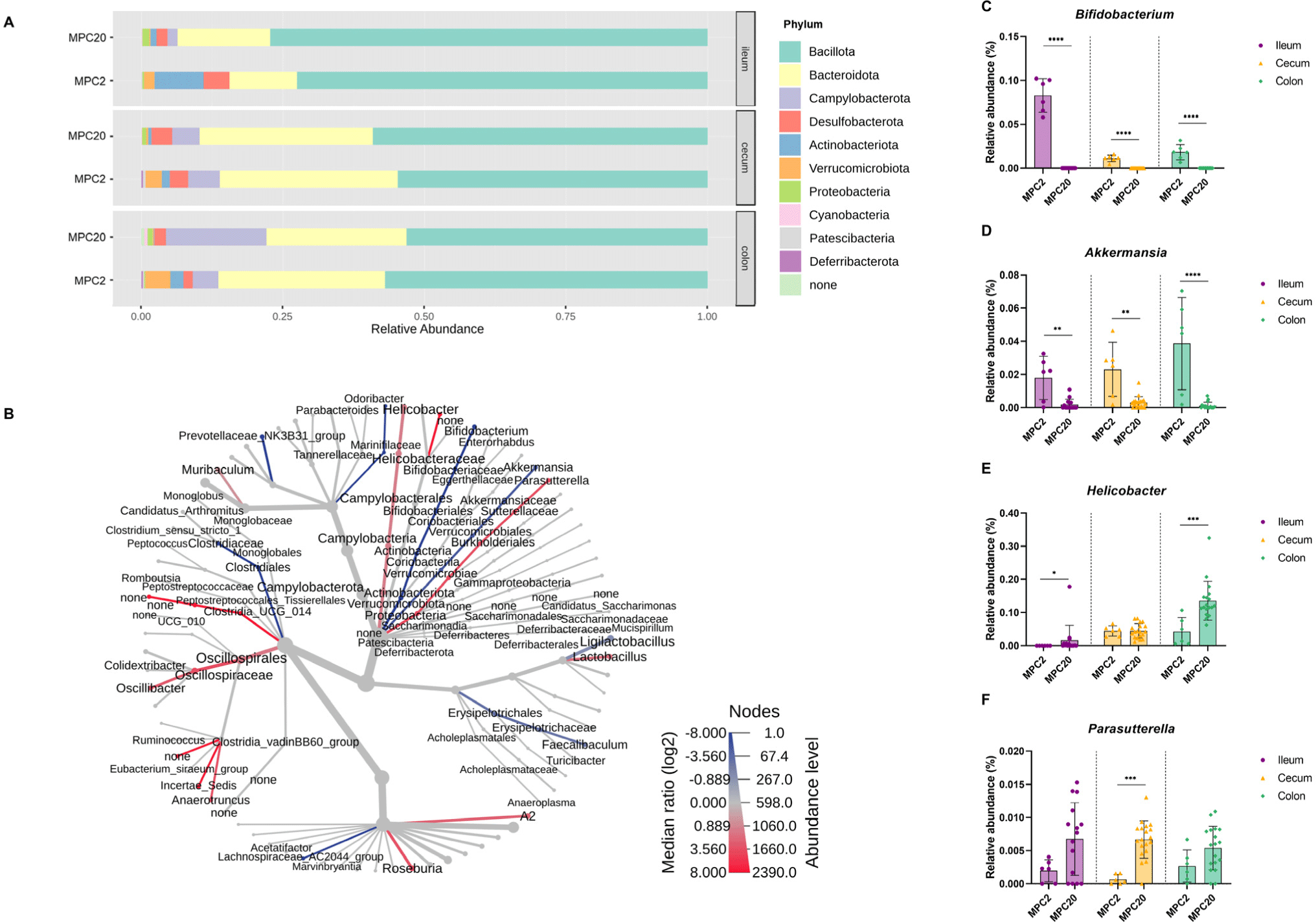
Different correlation patterns between nNOS and corticosterone were observed depending on the intestinal region: the ileum, cecum, or colon (Figs. 4A, B, and C). A tendency for a positive correlation was observed in the ileum (p=0.055; Fig. 4A). However, no significant correlation was found between nNOS and corticosterone levels in the cecum or colon (Figs. 4B and C). This result was presumed to be due to the significantly increased expression of nNOS in the ileum, as shown in Fig. 1C, which was not observed in the cecum or colon.
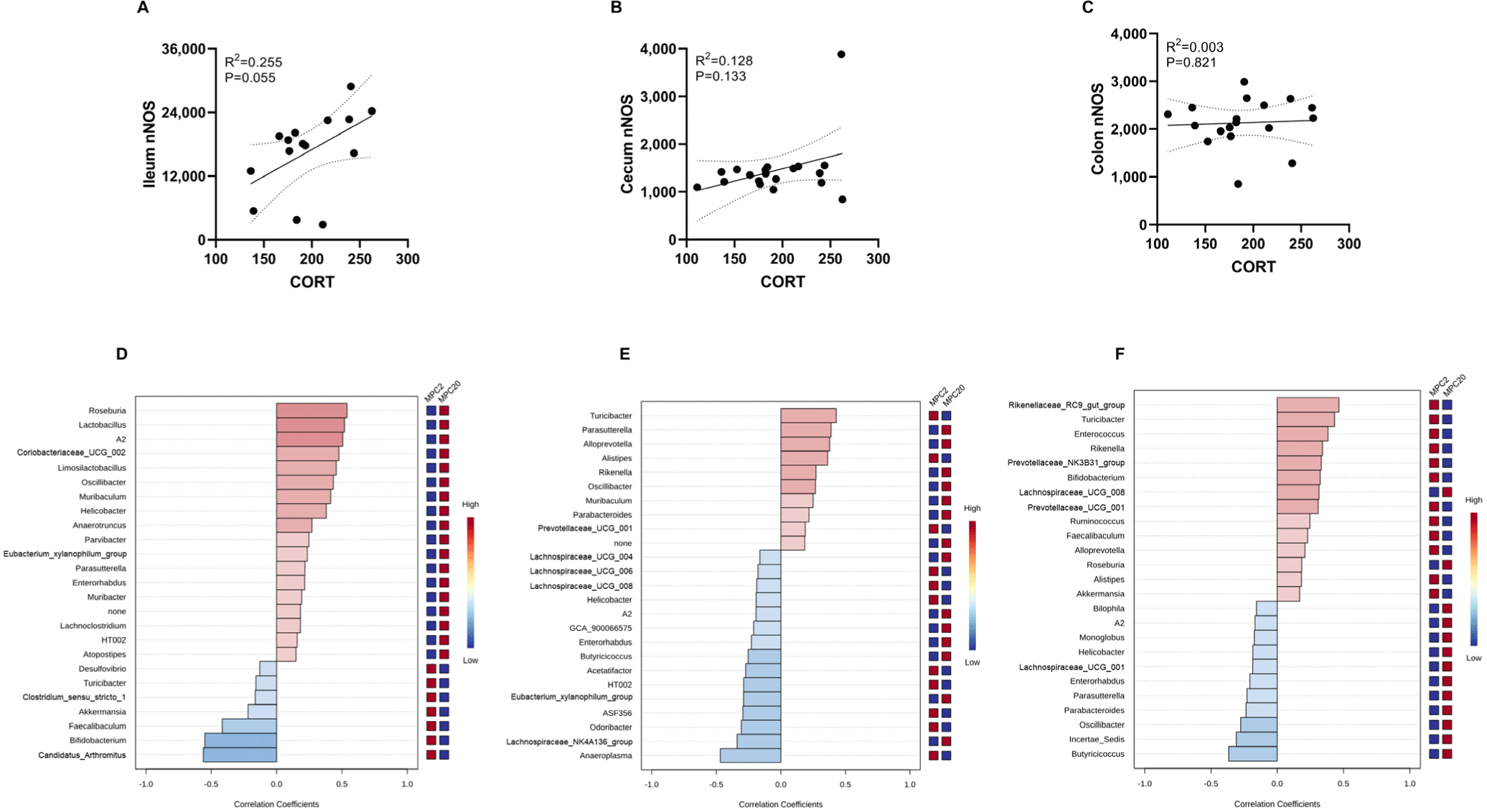
The correlation between nNOS and microbial taxa at the species level in the ileum, cecum, and colon was analyzed (Figs. 4D, E, and F). Distinct correlation patterns were observed in each intestinal region. Specifically, A2, Helicobacter, and Enterorhabdus showed a positive correlation in the ileum but a negative correlation in the cecum and colon. Oscillibacter and Parasutterella were positively correlated in the ileum and cecum yet negatively correlated in the colon. Turibacter exhibited a negative correlation in the ileum but a positive correlation in the cecum and colon.
Furthermore, we used a multiple linear regression model to elucidate the association between the covariates (nNOS and corticosterone) and microbiota composition (Table 1). Remarkably, Bifidobacterium abundance decreased significantly across all three intestinal regions. This indicates that Bifidobacterium is vulnerable to overcrowding stress. Furthermore, the faecalibaculum and prevotellaceae_NK3B31_groups showed a significant decrease in the cecum and colon. Odoribacter and Bacteroides were decreased in the cecum and colon, respectively.
Discussion
Stress causes an increase in nNOS expression mainly in the hypothalamus (Chen et al., 2015; Mogor et al., 2021; Shirakawa et al., 2004), but it also significantly affects nNOS expression in the intestine (Schneider et al., 2023). The enteric nervous system functions independently of the central nervous system. Because of this functional autonomy, enteric nerves have the plasticity to respond flexibly depending on the situation (Yunker and Galligan, 1998). Therefore, distinct responses to the exact circumstances may occur depending on the region in the gastrointestinal tract.
Motor activity in the small intestine is reduced in response to psychological stress (Kellow et al., 1992; Mönnikes et al., 2001). Stress and mechanical stimulation caused by fasting or feeding increase nNOS expression in the small intestine (Ito et al., 2017). Additionally, nNOS immunohistochemistry of the small intestine showed a significant increase in nNOS-containing cells in patients with intestinal pseudo-obstruction, who had symptoms of intestinal obstruction but no physical blockage (Wang et al., 2000). We also found that chronic stress induced by overcrowding increased nNOS expression in the ileum.
The cecum contains a large proportion of vagally innervated myenteric ganglia (Berthoud et al., 1990). About 65%–66% of the vagus nerve is found in the cecum, whereas the ileum accounts for 35% and the distal colon for 16% (Berthoud et al., 1990). In an experiment on nNOS expression following neurectomy, splanchnic ganglionectomy, which removes the intestinal ganglion, or 6-OH-dopamine treatment, which mainly suppresses the sympathetic nervous system by chemically destroying specific nerves, increased intestinal nNOS expression (Nakao et al., 1998). However, vagotomy, which involves removal of the vagus nerve, had no significant effect on nNOS mRNA expression (Nakao et al., 1998). Therefore, high vagal nerve distribution is presumed to be responsible for the unaffected nNOS levels in the cecum.
Chronic psychological stress is closely associated with colonic inflammation (Duffy et al., 1991; Garrett et al., 1991; Levenstein et al., 2000). When colitis develops, the physical length of the colon decreases, and peristalsis decreases as the colon shortens (Delaroque et al., 2021; Reber et al., 2006). In the colon of a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mouse model, the number of nNOS-immunopositive cells, NOS activity, and nNOS synthesis decreased (Mizuta et al., 2000). Recently, it has been demonstrated that stress directly affects the enteric nervous system, lowering the number of nNOS-expressing neurons in the colon (Schneider et al., 2023).
We extrapolated that overcrowding stress affects the nervous system and intestinal motility, altering gut microbiota composition. To the best of our knowledge, little is known about the impact of overcrowding stress on the gut microbiota. According to Delaroque et al. (2021), overcrowding stress in mice results in hyperglycemia, moderate chronic inflammation, and changes in the gut microbiota. We found that Bifidobacterium (Chen et al., 2021; Tojo et al., 2014), a representative probiotic, and Akkermansia (Ding et al., 2021; Zhai et al., 2019), a next-generation probiotic, significantly decreased in response to overcrowded stress. Conversely, Helicobacter (Guo et al., 2009; Li et al., 1998; Maltz et al., 2019), which is associated with gastrointestinal inflammation, and Parasutterella (Everard et al., 2011; Henneke et al., 2022), which is associated with the onset of obesity and diabetes, were significantly increased. These results suggest that overcrowding stress has an unfavorable impact on the composition of the gut microbial community.
Akkermansia has a protective effect against obesity, diabetes, colitis (Wang et al., 2020; Zhai et al., 2019), and neurological diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Blacher et al., 2019), Alzheimer’s disease (Ou et al., 2020), and autism (Wang et al., 2011). Psychological stress diminishes the presence of intestinal Akkermansia (McGaughey et al., 2019). More specifically, Akkermansia muciniphila alleviates depression caused by chronic stress by modulating the gut microbiota and serum metabolomics (Cheng et al., 2021; Ding et al., 2021). Helicobacter has primarily been studied as the cause of upper digestive tract diseases; however, it has also been linked to dyspepsia and visceral hypersensitivity in the lower digestive tract (Budzyński and Kłopocka, 2014; Gerards et al., 2001; Li et al., 1998; Su et al., 2000). Psychological stress promotes gastric colonization by Helicobacter pylori and contributes to developing peptic ulcers (Guo et al., 2009). However, there is ongoing controversy over the potential health effects of Helicobacter colonization of the lower digestive tract due to chronic stress. Parasutterella has been associated with the development of inflammatory bowel disease (Chen et al., 2018), obesity (Everard et al., 2011; Henneke et al., 2022), and diabetes (Henneke et al., 2022). This bacterium suppresses energy metabolism and short-chain fatty acid synthesis in intestinal microorganisms (Luo et al., 2018). Furthermore, a strong correlation has been detected between high Parasutterella abundance and low intracranial volume (Hu et al., 2024). Thus, it is assumed that Parasutterella is connected to the brain-gut-microbiome axis; however, its significance in stress mechanisms requires further research.
Meanwhile, Bifidobacterium was decreased in all three intestinal regions (ileum, cecum, and colon) when the correlation with changes in the gut microbiota was analyzed using nNOS and corticosterone as covariates. Previous studies have confirmed that Bifidobacterium abundance is reduced in various digestive diseases and under conditions of chronic stress (Chen et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2017). Animal studies have demonstrated that Bifidobacterium supplementation alleviates stress and enhances immune function. Bifidobacterium was below the detection limit in social defeat stress-induced mice but was significantly present in the stress-resilient group (Yang et al., 2017). Oral administration of Bifidobacterium LAC-B improves resilience to chronic social defeat stress (Yang et al., 2017). In another mouse experiment that induced social defeat stress, the oral administration of Bifidobacterium longum R0175 increased anti-inflammatory responses and stress resistance (Partrick et al., 2021).
In studies involving livestock such as broilers, pigs, beef cattle, and dairy cows, Bifidobacterium supplementation has been shown to boost immunity, improve the quality of livestock products, and increase overall productivity. In broilers, the addition of Bifidobacterium has been linked to improved gut health and reduced disease incidence, thereby enhancing growth performance (Estrada et al., 2001; Kabir et al., 2004). Similarly, in pigs, Bifidobacterium supplementation enhances immune response and growth rates, resulting in higher-quality meat (Méndez-Palacios et al., 2018; Pang et al., 2022). For beef cattle, the inclusion of Bifidobacterium in their diet has been associated with improved feed efficiency and weight gain, contributing to enhanced meat quality (Alawneh et al., 2020; Uyeno et al., 2015). Additionally, in dairy cows, Bifidobacterium supplementation has been shown to improve milk yield and quality, while also promoting overall health (Krishnan et al., 2020; Nalla et al., 2022). These finding collectively highlight the potential of Bifidobacterium as a beneficial probiotic for improving livestock health and productivity, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of livestock products.
Overall, overcrowding stress induced ileum nNOS and serum corticosterone levels, altering the gut microbiota composition. Specifically, overcrowding stress led to a decrease in Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia, along with an increase in Helicobacter and Parasutterella. Notably, Bifidobacterium was found to be especially vulnerable to overcrowding stress, as it consistently declined, regardless of the intestinal region. This study supports previous findings indicating that Bifidobacterium plays a significant role in regulating the brain-gut-microbiome axis. However, further studies are needed, as our research is not sufficient to fully explain the complex interaction between NO mechanisms and the gut microbiome. For example, NO produced by Bacillus is known to have an anti-aging effect (Ayala et al., 2017). Therefore, research that considers NO produced by gut microbiota separately from the host’s NO mechanism is also required.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have demonstrated that overcrowding stress can have negative effects on the intestinal health of animals. The findings of this study hold significant implications for livestock management practices. By understanding the effects of overcrowding stress on gut health and the microbiota, producers can implement strategies, such as the inclusion of probiotics like Bifidobacterium in feed, to mitigate stress-related issues. This approach not only enhances animal welfare but also improves the quality and safety of livestock products, ultimately contributing to greater economic sustainability in the livestock industry.













