Introduction
Since Alexander Fleming’s discovery of penicillin in 1928, antibiotics have been widely used in human and veterinary medicine to control bacterial infections (Kasimanickam et al., 2021; Tan and Tatsumura, 2015). In livestock production, antibiotics not only treat bacterial diseases to safeguard animal health but also promote growth in species, such as poultry, beef cattle, and swine, thus enhancing animal welfare and food safety (Kasimanickam et al., 2021; Marshall and Levy, 2011). However, the misuse and overuse of antibiotics have led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, rendering some infections untreatable (Hutchings et al., 2019). Antibiotic resistance refers to the ability of bacteria to survive and multiply despite antibiotic treatment, making these drugs ineffective (Chinemerem Nwobodo et al., 2022). When bacteria become resistant to three or more antibiotic classes, they are categorized as multidrug-resistant (MDR; Li et al., 2023); resistance to all but one or two classes is classified as extensively drug-resistant and resistance to all classes is termed pandrug-resistant (Magiorakos et al., 2012). Antibiotic resistance has escalated to a global health crisis, complicating bacterial infection treatment and threatening public health (Chinemerem Nwobodo et al., 2022). Antibiotic-resistant bacteria can easily spread through transmission between animals, animal products, and humans, resulting in severe infections.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports multiple foodborne Salmonella outbreaks in the US between 2013 and 2024, primarily linked to contaminated animal products (CDC, 2024). Notably, in 2024, an outbreak of Salmonella Enteritidis linked to contaminated eggs caused 65 illnesses and 24 hospitalizations, with investigations ongoing. Similarly, in 2021, outbreaks linked to raw frozen breaded stuffed chicken and ground turkey contaminated with S. Enteritidis and Salmonella Hadar caused 36 illnesses (12 hospitalizations) and 3 illnesses (4 hospitalizations), respectively. Other vehicles of Salmonella infection have included ground beef, raw chicken products, chicken salad, shell eggs, raw cookie dough, and charcuterie meats (CDC, 2024). In Korea, Salmonella was the leading cause of foodborne outbreaks from 2019 to 2023, affecting 6,449 patients across 163 outbreaks. Other pathogens responsible for foodborne outbreaks included Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Campylobacter jejuni, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus spp., and Vibrio spp. (Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [MFDS], 2024). According to Batz et al. (2011), Salmonella infections in the US result in an estimated loss of approximately 17,000 quality-adjusted life years annually and incur costs of around $3.3 billion due to medical expenses and reduced productivity.
The persistence of Salmonella-derived foodborne outbreaks has heightened concerns about antibiotic-resistant Salmonella strains. Chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella strains were first reported in the early 1950s, followed by resistance to antibiotics such as tetracycline, ampicillin, kanamycin, and trimethoprim (Jamilah et al., 2020; van Leeuwen et al., 1982). MDR Salmonella strains originating from livestock and animal products can be transmitted to humans. For instance, during 2021–2022 in the US, 87% (1,110 out of 1,281 samples tested positive) of MDR Salmonella Newport were linked to beef products (Ford et al., 2023). To manage foodborne outbreaks effectively, it is essential to investigate the transmission routes of MDR Salmonella. Moreover, given that the efficacy of antibiotics is based on targeting specific bacterial functions, elucidating the mechanisms underlying antibiotic resistance is vital for ensuring the effective application of antibiotics (Abushaheen et al., 2020). Identifying critical transmission pathways can guide the development of prevention and control strategies. This review examines Salmonella detection cases in animal products, analyses antibiotic resistance patterns, outlines mechanisms of resistance acquisition, and proposes solutions to control antibiotic-resistant Salmonella outbreaks.
Prevalence of Salmonella in Animal Products
Salmonella species are among the leading bacterial causes of foodborne gastroenteritis globally (Sanchez et al., 2002). These gram-negative, facultative anaerobic bacteria belong to the Enterobacteriaceae family and are commonly found in the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and animals (Agbaje et al., 2011). There are two Salmonella species, S. bongori (V) and S. enterica, with S. enterica divided into six subspecies: enterica (I), salamae (II), arizonae (IIIa), diarizonae (IIIb), houtenae (IV), and indica (VI) (Giammanco et al., 2002; Popoff and Minor, 1997). Among these, the S. enterica subspecies is most associated with human infections, with Salmonella Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis being the most significant serotypes of the more than 1,530 identified (Giammanco et al., 2002; Grimont and Weill, 2007).
Animal products, such as poultry (duck, chicken, and turkey), pork, and eggs, are primary sources of Salmonella infections. However, other food sources, including vegetables and fruits, have also been implicated (Sanchez et al., 2002). A meta-analysis by Ferrari et al. (2019) detected diverse Salmonella serovars, including S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, Salmonella Kentucky, and Salmonella Sofia, as well as in pork, including S. Typhimurium, S. Hadar, Salmonella Derby, and Salmonella Meleagridis, across all five continents. Below, we summarize global data on Salmonella prevalence and serovar distribution in animal products reported from 2013 to 2024 (Table 1).
| Food | Sample | No. of positive samples/no. of samples tested (% positive) | Serovars of Salmonella | Place of purchase | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poultry | Poultry | 150/1,322 (11.3) Top two product types - Ground chicken 18/97 (15.6) - Ground turkey 23/180 (13.3) |
Salmonella Heidelberg, Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Kentucky, Salmonella Hadar, Salmonella Schwarzengrund, Salmonella Agona, Salmonella Senftenberg, Salmonella Berta, Salmonella Litchfield, Salmonella Mbandaka, Salmonella Typhimurium |
Retail chain stores, USDA-permitted processing establishments | United States | Mazengia et al. (2014) |
| Duck | 56/109 (51.3) | S. Typhimurium, S. Enteritidis, Salmonella Stanley, Salmonella Regent, Salmonella Winterthur, Salmonella Westhampton |
Supermarkets, traditional markets, internet shopping, wholesale market | Korea | Yoon et al. (2014) | |
| 11/18 (61) | S. Enteritidis | Supermarkets, traditional market | Korea | La et al. (2021) | ||
| 87/309 (28.2) | S. Enteritidis | Retail markets | Korea | Kang et al. (2024) | ||
| Chicken | 3/80 (3.7) | S. Typhimurium, S. Enteritidis |
Supermarkets, traditional markets, internet shopping, wholesale market | Korea | Yoon et al. (2014) | |
| 51/200 (26) | Salmonella Paratyphi, S. Heidelberg, Salmonella Lome, Salmonella Muenster |
Independent stores, main chain distributor |
United States | Donado-Godoy et al. (2015) | ||
| 170/525 (32.4) | S. Heidelberg, S. Kentucky, S. Typhimurium, Salmonella Infantis, S. Senftenberg, Salmonella Thompson |
Supermarket stores | United States | Guran et al. (2017) | ||
| 41/291 (14.1) | S. Enteritidis | Local supermarkets, traditional markets, the internet |
Korea | La et al. (2021) | ||
| 200/235 (85.1) | S. Schwarzengrund, S. Infantis, Salmonella Manhattan |
Retail stores and chicken processing plants | Japan | Sasaki et al. (2021) | ||
| 97/555 (17.5) | S. Enteritidis | Retail markets | Korea | Kang et al. (2024) | ||
| Raw chicken | 12/132 (9.1) | S. Infantis | Private production units | Romania | Tîrziu et al. (2020) | |
| Eggs | Egg contents | 42/650 egg pools (20 eggs per pool; 6.5) | Salmonella Gallinarum | Conventional farm, organic farms | Korea | Lee et al. (2013) |
| Eggshells, egg contents | 2 Strains from eggshell, 1 Strain from egg contents | S. Enteritidis | Grocery stores | Korea | Kim et al. (2013) | |
| Liquid egg | 9/195 (4.6) | S. Typhimurium, Salmonella Bareilly, Salmonella Tennessee, Salmonella Richmond |
Egg-breaking plants, a farm | Korea | Kim et al. (2015) | |
| Eggshells | 3/48 (6.3) | S. Enteritidis, S. Infantis | Private production units | Romania | Tîrziu et al. (2020) | |
| Eggshells, egg contents | Eggshells 11/60 (18.3), Egg contents 12/60 (20.0) |
S. Infantis, S. Bareilly, S. Agona, S. Enteritidis, Salmonella Montevideo, Salmonella Newport, S. Senftenberg, Salmonella Derby |
Grading and packing plant | Korea | Jung and Lee (2024) | |
| Pork | Ready-to-eat (RTE) pork (salami) | 6/100 (6) | Salmonella Brandenburg, S. Typhimurium, Salmonella Rissen, Salmonella London |
Retail | Italy | Bonardi et al. (2018) |
| Raw pork | 33/146 (22.6) | S. Typhimurium, S. Rissen, S. Infantis, Salmonella Bredeney, S. Derby, S. Brandenburg, S. Enteritidis, Salmonella Gloucester, Salmonella Goldcoast, Salmonella Kottbus, Salmonella Ruziz |
Private production units | Romania | Tîrziu et al. (2020) | |
| RTE pork (sausages) | 3/62 (4.8) | S. Typhimurium | Retail markets | Romania | Tîrziu et al. (2020) | |
| Pork | 7/503 (1.4) | Not analyzed | Retail markets | Korea | Kang et al. (2024) |
Salmonella prevalence in poultry has been widely documented. Mazengia et al. (2014) analyzed 1,322 poultry samples, including whole chickens, ground chicken, and ground turkey, collected from US retail stores and USDA-approved processing facilities in 2011 and 2012, reporting a Salmonella prevalence of 11.3%. The most common serotypes identified were Salmonella Heidelberg, S. Enteritidis, and S. Kentucky. In Korea, Yoon et al. (2014) reported Salmonella in 51.3% of ducks and 3.7% of chickens sold at various market types, including supermarkets, traditional markets, internet outlets, and wholesale stores, in 2013. Common serotypes included S. Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis, while serotypes such as Salmonella Stanley, Salmonella Regent, Salmonella Winterthur, and Salmonella Westhampton were detected only in ducks. La et al. (2021) focused on S. Enteritidis and isolated Salmonella in 61% of retail ducks and 14.1% of chickens between 2019 and 2020. Similarly, Kang et al. (2024) reported a Salmonella prevalence of 28.2% in ducks and 17.5% in chickens, while beef samples showed no Salmonella contamination. In the US, Guran et al. (2017) detected Salmonella in 32.4% of chicken samples, with serovars including S. Heidelberg, S. Kentucky, S. Typhimurium, Salmonella Infantis, Salmonella Senftenberg, and Salmonella Thompson. Donado-Godoy et al. (2015) identified Salmonella Paratyphi, S. Heidelberg, Salmonella Lome, and Salmonella Muenster in 26% of chicken meats. In Japan, Sasaki et al. (2021) detected Salmonella in 85.1% of chicken products (minced meat, breast, neck skin, thigh, and liver) purchased from processing plants and retail stores between 2018 and 2021. The most frequently detected serovars included Salmonella Schwarzengrund, S. Infantis, and Salmonella Manhattan.
Eggs are another significant vector for Salmonella infections. In Korea, eggs and egg-based foods, such as kimbap, are major sources of Salmonella outbreaks. Hong et al. (2015) classified eggs and processed egg products, including whole egg liquid and egg powders, as high-risk (Group I) due to their frequent Salmonella contamination. Jung and Lee (2024) found Salmonella in 18.3% of eggshells and 20% of egg contents sampled from 60 grading and packing plants, with S. Infantis as the predominant serovar. Similarly, in Europe, eggs and egg-based products are leading sources of Salmonella outbreaks, followed by pork and bakery products (European Food Safety Authority [EFSA] and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control [ECDC], 2021). Tîrziu et al. (2020) reported a 6.3% prevalence of S. Enteritidis and S. Infantis in eggshells in Romania.
Pork and beef also pose risks for Salmonella transmission. In Korea, Kang et al. (2024) found a 1.4% prevalence of Salmonella in pork samples. In Italy, Salmonella Brandenburg, S. Typhimurium, Salmonella Rissen, and Salmonella London were detected in ready-to-eat (RTE) pork salami at a 4.8% prevalence, while in Romania, raw pork had a 22.6% prevalence, with RTE pork (primarily sausages) showing a 4.7% prevalence of various serovars, including S. Typhimurium (Tîrziu et al., 2020). In beef, Salmonella serovars such as S. Newport, S. Typhimurium, S. Enteritidis, Salmonella Braenderup, Salmonella Dublin, Salmonella Uganda, Salmonella Idikan, S. Infantis, and Salmonella Muenchen were detected in ground beef, intact raw beef, and RTE beef. These findings were linked to 27 Salmonella outbreaks in the US between 2012 and 2019 (Canning et al., 2023).
In summary, animal products are significant vectors for Salmonella transmission to humans. The diversity of serovars, particularly S. Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis, highlights the potential for varied antibiotic resistance profiles, emphasizing the need for robust monitoring.
Status of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella
Although antibiotics are not always necessary for treating Salmonella infections, they are crucial for immunocompromised patients and those with severe cases. However, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics have accelerated the emergence of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella. Historically, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were the primary treatments for salmonellosis (Stoycheva and Murdjeva, 2006). As resistance to these drugs emerged, third-generation fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, became the preferred treatment (Bhandari et al., 2023). Increasing resistance among Salmonella strains has made managing salmonellosis more challenging (Argimón et al., 2022; CDC, 2023). The use of antibiotics in food animal production has significantly contributed to the emergence of resistant Salmonella strains.
The primary classes of antibiotics to which Salmonella has developed resistance are summarized in Table 2. Aminoglycosides, mainly effective against gram-negative bacteria, exert antibacterial effects by binding to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibiting protein synthesis (Gonzalez and Spencer, 1998; Hermann, 2005). Tetracyclines and amphenicols similarly inhibit protein synthesis by binding to bacterial ribosomes, with amphenicols specifically acting on the 50S ribosomal subunit (Frye and Jackson, 2013; Hermann, 2005). Sulfonamides, often combined with trimethoprim, interfere with bacterial folic acid synthesis, impairing DNA replication (Brumfitt et al., 1973; Eliopoulos and Huovinen, 2001). Fluoroquinolones inhibit bacterial DNA replication by targeting DNA gyrase but are prone to rapid resistance development (Drlica and Zhao, 1997; Redgrave et al., 2014). β-Lactams, the most widely used antibiotic class, inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, primarily targeting gram-positive bacteria but are also effective against some gram-negative bacteria (Tipper and Strominger, 1965). Carbapenems, a subset of β-lactams, exhibit strong resistance to β-lactamase and extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL), enzymes that can inactivate many β-lactam antibiotics (Vardakas et al., 2012).
In animal husbandry, antibiotics are widely used for disease control and growth promotion. This practice contributes to the development of antibiotic resistance in commensal and opportunistic bacteria in food animals (Cameron and McAllister, 2016). Antibiotic-resistant Salmonella is frequently detected in poultry, such as chicken and duck, as well as in pork, and is a major source of human infection through contaminated raw meat (Borges et al., 2019). Pavelquesi et al. (2023) reported high levels of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella isolates from 53 contaminated chicken samples in Brazil. Among 78 Salmonella strains, resistance rates were 83.3% for amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, 64.1% for sulfonamide, and 46.2% for tetracycline. Additionally, 65.4% of the strains showed either resistance or intermediate susceptibility to ciprofloxacin.
Similarly, Perin et al. (2020) analyzed 98 Salmonella strains isolated from frozen chicken samples and found that all strains were resistant to chloramphenicol, imipenem, meropenem, and amikacin. High resistance rates were also observed for nalidixic acid (95.9%), tetracycline (93.9%), amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (83.7%), and ciprofloxacin (75.5%). In the US, Punchihewage-Don et al. (2024) reported that 27.2% of the 213 Salmonella isolates from chicken were resistant to tetracycline and minocycline, the highest among antibiotics tested. Likewise, Lv et al. (2024) found tetracycline (49.1%), ampicillin (48.2%), and streptomycin (35.1%) were the most frequently observed resistant antibiotics in China, where tetracycline and streptomycin are commonly used as growth promoters (McDermott et al., 2016).
In Korea, the highest resistance rates were observed for nalidixic acid (75.9%), ampicillin (63.2%), streptomycin (61.3%), tetracycline (59.3%), and sulfisoxazole (57.3%). Salmonella spp. isolation rates were higher in poultry [chickens (n=278) and ducks (n=177)] compared to cattle (n=0) and swine (n=2). These results represent a marked increase compared to 2021, when resistance rates were lower: 64.5% for nalidixic acid, 30.2% for ampicillin, 25.0% for tetracycline, 23.0% for streptomycin, and 23.4% for sulfisoxazole (Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency [APQA] and National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation [NIFDS], 2024). Notably, resistance profiles differ between Salmonella isolated from pork and poultry. Gomes et al. (2022) reported that Salmonella isolated from pork had the highest resistance to azithromycin (95.0%), followed by ampicillin (51.7%), oxytetracycline (40.0%), and chloramphenicol (40.0%). In contrast, Salmonella isolates from poultry showed high resistance to quinolones, such as nalidixic acid (82.8%) and ciprofloxacin (74.1%), as well as sulfamethoxazole (81.0%), oxytetracycline (79.3%), and β-lactams (>69%).
Most studies reported antibiotic resistance data for Salmonella serotypes collectively as Salmonella spp. (Thung et al., 2016; Vaez et al., 2020); however, differences in antibiotic resistance have also been observed among individual serotypes. The antibiotic resistance patterns of S. Typhimurium frequently included the ASSuT profile (ampicillin, streptomycin, sulphonamides, and tetracycline; Liu et al., 2023; Mellor et al., 2019). Resistance rates in S. Typhimurium were higher compared to other serotypes (Busani et al., 2004; Listorti et al., 2022). In Italy, Busani et al. (2004) reported that S. Typhimurium isolates from animal and animal products showed higher resistance to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, nalidixic acid, tetracycline, and streptomycin. S. Enteritidis strains frequently showed resistance to ampicillin, streptomycin, and sulphonamides in animal products isolates. Additionally, S. Infantis strains showed higher resistance to sulphonamides and kanamycin. These observations highlight that S. Typhimurium consistently exhibits higher resistance rates across multiple antibiotics compared to S. Enteritidis or S. Infantis (Busani et al., 2004). Contrastingly, Abou Elez et al. (2021) reported that S. Enteritidis isolates had higher resistance rates than S. Typhimurium isolates to chloramphenicol, nalidixic acid, and imipenem in Egypt. The antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella may differ regionally depending on antibiotic usage practices or the sources from which they are isolated.
Given these high resistance rates highlighted in these studies emphasize the urgent need for international collaboration to address antibiotic resistance, particularly in food animal production, where extensive antibiotic use promotes resistance in zoonotic pathogens such as Salmonella. Furthermore, these data indicate that antibiotic resistance in Salmonella from animal products is a global concern, with significant regional variations influenced by antibiotic usage practices. These illustrate how antibiotic use directly impacts resistance development in food animals. A summary of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella isolated from animal products is presented in Table 3.
| Food | Resistant antibiotics | % Resistance (No. of positive samples/no. of samples tested) | % MDR (No. of positive samples/no. of samples tested) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw meat | Chicken | Ampicillin Sulfamethoxazole Neomycin Erythromycin |
100% 52.6% 44.7% 39.4% |
(38/38) (20/38) (17/38) (15/38) |
65.7% (25/38) | Tagar and Qambrani (2023) |
| Erythromycin Cephalothin Nalidixic acid Streptomycin |
100% 87.2% 87.2% 70% |
(47/47) (41/47) (41/47) (33/47) |
87.2% (41/47) | Kim et al. (2012) | ||
| Poultry | Nalidixic acid Ampicillin Streptomycin Tetracycline Sulfisoxazole Cefotaxime |
76.0% 63.1% 61.3% 59.3% 57.3% 55.8% |
(346/455) (287/455) (279/455) (270/455) (261/455) (254/455) |
61.3% (279/455) | APQA and NIFDS (2024) | |
| Nalidixic acid Sulfamethoxazole Oxytetracycline Ciprofloxacin Ceftiofur Ampicillin |
82.8% 81.0% 79.3% 74.1% 70.7% 70.7% |
(48/58) (47/58) (46/58) (43/58) (41/58) (41/58) |
79.3% (46/58) | Gomes et al. (2022) | ||
| Pork | Azithromycin Ampicillin Oxytetracycline Chloramphenicol Nalidixic acid |
95.0% 51.7% 40.0% 40.0% 38.3% |
(57/60) (31/60) (24/60) (24/60) (23/60) |
50.0% (30/60) | ||
| Streptomycin Tetracycline Ampicillin Chloramphenicol Ciprofloxacin |
90.5% 88.1% 81.0% 71.4% 50.0% |
(38/42) (37/42) (34/42) (30/42) (21/42) |
80.9% (34/42) | Viana et al. (2019) | ||
| Poultry Buffalo Beef Goat |
Erythromycin Cefepime Colistin Azithromycin Tetracycline Ciprofloxacin |
100% 98.2% 94.7% 93.0% 87.7% 84.2% |
(57/57) (56/57) (54/57) (53/57) (50/57) (48/57) |
19.3% (11/57) | Fatima et al. (2023) | |
| Beef | Ampicillin Oxytetracycline Amoxicillin Neomycin Tetracycline Ciprofloxacin Cefepime |
91.0% 89.2% 82.1% 80.4% 76.7% 60.7% 48.2% |
(51/56) (50/56) (46/56) (45/56) (43/56) (34/56) (27/56) |
69.6% (39/56) | Hussain et al. (2020) | |
| Chilled meat | Chicken | Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid Sulfonamide Tetracycline |
83.3% 64.1% 46.2% |
(65/78) (50/78) (36/78) |
53.8% (42/78) | Pavelquesi et al. (2023) |
| Meropenem & Imipenem Chloramphenicol Amikacin Nalidixic acid Tetracycline Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid Ciprofloxacin |
100% 100% 100% 95.9% 93.9% 83.7% 75.5% |
(98/98) (98/98) (98/98) (94/98) (92/98) (82/98) (74/98) |
85.7% (84/98) | Perin et al. (2020) | ||
| Tetracycline Minocycline Nitrofurantoin Cefazolin Ampicillin |
82.6% 42.3% 40.3% 38.0% 32.4% |
(176/213) (90/213) (86/213) (81/213) (69/213) |
45.5% (97/213) | Punchihewage-Don et al. (2024) | ||
| Sulphafurazole Streptomycin Nalidixic acid |
92.0% 74.0% 68.0% |
(46/50) (37/50) (34/50) |
92.0% (46/50) | Moon et al. (2016) | ||
| Swine | Tetracycline Streptomycin Sulphafurazole |
95.2% 90.5% 88.1% |
(40/42) (38/42) (37/42) |
88.1% (37/42) | ||
In 2015, the World Health Organization undertook efforts to improve global monitoring systems for antibiotic use, recognizing antibiotic resistance as a critical public and animal health issue. The World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH) similarly acknowledged the impact of antibiotic use on resistance development (Jibril et al., 2021; WOAH, 2015). Multiple studies have demonstrated a correlation between antibiotic use, especially of critically important antibiotics, and resistance rates in Salmonella from farms and products. For instance, chickens treated with ceftiofur for Salmonella infections exhibited resistance to ceftiofur (Dutil et al., 2010). In Nigerian poultry farms, widespread use of tetracycline and sulfonamides was significantly associated with resistance to these antibiotics in Salmonella strains isolated from poultry meat (Igbinosa et al., 2023).
In the US, between 2018 and 2019, MDR S. Newport with reduced susceptibility to azithromycin caused 255 illnesses and 60 hospitalizations. These cases were linked to Mexican-style soft cheese and beef, contaminated with azithromycin- and ciprofloxacin-resistant S. Newport (Plumb et al., 2019). In Pakistan, significant resistance levels were detected in antibiotics commonly used as growth promoters and therapeutic agents in livestock and poultry, including erythromycin (100%), colistin (94.7%), tetracycline (87.7%), ciprofloxacin (84.2%), and ampicillin (64.9%). Resistance to clinically important antibiotics, such as azithromycin, was notably high at 93.0%, potentially linked to the widespread use of azithromycin for the treatment of COVID-19 in Pakistan (Fatima et al., 2023; Saeed et al., 2021). These findings underscore the substantial relationship between antibiotic use in livestock and the emergence of resistant Salmonella strains, highlighting the urgent need for strengthened antibiotic stewardship in animal agriculture to mitigate public health risks.
Antibiotic resistance in Salmonella from animal products arises primarily through two mechanisms: co-resistance, where a single gene imparts resistance to multiple antibiotics, and the presence of multiple genes conferring resistance to different antibiotics (Huo et al., 2024). Co-resistance allows Salmonella to resist various antibiotics, contributing to the prevalence of MDR strains, which are resistant to three or more antibiotic classes. The spread of MDR Salmonella represents a significant public health threat, as these strains are often resistant to critical antibiotics, including fluoroquinolones, third-generation cephalosporins, and carbapenems (Ejo et al., 2016; Hussain et al., 2020). Co-resistance is particularly common in Salmonella strains resistant to both nalidixic acid and fluoroquinolone antibiotics (Oteo et al., 2000). Nalidixic acid, a first-generation quinolone, has historically been used to treat human and animal infections and as a growth promoter in food animals. However, excessive use has led to an increase in quinolone-resistant Salmonella strains and reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones (Cho et al., 2019; Tamang et al., 2011).
Kapil et al. (2002) found that 56 nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella strains exhibited significantly lower susceptibility to ciprofloxacin than 34 nalidixic acid-sensitive strains. Similarly, Ryan et al. (2011) demonstrated reduced ciprofloxacin susceptibility in 19 nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella strains, while nalidixic acid-sensitive strains showed no change in susceptibility. Kang et al. (2024) reported that 61.9% of S. Infantis isolates (253/409) from food animals (chickens, swine, cattle, and ducks) were resistant to ceftiofur, an important cephalosporin antibiotic. Notably, most resistant isolates obtained from chickens (249/253, 98.4%). Ceftiofur-resistant isolates also showed increased resistance to non-β-lactam antibiotics, including nalidixic acid, streptomycin, tetracycline, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Kang et al., 2024; Yarar et al., 2023). Resistance to third-generation cephalosporins, such as ceftiofur, is primarily driven by the bacterial synthesis of ESBL and/or AmpC β-lactamases, which inactivate cephalosporins (Burke et al., 2014). ESBL-producing Salmonella strains from animal products frequently display resistance to cephalosporins and multiple other antibiotic classes, including aminoglycosides, tetracycline, and fluoroquinolones, further contributing to MDR (Jeon et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2001).
Jeon et al. (2019) observed that ESBL/pAmpC-positive Salmonella strains exhibited resistance to four or more antibiotics, including cephalosporins as well as non-cephalosporin antibiotics such as amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, tetracycline, ampicillin, ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid, and gentamicin. The rising prevalence of MDR Salmonella in animal products presents a significant global health concern, emphasizing the need for international cooperation and stricter controls on agricultural antibiotic use to protect public health.
How Salmonella Becomes Antibiotic Resistant?
Salmonella employs several mechanisms to neutralize antibiotic action. The first is the acquisition of antibiotic resistance genes, the second is the neutralization of antibiotics through enzymes, and the third is the control of the efflux and influx of antibiotics into and out of bacterial cells (Fig. 1).
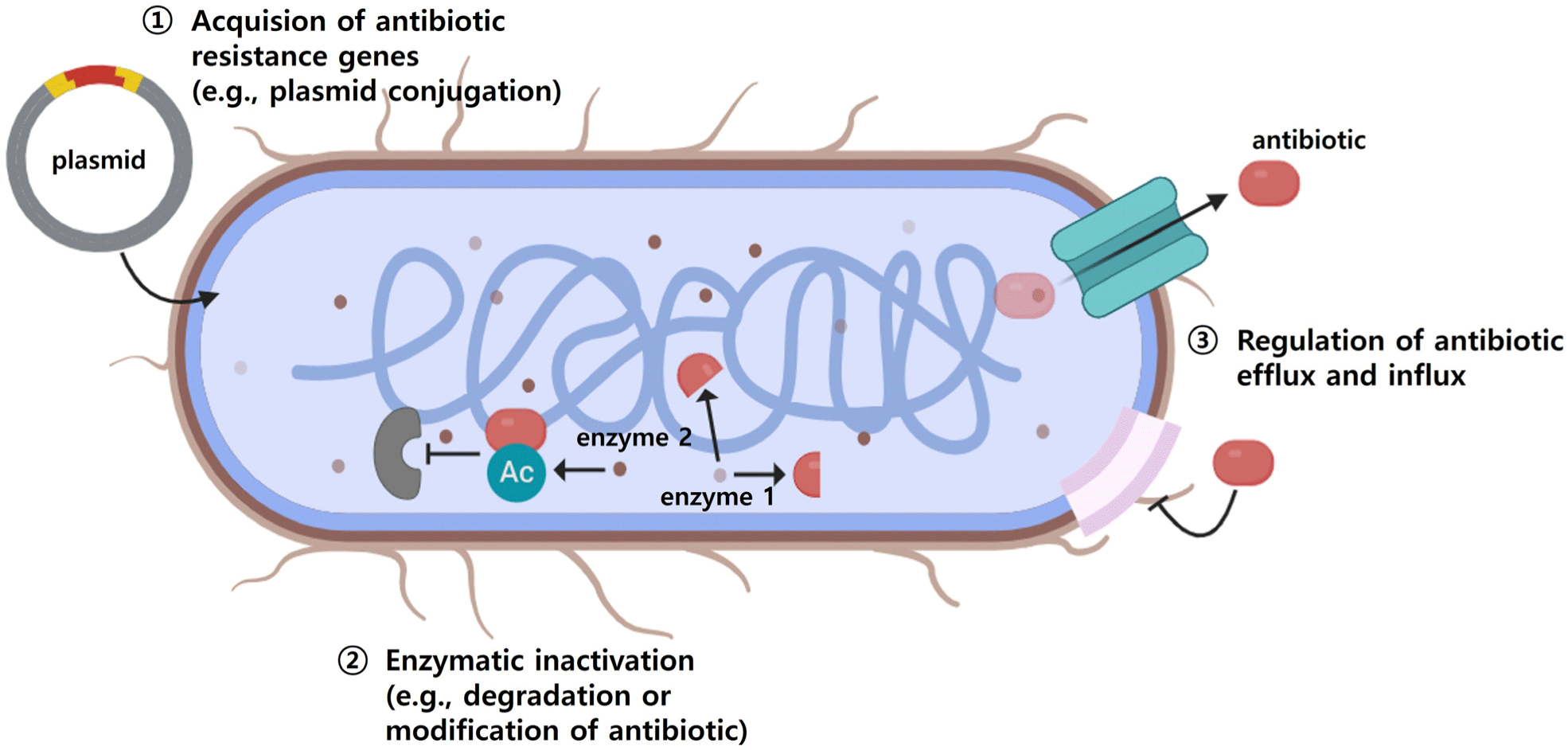
Salmonella primarily acquires resistance through the transfer of plasmids or resistance islands carrying antibiotic-resistance genes (Okaiyeto et al., 2024). Plasmids maintain stability within bacterial populations by employing post-segregational killing systems, which eliminate daughter cells lacking the plasmid (Aviv et al., 2014). The SalmonellatetA gene, responsible for tetracycline resistance, resides on a plasmid, facilitating its transfer among other Salmonella strains (Alcaine et al., 2007). Additionally, some Salmonella isolates carry multiple plasmids encoding resistance to antibiotics such as ampicillin, kanamycin, streptomycin, and tetracycline, leading to the development of MDR strains (Gebreyes and Altier, 2002; Rozwandowicz et al., 2018).
The IncHI1 plasmid, which carries ESBL genes and resistance genes for aminoglycosides and tetracyclines, has been detected in humans and animals across Europe (Rozwandowicz et al., 2018). IncHI1 has been notably implicated in MDR in Salmonella Typhi (Holt et al., 2011). Ferreira et al. (2024) demonstrated that Salmonella strains (S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, and S. Heidelberg) acquired resistance by artificial conjugation with a plasmid carrying resistance genes, resulting in a 4,096-fold increase in the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for β-lactams.
The AmpC β-lactamase enzyme, encoded by plasmids, is particularly robust against inhibitors such as clavulanic acid and sulbactam (Jacoby, 2009; Le Terrier et al., 2024). For example, 16 Salmonella isolates from US food animals were found to possess IncA/C plasmids encoding AmpC β-lactamase (Glenn et al., 2011). Megaplasmids, identified by Rosenberg et al. (1981), are significantly larger than standard plasmids, carry diverse resistance and virulence genes. The pESI megaplasmid, primarily identified in S. Infantis, is approximately 280 kb in size and confers resistance to various antibiotics while enhancing virulence (Aviv et al., 2014). Recent studies have documented the emergence of similar pESI-like megaplasmids globally (Cohen et al., 2020; Hall et al., 2021). For example, pESI-like plasmids in Russian broiler Salmonella isolates encoded resistance genes for spectinomycin (aadA1), doxycycline (tetA/tetR), tetracycline (tetM), trimethoprim (dfrA14), and sulfonamides (sul1). In Korea, Salmonella isolates from poultry farms classified as pESI-positive exhibited a 99.2% MDR rate, significantly higher than the 6.7% MDR rate of pESI-negative isolates (Kim et al., 2024).
Salmonella produces enzymes that neutralize antibiotics by breaking them down or chemically modifying them. Chloramphenicol resistance arises from chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) an enzyme that attaches an acetyl group to chloramphenicol, preventing it from binding to the A-site on the bacterial ribosome and thereby inhibiting its ability to disrupt protein synthesis (Goodale et al., 2020). Brunelle et al. (2015) demonstrated that Salmonella isolates harboring the cat gene, which encodes CAT, displayed high resistance to chloramphenicol (MIC>512 μg/mL). Additionally, exposure to chloramphenicol has been linked to increased cellular invasion in Salmonella, suggesting that resistance may enhance infection risk. Guerra et al. (2000) indicated that integron-mediated cat transmission provides Salmonella with chloramphenicol resistance.
Carbapenems, critical last-resort antibiotics, are rendered ineffective by carbapenemase-producing non-typhoidal Salmonella, with resistant isolates reported from food, human, and animal sources (Fernández et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2017). S. Infantis from minced pork and Salmonella Indiana from chicken carcasses showed carbapenem resistance (Borowiak et al., 2017; Fischer et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2017). In Europe, S. Infantis, is considered a major carrier of carbapenem resistance (Borowiak et al., 2017), with the first carbapenem-resistant isolates detected in German livestock (Fischer et al., 2013).
β-Lactams, enzymes produced by gram-negative bacteria including Salmonella, hydrolyze the β-lactam ring, neutralizing β-lactam antibiotics. ESBL are more potent than standard β-lactamase and target third-generation- and fourth-generation β-lactams including cephalosporins and aztreonam, complicating treatment (Chaudhary and Aggarwal, 2004). ESBL-producing Salmonella isolated from the stool samples of patients with acute gastroenteritis, were significantly more resistant to quinolones underscoring the need for regular monitoring and management of ESBL-producing Salmonella.
Additionally, Salmonella inactivates aminoglycosides through enzymatic modification by acetyltransferase and phosphotransferase. These enzymes alter the conformation of the 30S ribosomal subunit, preventing aminoglycosides from binding to their target ribosome and rendering them ineffective (Frye and Jackson, 2013).
Salmonella reduces the intracellular concentration of antibiotics by actively using efflux pumps and controlling membrane permeability. As a gram-negative bacterium, Salmonella requires antibiotics to penetrate its outer membrane to reach intracellular targets (Delcour, 2009). The outer membrane contains channels such as efflux pumps and porins that mediate the entry and exit of substances, including antibiotics. Efflux pumps like AcrAB-TolC, which are regulated by specific transporters, actively expel antibiotics from the cell, while porins such as OmpF selectively regulates antibiotic entry (Mahendran et al., 2010; Piddock, 2019). Overexpression of efflux pumps limits drug access, contributing to resistance (Blair et al., 2014). Inhibiting this overexpression, might make it possible to render Salmonella more sensitive to drugs. Siew et al. (2009) demonstrated that Salmonella, highly resistant to ciprofloxacin (256 μg/mL), exhibited a substantial decrease in resistance (to 0.25 μg/mL) when the AcrB component of the AcrAB-TolC efflux system was inactivated. Dowd et al. (2008) created a Salmonella strain (referred to as 2a) that developed resistance following continuous exposure to nalidixic acid. Comparative gene expression analysis indicated upregulation of efflux pump-related genes and downregulation of porin genes. Collectively, these findings suggest that Salmonella can develop antibiotic resistance by inducing efflux pump activity and reducing antibiotic influx. Furthermore, as efflux pump genes can reside on plasmids, antibiotic resistance can also be disseminated via horizontal gene transfer (Nishino, 2016).
Antibiotic Alternatives
As part of the effort to manage MDR bacteria, alternative methods are emerging to replace antibiotics. In the long term, alternatives to antibiotics could reduce the use of antibiotics and slow the emergence of MDR bacteria. Antibiotic alternatives that are gaining attention include phage-based, antimicrobial oligonucleotides, and immunological approaches [e.g., monoclonal antibodies (mAb); Streicher, 2021]. Phages are viruses that use bacteria as their hosts lytic phages, which replicate and immediately destroy bacterial cells, are particularly promising as they lack the ability to transfer genetic elements to host cells, unlike lysogenic phages (Ly-Chatain, 2014; Sulakvelidze et al., 2001). They are also easy to genetically modify, isolate, and mass-produce, making them simpler to develop than new antibiotics (Khan and Rahman, 2022). Antimicrobial oligonucleotide are short base sequences that bind to specific bacterial mRNA, leading to mRNA degradation or inhibition of ribosomal binding (Chi et al., 2017; Streicher, 2021; Watts and Corey, 2011). The binding target mRNA can be a gene essential for the bacterial survival or an antibiotic resistance gene. It can also bind to a mRNA related to virulence (Streicher, 2021). mAbs neutralize bacterial exotoxins by preventing their binding to ligands, reducing their pathogenic effects (Garland et al., 2017). It is usually used as an adjuvant for antibiotics or as a preventive measure for high-risk groups (Sparrow et al., 2017). FDA-approved mAbs are already in use for treating various diseases, including cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders (Elgundi et al., 2017).
Conclusion
Antibiotic resistance in Salmonella is increasingly concerning as resistance levels rise and MDR strains become increasingly prevalent. Megaplasmids carrying multiple resistance genes exacerbate. Despite regulations on antibiotic use in food animals in many countries, past antibiotic residues, as well as ongoing overuse and misuse, contribute to the persistence of MDR Salmonella in food animals, which posing a significant public health risk. MDR Salmonella infections are a serious concern, especially as resistance emerges to last-resort antibiotics, such as carbapenems. Alternative therapies, such as phage-based treatments and immunotherapies offer promising solutions and should be rapidly developed and applied in real-world settings. Also, prevention requires stringent measures, including regular monitoring and limiting the misuse of antibiotics in food animals. Collaboration between governments, industries, academia, and consumers is essential to address the severity of antibiotic resistance and implement effective solutions.













