Introduction
Globally, there is a growing demand for dairy and other animal-based products, with consumption driven by population growth, advancing dietary preferences, increasing income levels, and urbanization. People in emerging economies tend to increase their consumption of animal-based food products over time, resulting in a surge in the consumption of protein- and nutrient-rich diets. Animal-based foods are abundant in essential proteins, vitamins, and minerals that are crucial for human nutrition (OECD and FAO, 2021). Since animal-based foods are vital resources of nutrients, it is essential to ensure their microbial safety.
Healthy animals have the potential to transfer microbial hazards such as Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Cryptosporidium, Clostridium perfringens, Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella, Yersinia enterocolitica, and Salmonella to humans causing major foodborne diseases (Turantaş et al., 2015). According to the World Health Organization (2024), 600 million people get ill and 420,000 deaths occur annually from unsafe foods. Hoffmann (2020) reported that the pathogens responsible for foodborne illnesses mostly originate from animal-based food sources, and eight among them could cause 13 food-borne illnesses. Due to food-borne diseases, 86% of “disability-adjusted life years” (number of years of life lost due to early death or spent in poor health because of the foodborne illness) were lost due to six pathogens, and 77% of this burden occurred majorly by Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Taenia solium. Among these, Salmonella and Campylobacter frequently trigger food-borne illnesses in meat and dairy products. In Southeast Asia, Salmonella contributes to 33%–50% of foodborne diseases. Foodborne diseases can have negative economic impacts, such as workforce productivity reduction, social costs related to healthcare, and premature death (Hoffmann, 2020). Hence it is essential to decontaminate animal-based foods to ensure microbial food safety to safe consumption.
Conventional preservation methods for improving food safety, such as maintaining a low temperature, water activity reduction, addition of preservatives, modified atmospheric packaging, food acidification, fermentation, regulation of osmotic pressure, and Redox potential alteration, have been utilized to inactivate microorganisms. Nevertheless, these methods’ effectiveness is questionable regarding microbial viability after practice in microbial inactivation (Beales, 2004; Rosario et al., 2021). Thermal and nonthermal food preservation methods, such as thermal preservation, sterilization, pasteurization, and aseptic packaging, are widely used in the food industry for effective microbial inactivation. However, heat treatment degrades the nutritional value, physicochemical properties, and sensory qualities of food (Valdramidis and Koutsoumanis, 2016). Consequently, non-thermal sterilization methods have emerged to ensure microbial inactivation while preserving food quality, including ultrasound sterilization, cold plasma sterilization, ultrahigh-pressure sterilization, pulsed strong light sterilization, ozone treatment, and ultraviolet sterilization with a pulsed electric field (Zhang et al., 2022).
Recently, ultrasound sterilization methods have been used in the food industry to improve food safety. Ultrasound is known to be environmentally friendly due to its low energy consumption, short processing times, and lack of chemical risk while also being effective in microbial inactivation. Also, ultrasound is cost-effective compared to other non-thermal technologies, such as high-pressure processing or irradiation (Gavahian et al., 2018; Yuan et al., 2021). When ultrasound was treated to animal-based as medium, it creates a continuous wave movement. This vibration generates and collapses of bubbles and makes some mechanical energy, radicals, etc. (Mustapha et al., 2024; Nowacka and Wedzik, 2016). This ultrasound action causes microbial inactivation in animal foods by mechanical destruction of microbial cell walls, separation of cytoplasmic membranes, and denaturation of microbial proteins and enzymes (Kordowska-Wiater and Stasiak, 2011).
Interestingly, the mechanical energy generated by ultrasound not only inactivates microorganisms but can also affect the quality of animal-based food qualities. Excessive ultrasound processing conditions can cause quality deterioration, but using the proper conditions can positively affect animal-based food processing efficiency. Chemat et al. (2011) revealed that ultrasound can be utilized for the thawing, extraction, and emulsification process. The implosion of the cavitation bubble by ultrasound can increase the temperature of frozen food so that it can be applied to the thawing process (Wu et al., 2017). Ultrasound can be used in the extraction process. Because the bubble burst by ultrasound cavitation disrupts the cell wall in food and promotes the extraction of the inside material of the cell (Yang et al., 2017). In addition, ultrasound can be used to produce emulsions. Ultrasound’s physical effect of cavitation enhances the generation of smaller oil droplets and promotes the creation of more stable emulsions (Taha et al., 2020).
This review emphasizes the application of ultrasound for improving the microbial safety and application efficacy of animal-based foods. It further discusses the ultrasound generation mechanism, ultrasound technique for inactivation of microorganisms, and application of ultrasound in various processing operations, namely emulsification, thawing, and extraction.
Generation of Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the sound waves beyond the human audible range which has frequencies greater than 20 kHz. When ultrasound waves move through a medium, they generate compression and decompression of particles in the medium. This effect creates energy using turbulence and elevates mass transfer. Similar to the light wave behavior, ultrasound behaves by scattering and reflecting sound (Režek Jambrak, 2012). Two categories of ultrasound can be used for food processing: low-frequency, high-intensity (20–100 kHz, 10–1,000 W/cm2) and high-frequency, low-intensity (>1 MHz, <1 W/cm2; Mason et al., 2011).
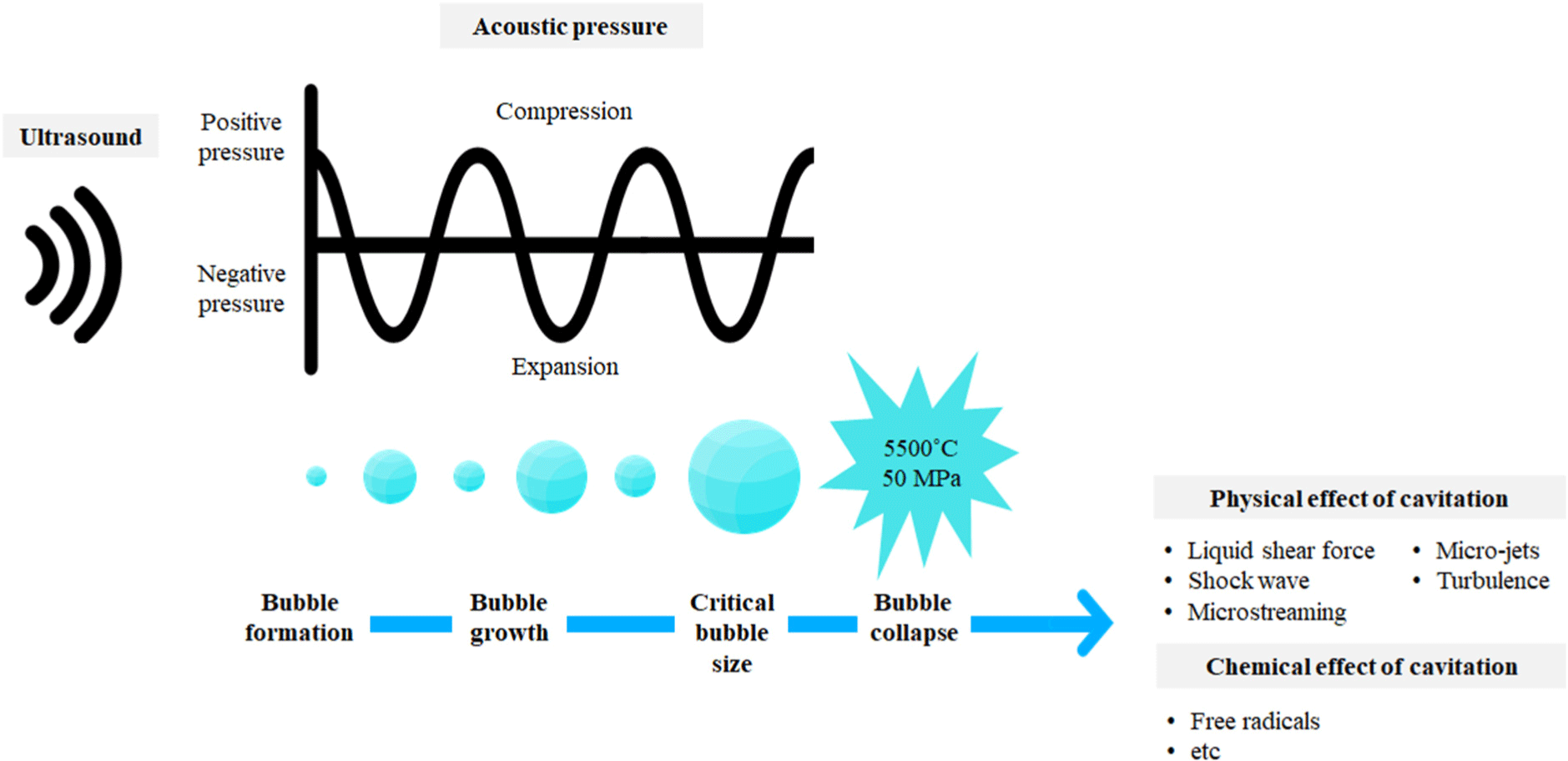
According to Kasaai (2013), ultrasound refers to a pressure wave that moves in one direction. The speed of ultrasound depends on the acoustic properties of the medium. Therefore, the ultrasound speed is higher in solids, followed by in liquids, with the slowest speed observed in gas. During ultrasound, electrical energy is transformed into vibrations. While a portion of the supplied energy is lost as heat, the remaining energy is converted into mechanical energy, creating mechanical oscillations and formulation of cavitation, resulting in the generation and collapse of bubbles (Alarcon-Rojo et al., 2019; Nowacka and Wedzik, 2016).
Mustapha et al. (2024) mentioned that ultrasound with a higher frequency increases cavitation but decreases the penetration depth. Contrastingly, lower-frequency ultrasound shows greater penetration but results in less cavitation. According to Chemat et al. (2011) and Nowacka and Wedzik (2016), the ultrasound process relies on acoustic cavitation. The moving bubbles endure irregular oscillations and violently burst. This collapse produces high temperature and pressure, which cause the generation of free radicals, cell deterioration, microscopic channel creation, and enzyme denaturation.
In the process of ultrasound generation, the transducer is used to generate ultrasound by converting electrical pulses into acoustic energy. Magnetostrictive transducers generate ultrasound based on the principle of magnetostriction, whereas piezoelectric transducers transform electrical and acoustic energy. Ultrasound applications are performed directly or indirectly by using tools such as sonotrodes and ultrasonic water baths. The sonotrode directly applies acoustic energy to food, whereas in an ultrasonic water bath, a piezoelectric transducer is attached to the bottom of the water bath or submerged in the liquid and converts a low-frequency alternating current into a high-frequency sound wave (Bhargava et al., 2021).
Mechanism for Microbial Inactivation
Ultrasound is an environment-friendly and cost-effective method for inactivating microorganisms and microbial enzymes that cause food spoilage and foodborne illnesses. Ultrasound waves are a non-toxic and safe method for microbial inactivation and have been used for microbial inactivation since the 1960s (Kentish and Ashokkumar, 2010). According to Joyce et al. (2011), high-power ultrasonic waves of 20–100 kHz create high-temperature and pressure gradients that disrupt microbial cell membranes and DNA. The effectiveness of microbial inactivation by ultrasound relies on the cell type, shape, size, and physiological state of the contaminating microbe; frequency, intensity, and treatment duration of ultrasound, and the food type that is contaminated, as reported by Turantaş et al. (2015). Herceg et al. (2012) also revealed that the effectiveness of ultrasound varies between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are more resistant to ultrasound treatment than gram-negative bacteria because gram-positive bacteria have a thicker cell wall and tightly attached peptidoglycan layer (Chemat et al., 2011; Herceg et al., 2012). As mentioned by Chemat et al. (2011), in addition to the bacterial type, bacterial cell shape also influences ultrasound inactivation. Because of the ratio between the cell surface and volume, cocci bacteria are more resistant than bacilli bacteria. Furthermore, Beatty and Walsh (2016) showed that whether microorganisms are in a vegetative or spore state influences the effectiveness of ultrasound. Spore inactivation has become more challenging since spores are the most resistant forms of microbial cells (Van Impe et al., 2018). Microbial spores can survive under extreme conditions such as mechanical shocks, pH fluctuations, high temperature, and osmotic pressure. For instance, endospores of Clostridium and Bacillus spp. are highly resistant to extreme conditions. Bacillus thermophilus spores can be inactivated by exposure to 100°C for 4 h (Chemat et al., 2011). According to the spore inactivation mechanism of ultrasound proposed by Onyeaka et al. (2023); shear forces, local erosion, fragmentation, and sonoporation by ultrasound facilitate sporicidal effects that alter permeability and disrupt spores. Ultrasound can separate the outer spore exosporium and result in core hydration, cortex degradation, and breakdown of the spore’s internal structure and components. Additionally, ultrasound destroys the spore coat and inner membrane. Moreover, ultrasound interrupts the synthesis of metabolic enzymes, proteins, and nucleic acids in spores.
Single or multiple strains can cause microbial contamination of products in the food industry. Among them, bacteria often form biofilms, which enhance their antibacterial resistance and reduce the effectiveness of some sterilization techniques (Cui et al., 2020). In this context, ultrasound has a greater potential to exert antibacterial effects through mechanical vibration, acoustic streaming, and acoustic cavitation (Piñon et al., 2020).
The microbial inactivation mechanism of ultrasound is attributed to the formation of intracellular cavitation, which leads to the generation of free radicals, thinning of the microorganism’s cell membrane, and localized heating (Butz and Tauscher, 2002; Chemat et al., 2011). Throughout the ultrasound process, ultrasound longitudinal waves interact with the liquid media and create compression and expansion. These oscillations result in cavitation and gas bubble formation. During the expansion cycle, the bubbles have a larger surface area, leading to the diffusion of more gas and bubble expansion. Over time, the energy supplied by the ultrasound is not adequate to maintain the vapor phase of the bubble, which leads to rapid condensation, resulting in bubble collapse and shock wave generation. These shock waves form at a high temperature of 5,500°C and a pressure of 50,000 kPa. This high temperature and pressure are responsible for the antimicrobial properties of ultrasound waves (Piyasena et al., 2003). Along with bubble collapse, several physical effects such as microjets, turbulence, and liquid shear force can occur. Rapid changes in the pressure and temperature generate reactive radicals and emission of light (Fig. 1). In aqueous medium, homolysis of water vapor molecules occurs due to the cavitation bubble resulting in the generation of hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide (Ashokkumar, 2011).
The severity of cavitation and ultrasound microbial inactivation depends on several factors, including amplitude, frequency, and duty cycles of the ultrasound wave; viscosity, temperature, surface tension, and density of the medium; concentration of dissolved gas; application time of ultrasound; volume and composition of the food being treated (Ashokkumar, 2011; Ashokkumar et al., 2010; Turantaş et al., 2015).
Based on the physicochemical effects of acoustic cavitation, there are three antimicrobial strategies, namely sonoporation, sonochemistry, and sonoluminescence. In sonoporation, the physical effects of acoustic cavitation, such as bubble oscillation and collapse, form pores in the bacterial cell membranes. These pores increase cell permeability and allow antibacterial agents to penetrate the cell, and damage cellular proteins, DNA, and enzymes. In sonochemistry, the collapse of cavitation bubbles induces chemical reactions and generates reactive radicals such as hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide. These reactive oxygen species (ROS) cause oxidative damage to bacterial cell membranes, nucleic acids, and proteins. Sonochemical reactions are effective at high ultrasound frequencies when used to inactivate microorganisms. Sonoluminescence is a light emission that occurs during the collapse of cavitation bubbles. Sonoluminescence activates sonosensitizers (substances that generate additional ROS upon exposure to light), which induce oxidative damage in bacterial cells (Dai et al., 2020).
According to Mason et al. (2003), acoustic cavitation can be classified into two types: transient and stable cavitation. During transient cavitation (occurring in the low-frequency range of 20–100 kHz), bubbles saturated with gas or vapor undergo irregular oscillations and bursts. The pressure and temperature generated by the collapse of bubbles inactivate biological cells and microbial enzymes. Furthermore, the collapse of bubbles generates a liquid jet, and a higher shear force causes physical damage to the cell walls and membranes of microorganisms. Contrastingly, stable cavitation (which occurs in the high-frequency range of >200 kHz) includes bubbles that oscillate consistently over several acoustic cycles. Stable cavitation triggers microstreaming in a liquid medium and exerts stress on the microorganisms. According to Dai et al. (2020), during transient cavitation, within a few acoustic cycles’ bubbles grow to a critical size and violently collapse. This process generates strong physical forces. In stable cavitation, the bubble collapses over numerous acoustic cycles with minimum bubble size increment. The physical forces generated through stable cavitation are relatively lesser than the physical forces of transient cavitation.
At the end of the compression and decompression cycles, the formation of cavitation and negative pressure cause a reduction in cell permeability and disruption of the cell wall. Furthermore, hydroxyl radicals are formed during cavitation bubble bursts. These hydroxyl radicals lead to the generation of hydrogen peroxide and molecular hydrogen through a process involving microbial inactivation via various antimicrobial effects such as microstreaming, that induce thinning of the cell membrane and DNA damage (Butz and Tauscher, 2002; Kadkhodaee and Povey, 2008; Kentish and Ashokkumar, 2010).
Additionally, Lauteri et al. (2023) mentioned that cavitation formulates shockwaves, microstreams, and hotspots that damage bacterial cell walls; gram-negative bacteria are more sensitive than gram-positive bacteria to these effects. Hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide cause amino acid oxidation and lipid oxidation, which disturb bacterial functions and destroy cell membranes. Furthermore, hydroxyl radicals damage the DNA double helix, alter nitrogen bases, and damage nucleic acids in cells, eventually contributing to microbial inactivation. As well as free radicals generated by cavitation can change the membrane fluidity and permeability, leading to the disruption of bacterial cells.
Application for Microbial Inactivation on Different Animal Products
Meat is highly susceptible to microbial spoilage, which may lead to foodborne illnesses from pathogenic microorganism infections that alter intrinsic factors of meat such as pH, nutrient levels, and water-holding capacity (WHC), as well as extrinsic characteristics such as processing, transportation, and storage. Common pathogenic microorganisms in meat include Campylobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp., E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and lactic acid bacteria (Aymerich et al., 2008; Linscott, 2011).
According to previous studies, ultrasound can potentially reduce microorganisms in meat; poultry, pork, and beef. Caraveo et al. (2015) evaluated the effect of ultrasound on microbial inactivation in beef by applying ultrasound with 40 kHz frequency and 11 W/cm2 intensity for 60 and 90 min, followed by storage for up to 10 days at 4°C. Mesophilic, psychrophilic bacteria, and coliform bacteria significantly decreased during storage. Psychrophilic bacteria and coliform were most affected by ultrasound treatment.
During beef brining and curing, Kang et al. (2017) applied ultrasound to inactivate E. coli O157 and vegetative cells of Bacillus cereus. The ultrasound intensity levels were 2.39, 6.23, 11.32, and 20.96 W/cm2. The treatment temperature was 10°C and time durations were 30, 60, 90, and 120 min. Optimal bacterial reduction was observed after 120 min at 20.96 W/cm2. Both pathogens had approximately 40% of similar reductions. Furthermore, the efficacy of ultrasound microbial inactivation was significantly improved by using a combination of decontamination methods, such as irradiation, pressure, organic acids, and pulsed electric fields (Aronsson and Rönner, 2001; Kim et al., 2001).
In a study performed by Sams and Feria (1991), microbial inactivation was evaluated on a broiler drumstick using ultrasound (47 kHz) with 1% lactic acid solution at 25°C and 40°C for 15 or 30 min. The reduction in the total viable count (TVC) was insignificant at 0–0.8 Log CFU/cm2 (CFU- colony forming unit). They concluded that the microbial reduction was minimal because of the irregular skin surface on the boiler drumstick which creates protection for microbes, and low temperatures of 25°C and 40°C. However, Kordowska-Wiater and Stasiak (2011) revealed that ultrasound combined with lactic acid was an effective method for decontaminating poultry carcass skin. In this study, ultrasound 40 kHz, 2.5 W/cm2 was applied in 1% lactic acid solution for 3–6 min to chicken wing skin. This approach inactivated Salmonella enterica spp., Pseudomonas fluorescens Proteus spp., E. coli, Proteus spp., and Enterica sv. by 1.0 Log CFU/cm2 within 3 min and by 1.5 Log CFU/cm2 within 6 min. Furthermore, E. coli was the most sensitive to sonication in water, whereas P. fluorescens was the most sensitive to sonication with lactic acid.
Musavian et al. (2014) emphasized that steam ultrasound treatment is an effective method for broiler carcass decontamination. The experiment used a combination of ultrasound at 30–40 kHz and steam at 90°C–94°C. According to the study results, there was a significant reduction of approximately 0.7 Log CFU in TVC and approximately 1.0 Log CFU reduction in Campylobacter. Moreover, a combination of steam and ultrasound was used for microbial inactivation on pork jowl surfaces and meat by Morild et al. (2011). The ultrasound frequency was 30–40 kHz, steam temperature was 130°C, and pressure was 3.5–5 atm supplied at the time intervals of 0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, or 4.0 s. Microbial inactivation was higher on the skin (1–3.6 Log CFU/cm2) than on the meat surface (1–2.5 Log CFU/cm2). After 0.5 s, E. coli was significantly more sensitive to steam ultrasound than Salmonella Typhimurium and Y. enterocolitica.
According to Lillard (1993), ultrasound effectively separated S. Typhimurium from broiler skin and it caused more reachable inactivation of Salmonella ultrasound (sonication) in reducing the broiler breast skin. The highest S. Typhimurium reduction of 2.44 to 3.93 Log CFU was observed using a combination of ultrasound (20 kHz for 30 s) and chlorine. Vetchapitak et al. (2020) evaluated the efficacy of ultrasound in removing Campylobacter from broiler chicken carcasses. Feathers were vacuumed at 0.02 MPa to remove air from feathers and immersed in 0.1% cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) and 0.01% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Then ultrasound treatment was done at 130 kHz. The results revealed that a combination of CPC, vacuum, and ultrasonication was highly effective in reducing Campylobacter in chicken carcasses. This combination reduced the bacterial levels by 1.36–1.64 Log MPN/10 g (MPN - most-probable-number) on free-range chickens and by 0.94–1.16 Log MPN/10 g on broiler chickens.
Ultrasound and slightly acidic electrolyzed water have been used during the chicken breast prechilling process to evaluate microbial inactivation (Cichoski et al., 2019a). Prechilling of chicken breast was performed for 10 min and ultrasound was applied at frequencies of 25 and 130 kHz. The combination of ultrasound and slightly acidic electrolyzed water significantly reduced the abundance of mesophilic bacteria, psychrotrophic bacteria, enterobacteria, and lactic acid bacteria. Additionally, to enhance the shelf life and food safety of raw chicken meat, supercritical CO2 and high-power ultrasound were combined (Morbiato et al., 2019). This study emphasized that both supercritical CO2 and a combination of ultrasound and supercritical CO2 reduced mesophilic bacteria, yeasts, and molds (6 Log CFU/g). Other studies of microbial inactivation by ultrasound in meat are presented in Table 1.
| Food product | Treatment type | Ultrasound specification | Process conditions | Affected microorganisms | Microorganisms’ inactivation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat | ||||||
| Chicken breasts | Ultrasound | - Frequency: 40 kHz - Intensity: 9.6 W/cm2 |
- Ultrasound applied time: 0, 30, and 50 min - Storage: aerobic and anaerobic/48 h at 4°C |
- Psychrophilic bacteria - Staphylococcus aureus |
- S. aureus significant reduction after 50 min ultrasound treatment - Psychrophilic bacteria significant reduction under anaerobic packaging |
Piñon et al. (2020) |
| Chicken skin | Ultrasound and ethanol treatment combination | - Frequency: 37 kHz - Power: 380 W |
- Ultrasound applied for 5 min - Ethanol (30%, 50%, 70%) |
- Mesophilic aerobic bacteria (MAB) - Coliforms - Salmonella Typhimurium |
- In combination of 30% ethanol with ultrasound reduced S. Typhimurium by >1.0 Log CFU/g - Ethanol (30% or 50%) with ultrasound significantly reduced MAB 1.38–2.60 Log CFU/g and for coliforms 1.04 to 1.80 Log CFU/g |
Seo et al. (2019) |
| Dry-cured ham | Supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2), saline (SS), and high-power ultrasound (HPU) combination | - Frequency: 30 kHz - Power: 40±5 W |
- Pressure: 150–350 bar - Temperatures: 41°C–51°C - Time: 5–15 min |
- Escherichia coli | - For maximum inactivation optimal conditions are; · (SC–CO?+HPU+SS): 48.4°C, 12.2 min and 243.3 bar → 3.88 Log reduction · (SC–CO?+HPU): 51°C, 5 min and 350 bar → 3.88 Log reduction |
Castillo-Zamudio et al. (2021) |
| Bovine loins | Ultrasound | - Frequency: 37 kHz - Intensities: 16, 28, 90 W/cm2 - Ultrasonic baths models: S15H, S40H, and S60H |
- Sonication time: 20 and 40 min - Storage time: 0 and 7 days at 4°C |
- MAB - Psychrophilic bacteria - Coliform |
- Ultrasound at 90 W/cm2 effective in controlling - MAB and psychrophilic bacteria during storage at 4°C - At a sonication time of 40 min, coliform was reduced by ultrasound regardless of intensity |
Carrillo-Lopez et al. (2019) |
| Pork jowl | Steam-ultrasound | - Frequency: 30–40 kHz | - Steam at 130°C and 3.5–5 atm pressure - Time: 0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, or 4.0 sec |
- Yersinia enterocolitica - S. Typhimurium - E. coli |
- 0.5 s treatment had higher reductions of 0.9–1.5 Log CFU/cm2 for E. coli compared to 0.4–1.1 Log CFU/cm2 for S. Typhimurium and Y. enterocolitica | Morild et al. (2011) |
| Pork | Ultrasound combination | - Frequency: 25 kHz and power 300 W and 1 MHz with power 150 W | - Time: 10 min - Temperature: 12°C |
- Campylobacter jejuni - Brochothrix thermosphacta - Listeria monocytogenes |
- Ultrasound combined with red wine showed higher bacterial reductions compared with ultrasound or red wine alone. - C. jejuni, L. monocytogenes, B. thermosphacta had significant reduction of more than 1 Log |
Birk and Knøchel (2009) |
| Beef slurry | Thermo-sonication | - Frequency: 24 kHz - Intensity: 0.33 W/g - Amplitude: 100% |
- Temperature: 75°C - Time: 60 min |
- Clostridium perfringens NZRM 898 and NZRM 2621 spores - (NZRM 898 and NZRM 2621 refer to specific strains of C. perfringens spores) |
- At 75°C; thermo-sonication with 24 kHz ultrasound at 0.33 W/g achieved less than 1.5 Log reductions for both C. perfringens NZRM 898 and NZRM 2621 spores after 60 min | Evelyn and Silva (2015) |
| Eggs | ||||||
| Liquid whole egg | Ultrasound, lysozyme, and heat combination | - Power: 950 W - Power levels of 50% (605 W/cm2) and 80% (968 W/cm2) |
- Ultrasound and Lysozyme (US+Lys) combination treatment - Temperature: 35°C, - Time: 20 min |
- S. Typhimurium | - Best microbial inactivation by ultrasound and lysozyme (US+Lys) → 4.26 Log reduction | Bi et al. (2020) |
| Liquid whole eggs | Hugh intensity ultrasound (HIU) | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Amplitude: 80% |
- HIU treatment duration: 1, 5, 10, and 30 min (pulsed intervals: 30 s on/off) - Temperature: 20°C |
- Salmonella Enteritidis | - HIU 1 min → significant reduction of 1.9 Log CFU/mL | Techathuvanan and D'Souza (2018) |
| Liquid whole egg | Hydraulic high pressure (HHP), ultrasound (US), and pulsed electric field (PEF) | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Power 40 W |
- (HHP+US) combination · US: 5 min/55°C · HHP: 2–2–4 min (cyclic treatment) at 138 MPa, 20°C |
- S. Enteritidis | - Combination of HHP and ultrasound → highest reduction of S. Enteritidis (3.23 Log cycles) | Huang et al. (2006) |
| Japanese quail eggshell | Ultrasound | - Frequency: 35 kHz and 130 kHz | - U35 (35 kHz): 30 min - U130 (130 kHz): 30 min |
- Coliform - Salmonella - Staphylococcus |
- U130 initially reduced coliform, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus counts on eggshells | Yildirim et al. (2015) |
| Milk | ||||||
| Cow milk | Ultrasound | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Intensity: 118 W/cm2 - Power: 150 W - Amplitude: 100% |
- Batch ultrasound treatment: · Temperatures: 20±2°C and 57±2°C · Time: 1, 3, 4, and 6 min - Continuous flow ultrasound treatment: · Temperatures –20± 2°C and 57±2°C. · Time: 3, 9, 12, and 18 min |
- L. monocytogenes | - Continuous flow ultrasound treatment: · UHT Milk with L. monocytogenes → 5 Log reduction · Raw milk total aerobic bacteria → 5 Log reduction |
D’Amico et al. (2006) |
| Goat milk | Thermo-sonication | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Power levels: 150 W, 200 W, 300 W, 400 W - Temperature: 72°C |
- Time: 10 min | - MAB | - At 400 W, thermosonication significantly reduced the microbial count to less than 2.3 Log CFU/mL, compared with 5.94 Log CFU/mL in raw goat milk and 4.76 Log CFU/mL in pasteurized goat milk | Ragab et al. (2019) |
| Cow milk | Ultrasound | - Frequency: 24 kHz - Power levels: 400 W - Acoustic power: 160.4 J/s - Amplitude: 70% and 100% |
- Time: 50, 100, 200, and 300 s | - E. coli - S. aureus - Pseudomonas fluorescens - Debaryomyces hansenii |
- In the best treatment 100% amplitude for 300 s: · D. hansenii → 4.61 Log reduction · P. fluorescens → 2.75 Log reduction · E. coli → 2.09 Log reduction · S. aureus → 0.55 Log reduction |
Marchesini et al. (2015) |
| Cow milk | Thermo-ultra-sonication | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Power: 1,500 W - Amplitude: 95% - Temperature: 45°C |
- Time: 10 or 15 min - Storage: 1, 7, and 14 days |
- MAB - Enterobacteria |
- MAB → within accepted range (except for homogenized, thermo-ultrasound 10 min) - Homogenized milk, thermo-ultrasound 15 min had the lowest Enterobacteriaceae count |
Hernández-Falcón et al. (2018) |
| Whole milk and skimmed milk | Ultrasound | - Frequency: 24 kHz - Intensity: 85 W/cm2 |
- Temperature: 30°C–35°C | - E. coli - L. monocytogenes |
- E. coli had significantly higher D values (Decimal reduction time) in: · Whole milk: 2.43 min · Skim milk: 2.41 min - L. monocytogenes also had significantly higher D values in: · Whole milk: 9.31 min · Skim milk: 8.61 min - E. coli showed log-linear inactivation followed by tailing, whereas L. monocytogenes exhibited 1st-order inactivation throughout - Ultrasound waves caused mechanical damage to the bacterial cell wall and membrane, leading to their inactivation |
Gera and Doores (2011) |
Globally, milk and dairy products are widely consumed, and milk has a higher demand because it is nutritionally rich in carbohydrates, proteins, fats, essential vitamins, and minerals (Gao et al., 2014a). Due to its high nutrient composition, milk is highly perishable and susceptible to human pathogen contamination (Vijayakumar et al., 2015). To ensure milk and dairy products safety generally, traditional methods, namely pasteurization and ultra-high-temperature techniques, are utilized in the dairy industry to ensure milk and dairy product safety. Despite the effectiveness of heat treatment, it causes denaturation of milk protein, inactivation of enzymes, destruction of vitamins, Maillard reaction, and decreases milk’s nutritional value and sensory qualities. To overcome these disadvantages, nonthermal alternative preservation methods have emerged and ultrasound is one of the promising preservation methods in the dairy industry (Akdeniz and Akalın, 2022).
According to Gao et al. (2014b), low-frequency ultrasound at 20 kHz below 30°C is more effective in the inactivation of Enterobacter aerogenes in milk. However, high-frequency ultrasound (850 kHz) did not inactivate E. aerogenes, even after 60 min at 50 W power. Milk has excellent free radical scavenging ability because it contains antioxidants like milk proteins (caseins and whey proteins), vitamins, enzymes, and other hydrolysates, which mitigate radicals and hydrogen peroxide. The free radicals produced by high-frequency ultrasound are mostly neutralized by these milk antioxidants. Although high-frequency ultrasound can inactivate bacteria using its mechanical effects, it is less effective than low-frequency ultrasonication.
Dhahir et al. (2020) investigated microbial inactivation in camel milk by applying ultrasound at 900 W, 20 kHz, and 100% power for 15 min. After ultrasound treatment, the levels of E. coli and S. Typhimurium were significantly reduced. Furthermore, ultrasound treatment can be applied individually or in combination to increase microbial inactivation efficiency while preserving or enhancing the quality and sensory properties of milk and dairy products (Chandrapala and Zisu 2016; Vijayakumar et al., 2015).
Cameron et al. (2009) evaluated the effectiveness of ultrasound as a substitute for milk pasteurization. In this study, ultrasound (20–24 kHz) inactivated 100% of E. coli after 10 min, 99% of L. monocytogenes after 10 min, and 100% of P. fluorescens after 6 min. In addition, Gabriel (2015) studied the L. monocytogenes inactivation using ultrasound in full-cream milk, low-fat milk, and non-fat milk, where ultrasound frequencies of 28, 45, and 100 kHz were used. A temperature of 60°C was maintained during the 50 min treatment. During the lag phase, the lowest inactivation rate (0.24 Log CFU/min) was observed in full-cream milk, with the fastest inactivation (0.37 Log CFU/min) observed in low-fat milk.
Ultrasound was examined for the inactivation of thermally resistant spore-forming Bacillus spp. in skimmed milk by Khanal et al. (2014). Ultrasound was applied for 10 min at 5,000 W, 20 kHz, 80% amplitude. Ultrasound treatment reduced vegetative cells by 4.53 Log for Bacillus coagulans and 4.26 Log for Anoxybacillus flavithermus in skim milk. Engin and Yuceer (2012) compared ultrasound microbial inactivation with milk pasteurization and UV treatment. Ultrasound treatment was performed at 20 kHz and 75 W for 15 min and maintained temperature at 5°C. However, the ultrasound treatment was insufficient to reduce yeasts and molds.
Bermúdez‐Aguirre et al. (2009) studied the microbial inactivation in raw whole milk using thermosonication and heat pasteurization. Ultrasound at 400W power and 24 kHz frequency was applied for 10, 20, and 30 min at 63°C. After 16 days of storage, mesophilic bacteria did not show growth rates higher than 2 Log. Moreover, rennet cheese whey was treated with ultrasound and heat pasteurization by Jeličić et al. (2012). Ultrasound at 24 kHz and 240–400 W was supplied for 5, 6.5, and 8 min at 35°C, 45°C, and 55°C. Treatment at 400 W and 55°C for 8 min reduced the TVC (2.46 Log) to a greater extent compared with pasteurization.
Inactivation of Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores and vegetative cells using ultrasound was evaluated in skimmed milk powder (Beatty and Walsh, 2016). High-intensity ultrasound was applied for 5–30 s between 45°C and 75°C. Thermosonication was effective with a reduction in vegetative cells (4.8 Log) under optimized conditions of 19.75% total solids, 45°C, and 30 s. The optimum conditions for spore reduction (0.45 Log) were 31.5% total solids, 67.5°C, and 17.5 s.
In addition, Jalilzadeh et al. (2018) evaluated ultrasound microbial inactivation in ultrafiltered feta-type cheese produced using ultrasound-treated milk. Ultrasound was applied to milk at 20, 40, and 60 kHz frequencies with an intensity of 80% for 20 min. The ultrasound significantly reduced E. coli, S. aureus, Clostridium sporogenes, and Penicillium chrysogenum. At a frequency of 60 kHz, the highest inactivation was observed for E. coli and S. aureus.
Microbial inactivation in Mexican panela cheese was evaluated using ultrasound; the cheese was prepared using ultrasound-treated milk (Carrillo-Lopez et al., 2020). The milk was treated for 0, 5, and 10 min at an ultrasound frequency of 24 kHz and 400 W at 16°C. The amplitudes were 50% and 100%. Regardless of the treatment time, ultrasound at 50% amplitude reduced coliform bacteria levels. However, at 100% amplitude at 10 min, mesophilic bacteria were increased by 0.9 Log. Other studies of microbial inactivation by ultrasound in dairy and dairy products are presented in Table 1.
Eggs are frequently associated with foodborne disease outbreaks, mainly caused by Salmonella spp. contamination such as Salmonella Enteritidis. In addition, eggshell microbial flora contains Staphylococcus,Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and E. coli. At room temperature, Salmonella on eggshells penetrates the egg yolk and proliferates due to the high nutrient content in the egg yolk. Eggs can even be contaminated inside the poultry reproductive system or after laying through contact with contaminated environments. Under humid conditions, yeasts and molds such as Aspergillus, Penicillium, Rhizopus, Mucor, Rhodotorula, and Cladosporium can grow on eggshells (Aygun, 2017; Guan et al., 2006; Stadelman et al., 1996; Wilkin and Winter, 1947).
Eggs are commonly decontaminated by thermal pasteurization (limitations: nutrient loss, undesirable flavor, altered texture, and functional properties); chemical sanitization using chlorine, ammonium compounds, and hydrogen peroxide (limitations: harmful chemical residues, ineffective in removing bacteria in eggshell spores); and irradiation (limitations: reduced eggshell quality and strength). Because of the limitations of these methods, ultrasound is an effective nonthermal technology for microbial inactivation in the egg industry (Bermudez‐Aguirre and Niemira, 2023).
The inactivation of S. Typhimurium by ultrasound on liquid whole eggs was evaluated by Wrigley and Llorca (1992). Ultrasound was supplied at 20°C, 40°C, and 50°C for 15 and 30 min. According to the results, ultrasound treatment at 50°C reduced S. Typhimurium counts by 1–3 Log CFU. Manothermosonication involves a combination of ultrasound waves under pressure with lethal temperatures to inactivate microorganisms. Mañas et al. (2000) applied manothermosonication to inactivate Salmonella serotypes in whole eggs at an ultrasound amplitude of 117 microns, pressure of 200 kPa, and lethal temperature of 60°C. Manothermosonication significantly reduced Salmonella senftenberg levels by more than 99% inactivation (3 Log cycles) within 3.5 min.
Nagy et al. (2022) combined sonication and mild heat to reduce E. coli in liquid egg products using ultrasound with frequencies of 20 and 40 kHz and with the powers of 80 and 300 W for 30 or 60 min at 55°C. These combinations significantly reduced E. coli. At 300 W and 40 kHz for 60 min treatment, reduced E. coli from 5 Log CFU/mL to below 10 Log CFU/mL in liquid egg products. Additionally, 60 min treatment, regardless of the power and frequency, reduced E. coli concentration below 10 Log CFU/mL. Additionally, Huang et al. (2006) studied S. Enteritidis inactivation in liquid whole eggs using ultrasound. The optimum ultrasound conditions for inactivation were 40 W at 55°C for 5 min, with a pulsed electric field of 30 pulses at 5–67 kV/mm and 55°C, and hydraulic high-pressure (2–2–4 min cyclic treatments at 138 MPa, 20°C). The combination treatment of ultrasound and hydraulic high-pressure showed the highest microbial reduction of 3.2 Log cycles in liquid whole eggs. Other studies of ultrasound microbial inactivation in eggs are presented in Table 1.
Other Applications for Different Processing Steps
During the thawing process, frozen meat undergoes complicated heat and mass transfer, which can straightforwardly affect frozen food’s quality and physicochemical properties (Stinco et al., 2013). Furthermore, the thawing processes can facilitate the proliferation of survived microorganisms in frozen foods (Hanenian and Mittal, 2004). Due to that low temperature and accelerated thawing rates are crucial for reducing spoilage and preserving food quality during the thawing process. Ultrasound is more beneficial due to its high efficiency in thawing and low cost. The heat generation due to the cavitation bubbles collapses during the ultrasound process, increasing the temperature of frozen food, followed by the conversion of ice to water (Wu et al., 2017). Furthermore, more ultrasound energy is absorbed by frozen tissues than by their unfrozen counterpart. However, this energy is concentrated on the frozen/thawed boundary, which prevents overheating during the thawing process (Miles et al., 1999). Due to that the ultrasound with adequate power avoids localized overheating and accelerates thawing while preserving food quality.
The study of Liu et al. (2024) evaluated the effects of ultrasound thawing (power 300 W, frequency 30 kHz, for a 3 s on and 3 s off cycle) on the quality of Tibetan pork. The results revealed that ultrasound thawing accelerated the thawing process and reduced thawing time which led to the preservation of meat freshness. Additionally, it improved meat tenderness, decreased lipid oxidation and protein oxidation, improved water-protein binding, and retained the pork meat color. Ultrasound thawing alters amino acid metabolism and reduces the bitterness of pork by reducing hypoxanthine levels.
Wang et al. (2021) applied ultrasound (400 W and 45 kHz) to beef during various stages of freezing and thawing (before freezing, during freezing, during thawing, and after thawing) to evaluate the WHC of beef during ultrasound thawing. The WHC was enhanced by ultrasound at all stages, with the highest WHC (0.78) observed during the thawing stage. Moreover, ultrasound treatment increased the springiness and pH and reduced the hardness of beef. Moreover, Du et al. (2021) studied the reduction in egg yolk quality that occurred due to the freezing-thawing process and discovered ultrasound thawing had excellent emulsion stability and emulsion activity in egg yolk. These egg yolks had a uniform particle distribution, and the texture parameters (hardness, viscosity, and cohesiveness) were similar to those of fresh egg yolks.
The impact of ultrasound thawing on off-flavor and eating quality of frozen duck meat was measured by Sun et al. (2023). It exhibits that the range from 200 to 600 W reduced the thawing time by 30.96%–55.05%. Additionally, 400 W ultrasound thawing treatment reduced thawing loss, pressure water loss, CIE L*, CIE b*, pH, and shear force while improving the CIE a*, tenderness, and WHC. To examine the quality characteristics of pork, Hong et al. (2014) combined ultrasound thawing treatments (40 kHz, 150 W) with brine (2% NaCl, w/v) or water. The results showed that a combination of ultrasound and brine treatment reduced cooking loss and increased the thawing rate and tenderness. However, this combination caused pork discoloration.
Wang et al. (2020) evaluated the impact of novel thawing methods, including ultrasound thawing, on the myofibrillar protein’s gelling properties from porcine longissimus dorsi. According to the study results, ultrasound thawing (20°C, 45 min, and 500 W) resulted in less gel quality deterioration compared with microwave and water immersion thawing methods. Further, Chen et al. (2021) examined the impact of ultrasound on the quality and structural integrity of concentrated and pasteurized milk. Ultrasound thawing (200 W, 53 kHz, and 20°C) reduced the fat globule size and minimized the clustering. The brightness of both pasteurized and concentrated milk was preserved using ultrasound. As well ultrasound thawing sustained more favorable heat stability. Other studies of ultrasound-based thawing are presented in Table 2.
| Animal-based food type | Type of ultrasound | Ultrasound specification | Processing condition | Highlights | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beef, pork, and cod | High frequency-low power | - Frequency: 500 kHz - Intensity: 0.5 W/cm2 |
- Time: 2.5 h | - Surface heating↓ - Samples were thawed to a depth of 7.6 cm |
Miles et al. (1999) |
| Chicken | Low frequency- high power | - Frequency: 30 kHz - Power: 200, 300, 400, 500 W - Intensity: 0.62–2.09 W/cm2 |
- Water T°: 20±1°C | - Thawing time ↓, cutting force ↓ - Thawing loss ↓, cooking loss ↓ (especially 300 W) - Damage to myofibrillar protein ↓ (especially at 300 W) |
Zhang et al. (2021) |
| Pork | Low frequency- high power | - Frequency: 30 kHz - Intensity: 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 W/cm2 |
- Water T°: 15°C | - Thawing time ↓ (87%; 0.6 W/cm2), thawing rate ↓ (up to 1°C/min) - Textural properties were not impaired |
Gambuteanu and Alexe (2015) |
| White yak meat | Low frequency- high power | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Power: 200, 400, 600 W |
- Not reported | - Tawing time ↓ (by 0.95%–64.28%) - Thawing loss ↓, cooking loss ↓, CIE L* and CIE b* values ↓, and pH ↓ - CIE a* value ↑, cutting force ↑ at the lower 400 W power - Free amino acid ↑, mineral ↑, and vitamin ↑ (especially water-soluble vitamins) - Volatile compounds ↑ especially by 400 W power - Thawing efficiency ↑, unwanted changes ↓ by thawing white yak meat using ultrasound |
Guo et al. (2021) |
| Lamb meat | Low frequency- high power | - Frequency: 40 kHz - Power: 300 W |
- Water T°: 10°C | - Water-holding capacity (WHC) ↑, color ↑, sulfhydryl content ↓, drip loss ↓, cooking loss ↓ | Xu et al. (2022) |
| Beef | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 45 kHz - Power: 160–400 W (160, 240, 320, 400 W) |
- Time: 30 min - Water T°: 4±1°C |
- WHC ↑, springiness ↑, hardness ↓, pH ↑ | Wang et al. (2020) |
Using ultrasound as an extraction method is more beneficial than using conventional extraction methods such as Soxhlet extraction, maceration, and heat reflux, which have the drawbacks of requiring a large amount of solvent, extensive labor, high cost, and energy demands. Ultrasound extraction requires less energy, solvent, and time. Also, since ultrasound extraction utilizes low temperatures, it is applicable for heat-sensitive food extraction (Moreira et al., 2019; Ojha et al., 2020).
The bubble implosion and cavitation that occur due to ultrasound enhances cell wall disruption and facilitate mass transfer from the solid to liquid phase. Furthermore, ultrasound formulates microchannels within the tissue improving solvent penetration into the solid matrix and boosting mass transfer (Yang et al., 2017). Ultrasound extraction efficiency relies on frequency, ultrasonic power, solvent choice, and matrix-to-solvent ratio (Rodsamran and Sothornvit, 2019). Previous studies have evidence that ultrasound involved extraction in tracing organic compounds in animal tissues and plants, increasing extraction yields (Altemimi et al., 2016; McCracken et al., 2000).
Sun et al. (2006) found that ultrasound-associated extraction significantly enhanced the extraction of lutein from chicken livers. As well as ultrasound increases extraction efficiency and inhibits the chemical decomposition of exposed compounds. In this study, ultrasound treatment (10 W) was applied for 10 min. To extract macrolides from chicken fat, Lorenzetti et al. (2019) have developed a reverse ultrasound-assisted emulsification-microextraction technique. Ultrasound at 91 W was applied for 7.5 min. The results revealed that the reverse ultrasound-assisted emulsification-microextraction technique efficiently extracted macrolides from chicken skin with a recovery rate of 73%–117%. In addition, it proved the suitability of the reverse ultrasound-assisted emulsification-microextraction technique to apply in chicken fat-like complicated biological systems.
Ultrasound extraction has been used to efficiently extract insulin from the cow pancreas (Zayas, 1985). The optimum ultrasound parameters were 19.5 kHz intensity of 3.3 W/cm2 for 5–10 min. Furthermore, Zayas (1986) studied chymosin extraction from abomasum tissue using an ultrasound extraction technique. Under the optimal conditions of intensity of 3.34 W/cm2 at 15°C for 45 min, the ultrasound extraction technique significantly enhanced the chymosin yield. Additionally, Yue et al. (2006) used an ultrasound-assisted solvent extraction technique to extract lutein from egg yolks. The ultrasound-assisted solvent extraction method (10 W for 10 min) generated a significantly higher lutein yield, with a maximum yield of 89.9 μg/g. This method was more effective because it avoided degradation reactions compared to the traditional saponification solvent extraction technique.
Jain and Anal (2016) determined the effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis of eggshell membrane proteins. The optimal ultrasonic extraction conditions used were 24 kHz, 200 W, amplitude of 95.74%, 28.06 min, and a solid-to-solvent ratio of 1:30 (g/mL). According to the results, ultrasound pretreatment significantly enhanced the concentration of protein and enzymatic hydrolysis by papain and alcalase. Other studies of ultrasound-based extraction are presented in Table 3.
| Animal-based food type | Extracted compound | Type of ultrasound | Ultrasound specification | Processing condition | Highlights | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pork liver | Ferrochelatase | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 24 kHz - Power: 400 W |
- Time: 1, 2.5, and - 5 min - Extraction T°: 4±2°C |
- Extraction rate ↑ - Enzymatic activity ↑ (33.3% increment in 1 min), zinc-protoporphyrin formation ↑ |
Abril et al. (2021) |
| Mechanically separated chicken meat | Meatresidue collagen | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 24 kHz - Power: 400 W |
- Time: 0, 15, and - 30 min - Extraction T°: 4°C |
- Collagen yield ↑ (by 40%) - Collagen integrity was not disturbed - Thermal stability of collagen ↑ |
Schmidt et al. (2021) |
| Chicken blood | Erythrocyte haemoglobin | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Power: 600 W |
- Extraction T°: 20°C | - Highly effective for lysing blood to extract hemoglobin | Garcia et al. (2015) |
Ultrasound emulsification utilizes the cavitation effect, which involves micro-bubble generation, growth, and breakdown in ultrasonic fields. Emulsification relies on the physical effects of cavitation, such as shock waves, pressure, liquid jets, shearing, and turbulence (Ashokkumar, 2011). These physical effects break oil droplets into smaller droplets and generate a more stable oil-in-water emulsion (Cucheval and Chow, 2008). Ultrasound-treated emulsions usually undergo two steps. Initially, large droplets form in the dispersed phase, which are then broken down into smaller droplets by cavitation and shearing (Leong et al., 2018). According to Tang et al. (2013), cavitation impact directly breaks down emulsion droplets into smaller particles, forming a water-in-oil emulsion. However, Perdih et al. (2019) explain that the microjet generated by imploded cavitation bubbles pushes water near the oil phase into the oil phase. This process continues to form smaller droplets, creating a fine oil-in-water emulsion.
The study by Amiri et al. (2018) evaluated the ultrasound effect on emulsifying and stabilizing properties of myofibrillar proteins in beef. Ultrasound at powers of 100 and 300 W was applied to myofibrillar protein extract for 10, 20, and 30 min. These treatments improved the emulsification efficiency by increasing the surface hydrophobicity and surface-to-volume ratio. As well as Li et al. (2020) evaluated the impact of ultrasound on the emulsifying and stabilizing properties of myofibrillar proteins in chicken meat. After ultrasound application (20 kHz and 450 W for 0, 3, and 6 min) emulsion stability index (the ability of a protein to stabilize emulsions by being absorbed in the oil-water interface) and emulsion activity index (stability of an emulsion over time, particularly its resistance to phase separation or coalescence) significantly increased, leading to stable emulsions. Pinton et al. (2019) applied ultrasound at 230 W, 25 kHz, and 33 W/L for 0, 9, and 18 min to examine the effects of ultrasound on the oxidative, sensory, and technological qualities of meat emulsions with different phosphate contents. These results showed that ultrasound treatment for 18 min enhanced low-phosphate meat emulsions, suggesting that this process is beneficial for producing meat products with low phosphate levels.
Zhou et al. (2021) examined the effects of ultrasound (20 kHz, 240 W, 6 min) to improve the rheological properties and emulsifying ability of pork fat emulsion which stabilized with myofibrillar proteins using various protein: fat ratios. Ultrasound treatment increased the emulsifying activity, emulsion stability, and flow index of the emulsion while decreasing its viscosity coefficient of emulsion. Moreover, the size of fat particles was reduced, leading to a uniform distribution of the emulsion. In addition, Arzeni et al. (2012) examined the effects of high-intensity ultrasound on the emulsifying characteristics of egg white proteins. Egg whites were treated with ultrasound at 20 kHz and 20% amplitude for 20 min. The emulsion prepared using this ultrasound treatment showed higher foaming and creaming stability compared to the non-treated egg whites.
Shanmugam and Ashokkumar (2014), studied preparing stable flaxseed oil emulsions in dairy systems using ultrasound treatment at 20 kHz for 1–8 min. The study exhibits a minimum time of 3 min and ultrasound power of 176 W was adequate to generate finer stable droplets of emulsion (7% oil), which were stable at 4°C for at least 9 days. Furthermore, Aslan and Dogan (2018) formulated a dairy-based emulsifier-free emulsion by incorporating 7%, 10%, and 15% olive oil into a milk medium and treated with ultrasound (24 kHz) for 3 min. Ultrasound treatment enhanced the stability and zeta potential of these emulsions while decreasing their creaming index and droplet size, eventually leading to a finer and more stable emulsion. Other studies of ultrasound-based emulsification are summarized in Table 4.
| Animal-based emulsifier | Oil phase | Type of ultrasound | Ultrasound specification | Processing condition | Highlights | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk protein isolates | 10% (w/w) rapeseed oil | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Intensity: 34 W/cm2 |
- Time: 1–8 min - Solution T°: 45°C |
- Emulsifying performance ↑, emulsion stability ↑ - Size of the protein aggregates ↓ - Disruption of the molecules into the nano-scale ↑ |
O’Sullivan et al. (2015) |
| Bovine gelatin, fish gelatin, and egg white protein | 10% (w/w) rapeseed oil | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Intensity: 34 W/cm2 |
- Time: 2 min - Solution T°: 45°C |
- Emulsifying performance ↑ - Size of the protein molecules ↓, aggregate size ↓, hydrodynamic volume ↓ |
O’Sullivan et al. (2016) |
| Pork (77.5%) | 15% pork back fat | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 25 kHz - Intensity: 34 W/cm2 - Power: 154 W - Amplitude: 60% |
- Time: 5.5 min - Solution T°: 10°C |
- Emulsifying performance ↑ (88.7%), emulsion stability ↑ - T° of meat emulsion ↑ - Distribution of cavitation in the emulsion ↑, cohesiveness ↑, hardness ↑, and chewiness ↑ - Lipid and protein oxidation were not impaired |
Cichoski et al. (2019b) |
| Pork myofibrillar protein (30 g/L) | Pork fat (2, 3, 6, 30, 150, 300, and 450 mL/L) | Low frequency-high power | - Frequency: 20 kHz - Intensity: 12.38 W/cm2 - Power: 240 W |
- Time: 6 min - Solution T°: <20°C |
- Emulsifying activity ↑, emulsion stability ↑, flow index ↑ - Viscosity coefficient ↓, fat droplets’ particle size ↓ - Bindings between protein hydrophobic groups and fat particles ↑, protein solubility ↓ |
Zhou et al. (2021) |
Conclusion
Ultrasound is an environment-friendly, cost-effective, and nonthermal method that can be used to inactivate microorganisms that cause animal-based food spoilage and foodborne illnesses. This review elucidates that ultrasound, alone or in combination with other food preservation methods, has the potential to ensure the microbial safety of animal-based foods. The microbial inactivation mechanism by ultrasound involves the formulation of intracellular cavitation. The physical effects of acoustic cavitation disrupt cell membranes, increase membrane permeability, and cause leakage of intracellular components. The reactive radicals generated through cavitation cause oxidative damage to microbial cell membranes, proteins, and nucleic acids. Furthermore, this review shows that ultrasound is efficient in the application of thawing, extraction, and emulsification of animal-based products.
This study reviewed the positive aspects of ultrasound on animal-based food. However, excessive use of ultrasound might have a negative effect on the animal-based food quality. Therefore, further research should be conducted using ultrasound treatment to identify the effect of quality deterioration on animal-based food. Through this, exploring the optimal conditions that can prevent quality deterioration while increasing sterilization and processing efficiency is necessary. Furthermore, continuous research is needed to investigate the additional effects of ultrasound on animal-based foods. Ultrasound technology should be developed and expanded to suit specific applications in its respective fields. These kinds of researches can lead to next step for the application of ultrasound at industrial levels.