Introduction
Sausages, a dietary staple across various cultures, are traditionally seasoned with sodium chloride (NaCl) to enhance flavor and preserve the product. However, excessive sodium intake has been associated with health risks such as hypertension and cardiovascular diseases (World Health Organization [WHO], 2023). Therefore, the pursuit of healthier alternatives to NaCl is critical. However, existing salt substitutes, including potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, and other mineral blends, have not fully replicated the multifaceted role of NaCl in food processing (Horita et al., 2016; Kim et al., 2018; Vidal et al., 2023; Vinitha et al., 2022). Despite the numerous reports of KCl salt-based alternatives, they have been reported to produce bitter, pungent, metallic, and chemical flavors (Cepanec et al., 2017; Sinopoli and Lawless, 2012). To avoid affecting the taste, one still needs to use other ingredients to compensate for this deficiency.
Halophytes are salt-tolerant plants that inhabit soils or waters with high salt concentrations, such as mud plates, swamps, saline semi-deserts, and seashores, and are estimated to account for approximately 2% of all plant species (Flowers and Colmer, 2008; Panta et al., 2014). Halophytes have been used for medicinal, nutritional, and functional purposes (Panta et al., 2014). The reason is because of the health-beneficial ingredients contained in halophytes, including various minerals (Na, Ca, Mg, and K), vitamins (E and C), fatty acids (linolenic, linoleic, and palmitic acid), organic acids (citric and oxalic acid), alkaloids (capparisine, stachydrin, capparine, and spermidine alkaloids), saponins terpenes, phenolic compounds (catechin, coumarin, gallic acid, luteolin, quercetin, vanillic acid, etc.), and various metabolites (Petropoulos et al., 2018). The bioactive properties of halophytes, such as antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-hypertensive, anti-cancer, immunomodulatory, and antimicrobial activities, have made them valuable components of a healthy diet (Essaidi et al., 2013; Kim et al., 2011). Several halophytes, including wild beets (Beta vulgaris), capers (Capparis spinosa L.), and grassworts (Salicornia herbacea L.) have been evaluated for their medicinal and nutritional value (Panta et al., 2014; Petropoulos et al., 2018). These properties have attracted considerable attention owing to their potential use in various applications such as food and medicine (Panta et al., 2014).
Salicornia, a representative genus of halophytic plants, is a promising candidate for salt substitution (Lopes et al., 2020). Its high salinity tolerance, coupled with a unique nutritional profile rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, positions Salicornia as a potential natural and nutritious alternative to traditional salt (Alfheeaid et al., 2022; Chaturvedi et al., 2021). Salicornia herbacea has demonstrated considerable versatility as a natural salt substitute, particularly in processed foods. For instance, Lim et al. (2013) have reported that incorporating Salicornia herbacea powder (SHP) in beef jerky formulations reduced water activity and increased pH, which, in turn, enhanced the product’s antioxidant properties. In the context of frankfurters, Kim et al. (2014a) have found that adding Salicornia herbacea L. improved protein solubility and emulsion stability, enhancing cooking yield. Additionally, Kim et al. (2014b) have demonstrated that including red or green Salicornia herbacea L. (commonly known as glasswort) positively influenced the texture and water-holding capacity of reduced-salt cooked sausages without significantly altering the pH. Their study further suggested that red glasswort may be particularly effective in maintaining color stability. In another study, Lim et al. (2015) observed that using Salicornia herbacea L. hydrate in reduced-salt, reduced-fat frankfurters contributed to improved texture and water-holding capacity. Beyond meat products, Salicornia herbacea L. shows considerable potential in other food sectors, including the development of bread and condiments. Its seed oil, characterized by high oxidative stability, further enhances its suitability for various food processing applications (Cárdenas-Pérez et al., 2021; Patel, 2016). These findings collectively highlight Salicornia herbacea as an innovative and functional ingredient with broad applicability in the food industry, particularly for reducing salt content while maintaining or improving product quality. However, its use in fermented sausages has not been fully investigated.
The purpose of this study was to investigate SHP as a salt substitute for the production of three types of sausages (emulsion-type, semi-dried, and dried sausages). By reducing the NaCl content and adding SHP to the formulation, we evaluated its effects on the physicochemical properties of different types of sausages. This study could provide valuable insights into the potential of SHP as a natural and healthy alternative to traditional salts for sausage production.
Materials and Methods
All materials used to manufacture the sausages were purchased from a commercial market. Lean pork was prepared by removing the legs (n=5), and excessive connective tissue and fat were removed. The salt content of the SHP was determined using the AOAC (2000) method. Three types of sausages were prepared using the different formulations (Table 1). For the control group of emulsion-type sausages, lean pork with half the ice and curing agents (salt, sodium nitrite, sodium tripolyphosphate, and sugar) were mixed in a bowl cutter (Talsa K30, DSL Food Machinery, Cornellà del Terri, Spain) for 5 min, and the rest of the ice, back fat, and seasoning were added. The mixture was prepared by mixing for 5 min. The temperature of the batter was not exceeded 14°C. The batter was stuffed into plastic casings (polyvinylidene chloride, 29-mm diameter), cooked at 80°C for approximately 45 min until the internal temperature reached 74°C (Thematec Food Industry, Seongnam, Korea), and cooled to 10°C. The treatment (SHP group) of emulsion-type sausages was prepared using the same procedure as CON, except for the addition of salt substitute and other ingredients: 0.598% NaCl, 0.5% SHP (631 mg NaCl/g), 0.704% KCl, 0.5% transglutaminase, 1% egg white powder, and 2.5% cellulose. For making the control groups of semi-dried and dried sausages, lean pork, back fat, curing agents (salt, sodium nitrite, sodium tripolyphosphate, and sugar), seasoning, and starter culture were mixed in a mixer (RM-20, Mainca, Barcelona, Spain) for 10 min. Treatments of semi-dried and dried sausages were prepared with the same formulation as the controls, except for the addition of SHP (0.5%), KCl (0.704%), transglutaminase (0.5%), egg white powder (1%), and cellulose (2.5%). All batters for semi-dried and dried sausages were stuffed into fibrous casing (45-mm diameter, Viscofan, Navarra, Spain), fermented at 24°C and 95% relative humidity (RH) for 48 h, and dried under different conditions (18°C and 85% RH for 5 days; 16°C and 80% RH for 5 days; 14°C and 75% RH for 15 days) until the moisture content reached below 55% for semi-dried sausages and below 35% for dried sausages.
1) 0.05% monosodium glutamate and 0.4% mortadella seasoning for emulsion-type sausages; 0.05% monosodium glutamate and 0.6% grill beef powder for semi-dried and dried sausages.
The pH of the sausage samples was determined using a pH meter (MP230, Mettler-Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland) after homogenizing 3.0 g sausage with 27 mL of distilled water. The yield was determined by measuring the weight of the sausages after cooking (emulsion-type sausages) or drying (semi-dried and dried sausages) and was presented as a percentage of the weight before cooking or drying. The moisture content was determined using the AOAC (2000) method, with some modifications. In brief, approximately 10 g of ground sausages was dried in a dry oven at 102°C for 24 h. Moisture content was expressed as a percentage of the initial weight.
To measure the color of the sausage samples, sausages were cut, and the cut surface was exposed to air for 20 min. The color was measured using a colorimeter (CR-400, Minolta Camera, Osaka, Japan) equipped with a D65 light source, 10° observer angle, and 8-mm aperture. The colorimeter was calibrated using a white ceramic plate (Y=93.5, x=0.3132, and y=0.3198). The color of the sausages was determined using the Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage system (CIE, 1978) CIE L*, CIE a*, and CIE b*.
Textural properties such as hardness, cohesiveness, springiness, chewiness, and adhesiveness were analyzed from five cylindrical (1.0-cm-diameter) samples using a texture analyzer (TA1, Ametek, Largo, FL, USA). The conditions of the texture analyzer were set as 10 kg load cell, 200 mm/min cross-head speed, and a double compression cycle test. Textural properties were calculated according to the method described by Bourne (1978). To measure the shear force of the sausage samples, three cores (10 mm in diameter) were prepared for each treatment and cut vertically using an Instron 4400 (Instron, Norwood, MA, USA) equipped with a Warner-Bratzler shear blade. The measurement conditions were set as 3.00 mm/s speed and a load cell capacity of 490 N. The shear force (kg/cm2) of the samples is presented as the average value of the three cores.
All sausages were produced three different times and all data were collected from three batches with three or five experimental replications and presented as means and SE. Differences in the physicochemical properties between the two groups (CON and SHP) were compared within the same groups using a t-test (PROC TTEST) with SAS software (ver. 9.4, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Differences between the two groups were considered significant at p<0.05.
Results
The emulsion-type sausages formulated with SHP as a partial substitute for NaCl showed significant differences in quality characteristics compared to the control (CON) group (Fig. 1). The pH values were significantly lower in the SHP group than in the CON group (p<0.001). The SHP group exhibited a significantly higher yield (p<0.05) and a lower moisture content (p<0.01) compared to the CON group. Color analysis showed a sharply decrease (p<0.001) in CIE a*, and a significant increase (p<0.01) in CIE b*, a slight but non-significant decreasing trend (p>0.05) in CIE L* in the SHP group compared to the CON group. Texture profile analysis revealed no significant differences in cohesiveness, springiness, or chewiness between the CON and SHP groups (p>0.05). However, hardness (p<0.001), adhesiveness (p<0.001), and shear force (p<0.01) were dramatically increased in reduced-NaCl emulsion-type sausages upon substitution with SHP.
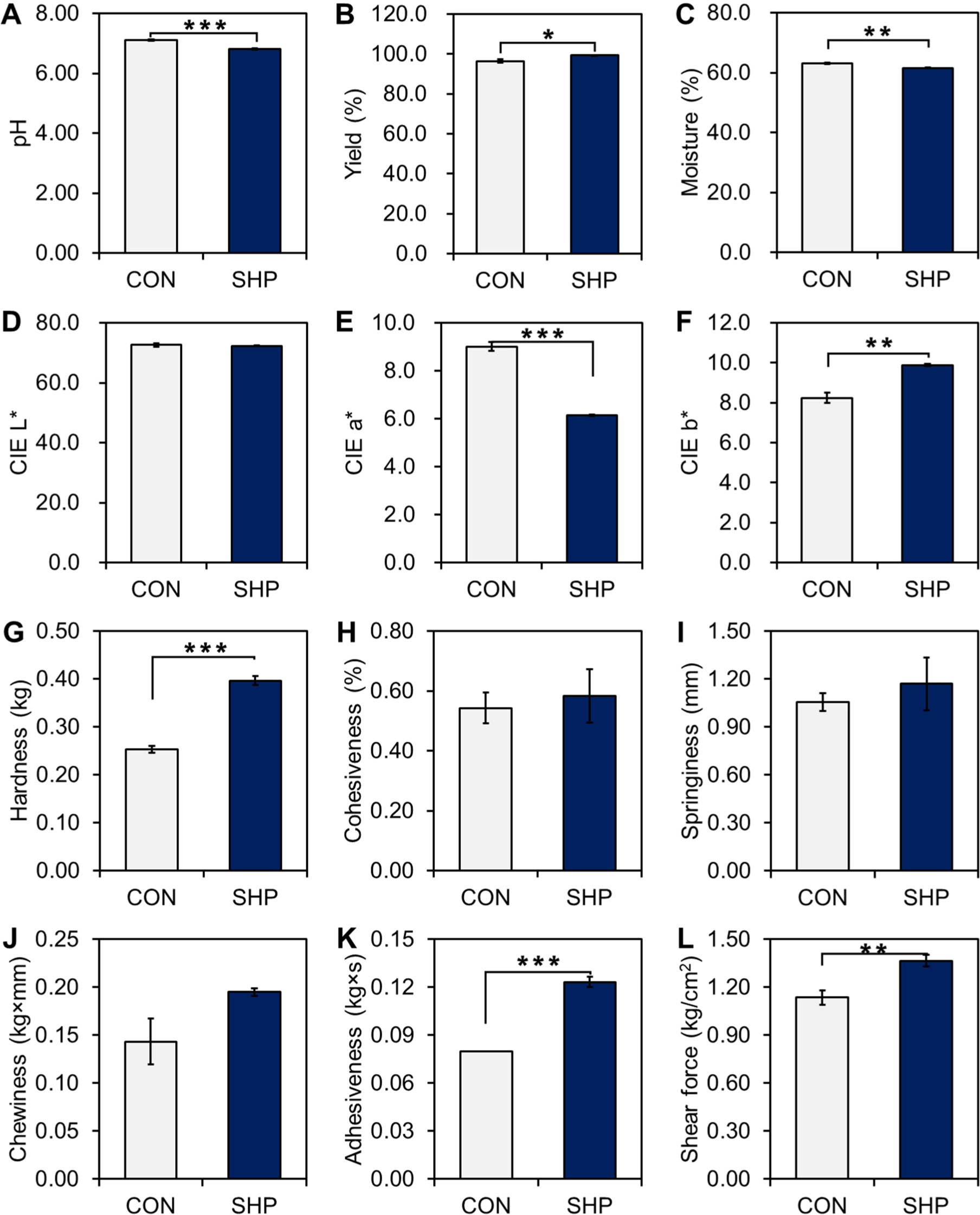
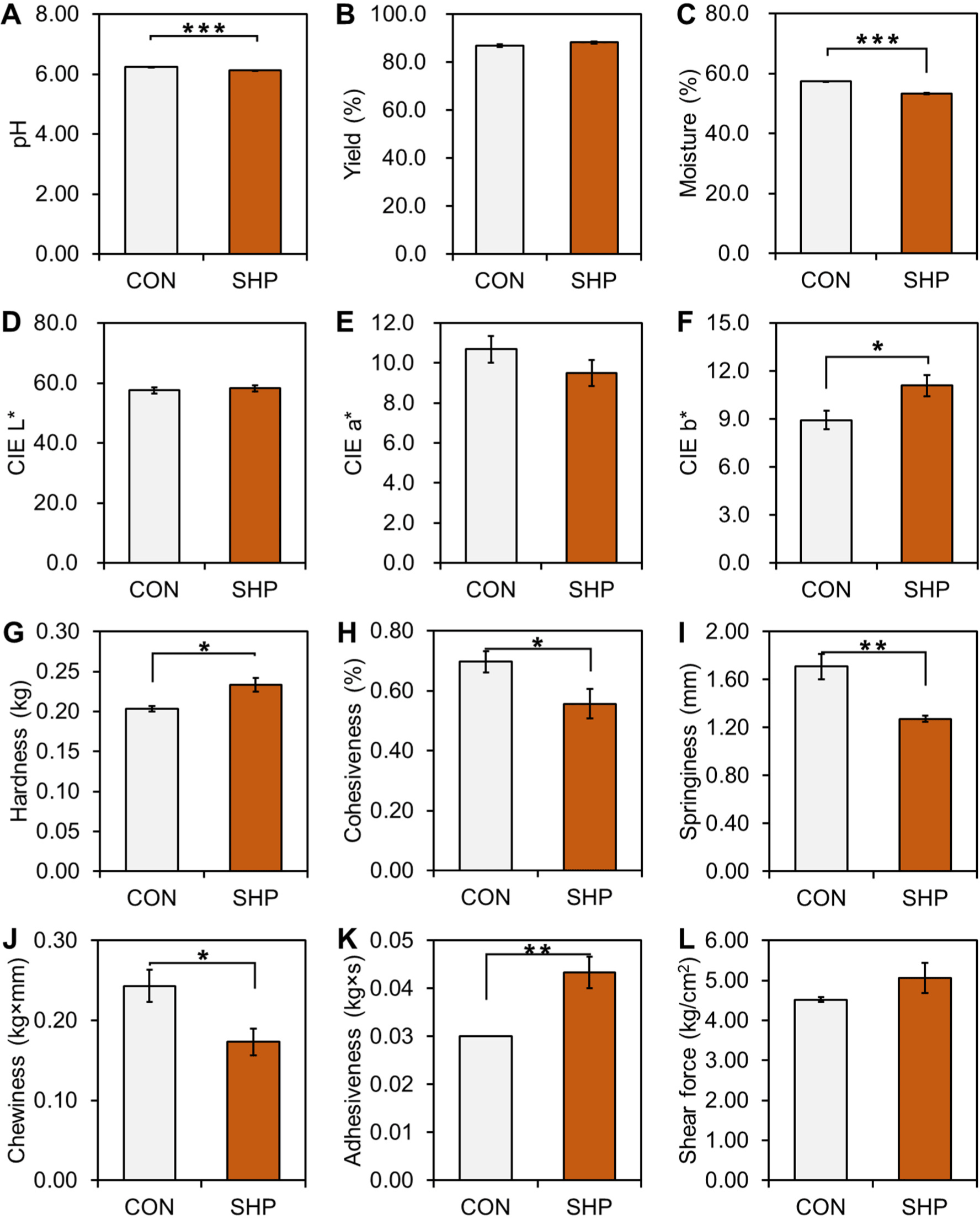
Fig. 2 shows comparative analysis of the quality characteristics of the semi-dried sausages. In semi-dried sausages, the substitution of NaCl with SHP had a more noticeable effect on the pH and moisture content, leading to lower levels compared to those in the CON group (p<0.001). However, there was no significant difference in yield percentage between the CON and SHP treatments (p>0.05). In addition, the color traits showed similar changes to the emulsion-type sausages, with a significant increase in CIE b* (p<0.05) and a slight but not significant decrease (p>0.05) in CIE a* in the SHP treatment compared to the CON. Furthermore, texture profile traits, except shear force, were observed to have noteworthy differences compared with those of the CON group (p<0.05).
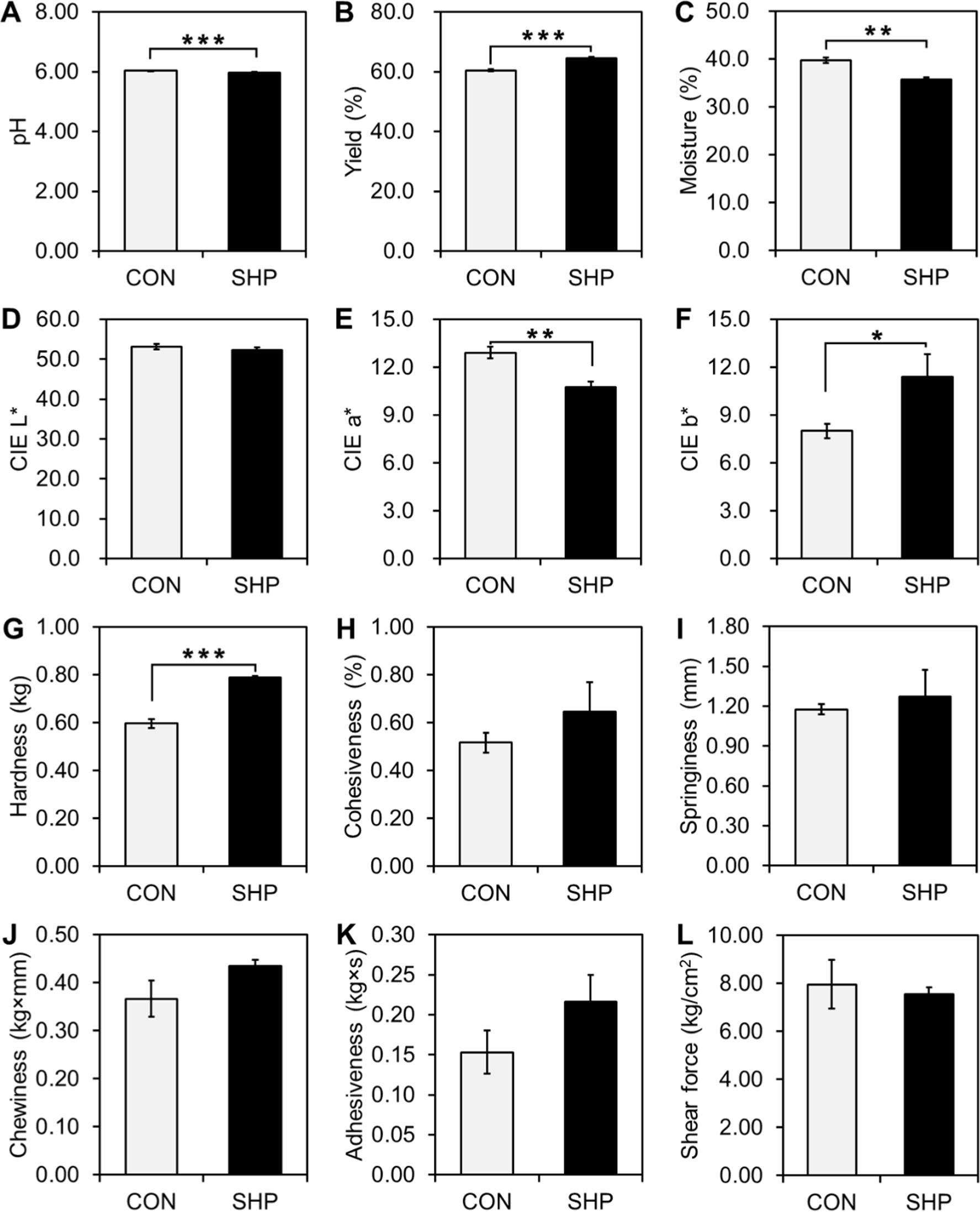
Dried sausages exhibited unique responses to the substitution of NaCl with SHP. The quality characteristics of the dried sausages are shown in Fig. 3. The pH (p<0.001) and moisture content (p<0.01) results of the SHP treatment were consistent with those of the other two types of sausages, which were significantly lower than those in the CON group. The color results remained stable in terms of CIE L*, with a decrease in CIE a* and an increase in CIE b*, similar to other sausage types. Interestingly, most of the texture profiles did not indicate significant differences (p>0.05), except for hardness, which was considerably higher in the SHP treatment than in the CON group (p<0.001).
Discussion
The use of SHP as a NaCl substitute in the formulation of various sausages, including emulsion-type, semi-dried, and dried sausages, is a potential study in the pursuit of healthier processed meat products with a low-salt composition.
A crucial observation among all sausage types was the consistent lowering of pH with SHP substitution compared to each CON group, which is in line with the documented effect of salt reduction on meat product pH (Kim et al., 2018; Ruusunen and Puolanne, 2005). The inclusion of additional factors such as sugar, KCl, TGM, EWP, and cellulose alongside SHP was deliberately selected to simulate the complex matrix of a commercial sausage formulation. This approach allows for a more realistic assessment of the potential industrial application of SHP, providing valuable insights into its functionality within a multi-component system. The main factors responsible for the pH drop may be the same or different depending on the type of sausage. In emulsion-type sausages, a decrease in pH is associated with fermentation and the formation of acids, suggesting that plant-derived powders such as SHP might possess distinct buffering capacities that affect the pH of meat emulsions. Our findings suggested that the dietary fiber content in SHP could play a significant role in moisture retention and texture changes, as dietary fibers affect water-holding capacity and gel formation in meat products (Huang et al., 2011). Kim et al. (2015) reported that phosphate and sea mustard affect reduced-fat/low-NaCl meat emulsion systems. In semi-dried and dried sausages, the pH reduction is closely related to the metabolic activities of microorganisms during fermentation (Ockerman and Basu, 2017; Rouhi et al., 2013). Typically, microorganisms such as lactic acid bacteria produce lactic acid during fermentation, leading to a decrease in the pH (Pasini et al., 2018; Sydykova et al., 2019). Additionally, research has shown that reduction in NaCl affects higher levels of lactic acid bacterial populations, thereby concentrating the acidic metabolic products and exacerbating the decrease in pH (Hu et al., 2020). Reducing salt and increasing SHP resulted in a significant reduction in sausage moisture, which occurred in all three types of sausages in the present study. These findings are supported by Choi et al. (2015), in which moisture showed a lower content of salt-reduced Frankfurters with sea tangle and sea mustard compared to control samples. This decrease in water content is due to reduced salinity, weakened ionic strength, and reduced water binding (Luo and Wan, 2013). Lower salt levels may reduce the solubility of meat proteins, thereby reducing their water-holding capacity (Desmond, 2006). At the same time, adding plant-based additives may change the protein structure and moisture retention mechanism of the sausage, further affecting its water-holding capacity (Pietrasik and Janz, 2010). Generally, the fat content in emulsified sausage can be as high as 30%. However, decreasing the fat content to 10% or less can lead to reduced cooking yields, altered sensory qualities, and a shorter shelf life (Berry and Leddy, 1984; Keeton, 1994). Based on the findings of Kim et al. (2018), fat content was reduced to 11.2%. SHP may increase yields by improving protein gelation, and studies have shown that a lower fat content can lead to less cooking loss and increased yield (Tobin et al., 2013). Our study found a significant increase in yield for both emulsified and dried sausages compared to the control group, indicating that SHP may positively affect production efficiency.
Color is an important factor for consumers when choosing sausages. Fermented sausages may change color during cooking, which is related to the color of the meat and the natural coloring of additives (Aykın-Dinçer et al., 2021; Bellucci et al., 2020). An increase in CIE b* was observed in the SHP groups regardless of the type of sausage, which could be ascribed to the natural colorants present in the SHP. Salicornia herbacea is a salt-tolerant plant that grows in saline environments and contains natural pigments such as chlorophyll and carotenoids (Chaturvedi et al., 2021; Guil et al., 1997). Its use as an additive to meat products with these natural pigments may influence the color of the final product. When carotenoids are incorporated into meat products or released from plant additives during processing, they can dissolve in fat content, contributing to an increase in CIE b*; heat treatment enhances this coloring effect (Gebregziabher et al., 2023; Meléndez-Martínez et al., 2022). The effect of naturally colored antioxidants from Moringa oleifera, propolis, and grape pomace on the coloration of chicken paté products was previously reported by Bordim et al. (2023), who highlighted the influence of such additives on the hue and chroma of the final product. The CIE a* of the emulsion-type and dried sausages decreased in the SHP groups, which might be associated with altered meat protein structure and pigment stability due to the presence of SHP, affecting the light-scattering properties and the perceived color. This is supported by Choi et al. (2015) and Vilar et al. (2020), who found that the addition of plant extracts can decrease the CIE a* of meat products. The decrease in CIE a* could be due to alteration of the chemical structure of the meat pigments or their interaction with additives. The addition of SHP had no negative effect on the CIE L* of the sausages.
The texture of the sausages was significantly affected by the addition of SHP. The reduction in moisture was accompanied by a sharp increase in hardness compared with that of the control group, a finding that was consistent with all sausage types. The increased hardness could be attributed to forming a more stable network between SHP and meat proteins, which has been observed in previous studies involving the addition of dietary fibers to meat products (Huang et al., 2011). The hardness and adhesiveness of the semi-dried sausages increased, whereas their cohesiveness, springiness, and chewiness decreased, indicating a firmer and stickier texture. This could be due to the interaction between SHP and meat proteins, which form a more stable network. Previous studies showed the SHP contains 73.31%–74.11% total dietary fibers (Han, 2004; Kim and Yoo, 2012; Kim et al., 2014b). Huang et al. (2011) demonstrated that increasing the concentration of dietary fiber resulted in a significant enhancement in textural hardness. However, the shear force did not change significantly in this study, suggesting that the overall structural integrity was not compromised. In contrast, dried sausages showed an increase in hardness; however, other textural parameters remained unaffected, indicating a more subtle influence of SHP on this type of sausage. Nevertheless, excessively soft textures can prolong the maturation process of sausages; thus, a firmer consistency is generally regarded as advantageous in terms of production efficiency and product quality (Essien, 2003). Thus, the higher the hardness, the better the texture and the shorter the storage time required for ripening (Martín-Sánchez et al., 2011). The emulsified sausages exhibited increased hardness, chewiness, and adhesiveness, suggesting a more pronounced effect on texture, possibly due to the emulsifying properties of SHP. These results are consistent with those of previous studies, which demonstrated enhanced hardness and chewiness in frankfurters or cooked sausages formulated with glasswort (Salicornia herbacea L.) compared to reduced-salt treatment (Kim et al., 2014a; Kim et al., 2014b).
Texture profile analysis indicated that SHP had a more pronounced effect on semi-dried sausages, which could be due to the specific conditions of the semi-dried fermentation process that allowed for a more significant interaction between SHP and meat proteins. The minimal impact on the dried sausages suggests that the drying process may limit the extent of this interaction, whereas the emulsified sausages showed a moderate effect, possibly owing to the emulsifying properties of SHP that facilitate the distribution of SHP within the sausage matrix. In summary, our study reveals that SHP as a salt substitute in fermented sausages has the potential to enhance yield and texture, qualities that are pivotal to the meat industry. The inclusion of SHP in a formulation that mirrors commercial practices, including additional ingredients like sugar, KCl, TGM, EWP, and cellulose, provides a realistic evaluation of its effects. While these findings are promising, we recognize the need for further research to understand how SHP’s distinct flavor profile might influence consumer acceptance and the overall sensory experience. Future studies should conduct comprehensive sensory evaluations to assess the impact of SHP on flavor and overall product appeal. Addressing these considerations will be crucial for optimizing the role of SHP in sausage production, ensuring that it meets both the functional needs and sensory expectations of consumers.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrated the potential of SHP as a novel ingredient in the formulation of low-salt sausages. The integration of SHP led to a significant enhancement in the yield and texture profiles of the sausages, particularly emulsified and semi-dried sausages. The reduction in pH and moisture content suggested a positive influence on the preservation and inhibition of microbial growth in sausages. Moreover, the increased hardness and adhesiveness of the semi-dried sausages indicated improved texture and safety, which are key factors for consumer preference. The results of this study emphasize the potential of SHP addition for salt reduction in fermented sausages, which may be a promising prospect for the development of healthier and more sustainable meat products. Building on these findings, future research should explore the long-term sensory effects of SHP in meat products, including changes in flavor and overall consumer acceptance over extended periods of storage. Additionally, investigating the application of SHP in various meat products beyond sausages, such as hams, bacon, and minced meats, could reveal new opportunities for formulating low-salt meat products. Furthermore, a comprehensive analysis of the nutrient composition in SHP-enriched sausages could provide valuable insights into the health benefits and potential dietary applications of these products. Evaluation of its long-term effects on sausage sensory properties and nutrient composition needs to be conducted in future studies. This study provides new insights for the development of healthier and natural meat products. By offering these specific directions for future research, we aim to contribute to the ongoing efforts to reduce salt intake while maintaining the quality and palatability of meat products.













