Introduction
Mycotoxins are toxic substances produced by fungi that can have detrimental effects on animal health (Abdallah et al., 2015). The majority of these toxins are produced by species belonging to the genera Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Penicillium. Approximately 72% of animal feed worldwide is contaminated with at least one type of mycotoxin (Gruber-Dorninger et al., 2019). In particular, deoxynivalenol (DON) is a trichothecene produced by a species of Fusarium. It is one of the most prevalent mycotoxins found in cereal grains, and has been detected in 88% of fodder samples in the Northern Hemisphere (Dolenšek et al., 2021; Holanda and Kim, 2021). In this regard, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) has set a DON concentration limit of less than 1 mg/kg while the European Commission has established a similar residual limit of less than 0.9 mg/kg (European Commission, 2016; Food and Drug Administration, 2010). Studies have demonstrated that the ingestion of feed contaminated with DON can lead to immune system problems, gastrointestinal damage, and oxidative stress, which can adversely affect the survival of farm animals (Pierron et al., 2016; Reddy et al., 2018).
Although the risks of DON apply to all farm livestock, pigs are particularly susceptible to DON toxicity due to the high proportion of grains in their diets and the lack of microbiota that can degrade mycotoxins in the rumen (Mwaniki et al., 2021; Pierron et al., 2016). High-DON levels can cause vomiting, diarrhea, and anorexia, which can cause pigs to feed less and fail to gain weight, resulting in economic losses to pig farms (Pestka et al., 2017; Wellington et al., 2020). DON intake by pigs induces intestinal damage, which results in reduced absorption and utilization of nutrients (Ghareeb et al., 2015). This damage may contribute to the poor growth characteristics in pigs (Liu et al., 2020). Furthermore, reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by DON can cause apoptosis, and chronic intake of high levels of DON can induce histological changes, such as fibrosis, necrosis, and hemorrhage (Skiepko et al., 2020; Weaver et al., 2013).
Metabolomics is the comprehensive examination of biological systems with the highest correlation with phenotypes (Krumsiek et al., 2016; Mishra et al., 2017). Metabolomics is necessary to improve our understanding of mycotoxin-contaminated biological systems. In this study, specific metabolites in the blood, liver, and other biological samples were used as biomarker indicators for monitoring DON contamination.
Although all pigs are susceptible to DON, the sensitivity of weaned pigs is greater than that of growing-finishing pigs (Savard et al., 2015). Studies have demonstrated that DON ingestion can exacerbate the imbalance in gut microbiota caused by rapid changes in piglet diet, severely affecting the growth of weaned piglets (Liu et al., 2020). We hypothesized that high-DON levels in this study have deleterious effects on the survival of weaned pigs. Previous studies had demonstrated that the adverse effects observed in pigs are variable and correlate with ingested concentrations of DON (Lessard et al., 2015). Consequently, accurate assess of the DON content in feed ingredients and complete diets is of paramount importance to mitigate the risk of DON in pig production (Wellington et al., 2020). Therefore, we aimed to examine the effects of different DON concentrations on growth performance, histological changes, fungal populations, and metabolomic profiles in pigs.
Materials and Methods
Castrated male pigs were obtained from Darby (Anseong, Korea). Twelve pigs (Landrace×Yorkshire, 13.5±2.3 kg) were housed in individual pens (1.3×2.45 m). During the study period, including acclimatization, the housing conditions maintained were a light-dark cycle of 12:12 h, a room temperature of 26±2°C to 22±2°C, and a relative humidity of 55±5%, according to the growth period. The pigs were separated into four distinct categories, namely 1) control group (n=3), basal diet; 2) T1 group (n=3), basal diet supplemented with 1 mg DON/kg feed; 3) T2 group (n=3), basal diet supplemented with 3 mg DON/kg feed; and 4) T3 group (n=3), basal diet supplemented with 10 mg DON/kg feed. The pigs were provided with food and water ad libitum over the course of the study period. A mixed into the diet using DON (TripleBond, Guelph, ON, Canada) was carried out in accordance with the established experimental concentrations. The mycotoxin was dissolved in ethyl alcohol (for alcoholic beverages) equivalent to 1%–5% of the diet in a beaker fully sterilized using an autoclave and stirred until it dissolved completely. The amount of solvent used was determined thoroughly by preliminary testing to ensure that it did not interfere with the fluidity of the diet depending on its moisture content. The dissolved toxins were mixed into the diet at a good mixing ratio using a blender.
The pigs were fed DON-contaminated feed for 28 days. When the experimental period ends, blood was collected a day before tissue sampling. All animals were anesthetized using T61. Following exsanguination, the ileum, liver, rectum, urine, and feces were collected rapidly. The collected samples were rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at –80°C. Additionally, for histological analysis, 10% neutral buffered formalin (NBF; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used for tissue fixation. The following formulae were employed to determine the average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI), and feed conversion ratio (FCR): ADG = (final weight – initial weight) / age (d), ADFI = amount of feed provided – amount of feed remaining, FCR = feed intake/average daily gain.
An analysis of the DON content was carried out on DON-containing feeds using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). A 1-gram homogenized DON sample was extracted with 20 milliliters of distilled water and shaken for 30 minutes. Subsequently, the extract DON sample (5 mL) was filtered through Whatman No. 1 paper and diluted in 20 mL of phosphate (PHOS)-buffer saline solution. The extracted sample was loaded separately onto the appropriate immunoaffinity chromatography columns. UPLC methods and mass spectrometry were performed as described previously study (Reddy et al., 2021). The amounts of DON in mixed feed were 0.73 mg/kg, 2.61 mg/kg and 9.52 mg/kg feed, respectively, which are similar to that of the original concentrations. There are no DON contaminations were observed in the control sample.
A Vacutainer tube was used to collect blood from the jugular vein. Serum was obtained by centrifugation at 700×g for 15 min and stored at –20°C. A total of 14 parameters were analyzed, namely alanine aminotransferase (ALT), albumin globulin (ALB), alkaline phosphatase (ALKP), amylase (AMYL), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), calcium (CA), cholesterol (CHOL), creatine (CREA), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), glucose (GLU), lipase (LIPA), PHOS, total bilirubin (TBIL), and total protein (TP). These parameters were determined on a VetTest chemistry analyzer (IDEXX, Westbrook, ME, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
For histological analysis, portions of the ileum, liver, rectum, and meat tissue were obtained from each of the pigs (0.5 cm×0.5 cm). The fixed samples in 10% NBF were embedded in paraffin. The following process was conducted: the fixed samples were dehydrated in ethanol, starting at 70% ending at 100% EtOH. They were embedded, sectioned, and heated at 45°C for two hours. For staining, the sections were deparaffinized in xylene, rehydrated in ethanol, and washed with water. The sections were stained using in-situ Cell Death Detection Kit (POD) and Masson’s trichrome (MT) staining reagent following the manufacturer’s instructions, and observed under a microscope at 200× magnification (MicrometricsTM; Nikon ECLIPSE E200, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
DNA for microbial sequencing was extracted from the cecal and rectal contents using the DNeasy PowerSoil Kit (12888-100, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Each sequenced sample is prepared according to the Illumina 16S metagenomic sequencing library protocols to amplify the V3 and V4 region. The input gDNA 5 ng was PCR amplified with 5× reaction buffer, 1 mM of dNTP mix, 500 nM each of the universal F/R PCR primer, and Herculase II fusion DNA polymerase (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The cycle condition for 1st PCR was 3 min at 95°C for heat activation, and 25 cycles of 30 s at 95°C, 30 s at 55°C and 30 s at 72°C, followed by a 5-min final extension at 72°C. The universal primer pair with Illumina adapter overhang sequences used for the first amplifications were as follows: ITS1 5’-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGTCC GTA GGT GAA CCT GCG G -3’ ITS4 5’-GTCTCGTGGGCTC GGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGTCC TCC GCT TAT TGA TAT GC -3’ The 1st PCR product was purified with AMPure beads (Agencourt Bioscience, Beverly, MA, USA). Following purification, the 2 μL of 1st PCR product was PCR amplified for final library construction containing the index using Nextera XT Indexed Primer. The cycle condition for 2nd PCR was same as the 1st PCR condition except for 10 cycles. The PCR product was purified with AMPure beads. To achieve the highest quality of data on Illumina sequencing platforms, it is important to create optimum cluster densities across every lane of every flow cell. This requires accurate quantification of DNA library templates, and therefore, we quantified prepared libraries using qPCR following the Illumina qPCR Quantification Protocol Guide (KAPA Library Quantification kits for Illumina Sequencing platforms) and qualified using the TapeStation D1000 ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany). The paired-end (2×300 bp) sequencing was performed using the MiSeq™ sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
A hundred microliter of serum was combined with 400 μL of cold acetone, placed in a refrigerator, and shaken for 1 h. The 400 μL supernatant was decanted, placed in a speed vacuum to dry completely, followed by dissolution in 100 μL of 20% methanol (internal standard–terfenadine). The resulting solution was analyzed using UPLC-Q-TOF MS (Waters, Milford, CT, USA). The liver, cecum, urine, and fecal samples were lyophilized and extracted as follows: liver, cecum, and fecal samples were dissolved in 80% methanol with an internal standard (terfenadine), whereas urine was dissolved in 20% methanol. Upon completion of metabolomic analysis of each pig sample, the samples were cross-mixed for further analysis. The samples were injected onto a C18 column using a mobile phase of water with 0.1% formic acid and acetonitrile. 0.1% formic acid (B) at a flow rate of 0.35 mL/min with an analysis time of 12–16 min for blood, liver, cecum, feces, and urine at a column temperature of 40°C. The column was analyzed using Q-TOF MS in ESI mode. TOF-MS data were scanned between 100 and 1,500 m/z with a scan time of 0.2 s. The capillary and sample cone voltages were 3 and 40 V. The de-solvation flow rate was 800 L/h and the source temperature was 100°C. Leucine-enkephalin was used as a reference compound. It was analyzed every 10 seconds. A quality control sample was analyzed after every 10 analyses. MS/MS spectra were obtained using a collision energy ramp (10–45 eV) at m/z 50–1,500. The data were processed using Makerlynx software (Waters), which calculated the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), retention time, and ion intensity. The Markerlynx program was used to normalize and align the LC-MS data obtained using UPLC-Q-TOF MS. Peak-to-peak baseline noise, noise elimination, peak width, and intensity threshold were used to identify the peaks. The mass window and retention time window were used to align the metabolite data. All data were normalized to the standards. Metabolites were identified using a combination of online databases, literature, and standards.
The liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC/MS) data was analyzed using SIMCA-P+ version 12.0.1 (Umetrics, Umea, Sweden). The results were visualized using partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). The PLS-DA was evaluated using R2X, R2Y, Q2, and permutation tests. R2X and R2Y measure how well the model fits the data, while Q2 measures how well it predicts future data. A permutation test validated the PLS-DA results. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Duncan’s test was used to analyze the relative abundances of metabolites (p<0.05). Heatmaps of the identified compounds were generated using R. The heatmaps use a red-white-blue color scale based on the z-score. Red indicates a decrease, blue indicates an increase, and white indicates no change. The paired-end method generated fastq files are converted into QIIME2 artifacts, which are available for further analysis. Demultiplexed data was processed using the DADA2 algorithm, including error correction and removal of rare taxa, to generate representative sequences and a feature table. The microbial classification of each representative sequence was confirmed by blasting against the 16S rRNA gene database. The Q2-Feature classifier is a Naive Bayes classifier trained based on the SILVA reference (region V3-V4) database (https://www.arb-silva.de/) to classify the dataset used in the experiment. A resultant table was then used to generate a phylogenetic tree for downstream alpha and beta analysis. The “core metrics analysis” command was used to generate Shannon diversity, Pielou’s evenness, observed operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and Simpson. analysis of compositions of microbiomes (ANCOM) analysis was used to verify the differences in feature composition between groups and the results were visualized. We used Prism 9.5.1 to assess growth performance and biochemical analyses with one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test. We presented the results as mean and SEM. We calculated p-values to determine statistical significance, with a value of less than 0.05 indicating a significant result.
Results
The effects of DON treatment on piglet growth performance from day 1 to 28 are presented (Table 1). The initial body weight (15.50±0.17 kg) did not differ significantly among the DON-treated groups. However, final body weight (27.00±0.59 kg) in the T3 group (10 mg/kg) was significantly lower than the other groups on day 28 (p<0.05). Moreover, the T3 group exhibited the lowest ADG (0.41±0.02 kg) and ADFI (0.89±0.02 kg) for 28 d, with a tendency for these values being lower than in the other groups (p<0.05 and p=0.08, respectively). FCR was not significantly affected by DON treatment, during the experimental period.
Control, basal diet; T1, basal diet+1 mg DON/kg feed; T2, basal diet+3 mg DON/kg feed; T3, basal diet+10 mg DON/kg feed.
Biochemical analysis of the blood samples revealed differences in exposure days and DON concentrations between the control group and DON-treated groups (Table 2). Analysis of biochemical parameters demonstrated significant differences in GLU, BUN, PHOS, CA, TP, ALB, globulin, ALT, ALKP, GGT, TBIL, and CHOL levels across the age groups. Significant differences in ALA and ALKP levels were observed in the DON treatment groups. Among these parameters, phosphatase levels showed a significant difference in age and DON interactions (p<0.05). Most of the examined parameters were within the normal ranges.
All characteristics in the table were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
Normal range value: GLU (85–160), CREA (0.5–2.1), BUN (6–30), PHOS (3.6–9.2), CA (6.5–11.4), TP (6.0–8.0), ALB (1.8–3.3), GLOB (2.5–4.5), ALT (9–43), ALKP (92–294), GGT (16–30), TBIL (0.1–0.3), CHOL (18–79), AMYL (271–1,198), LIPA (10–44).
DON, deoxynivalenol; GLU, glucose; CREA, creatinine; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; PHOS, phosphate; CA, calcium; TP, total protein (TP=ALB+GLOB); ALB, albumin globulin; GLOB, globulin; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALKP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase; TBIL, total bilirubin; CHOL, cholesterol; AMYL, amylase; LIPA, lipase.
MT staining and TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay for the analysis of histological changes in DON-contaminated piglet tissues are presented in Fig. 1. The degree of fibrosis in the liver, ileum, rectum, and meat of piglets increased proportionately with the concentration of DON (Fig. 1). The DON-treated groups showed a noticeable increase in histological changes with an increase in collagen fibers in the liver and meat tissue. The degree of fibrotic progression in groups T1 and T2 was relatively mild while that in T3 group was severely impaired. This group displayed clear fibrosis with dense fibrotic bands and nodular regeneration of the liver tissue. The portal vein, artery, and bile duct were stained blue by MT staining in the liver. There was also blue staining around the lobular boundary. The portal canals and lobular boundaries were larger, and there was more DON accumulation. The villi and lamina propria of the ileum were damaged and stained blue more than the control. Rectal tissue analysis revealed that the T1 group exhibited mild fibrosis in the submucosal glands, whereas the T2 and T3 groups demonstrated moderate fibrosis with more extensive collagen deposition. TUNEL staining results showed liver apoptosis (Fig. 2). The DON group had more TUNEL-positive staining than the control group, suggesting severe apoptosis.


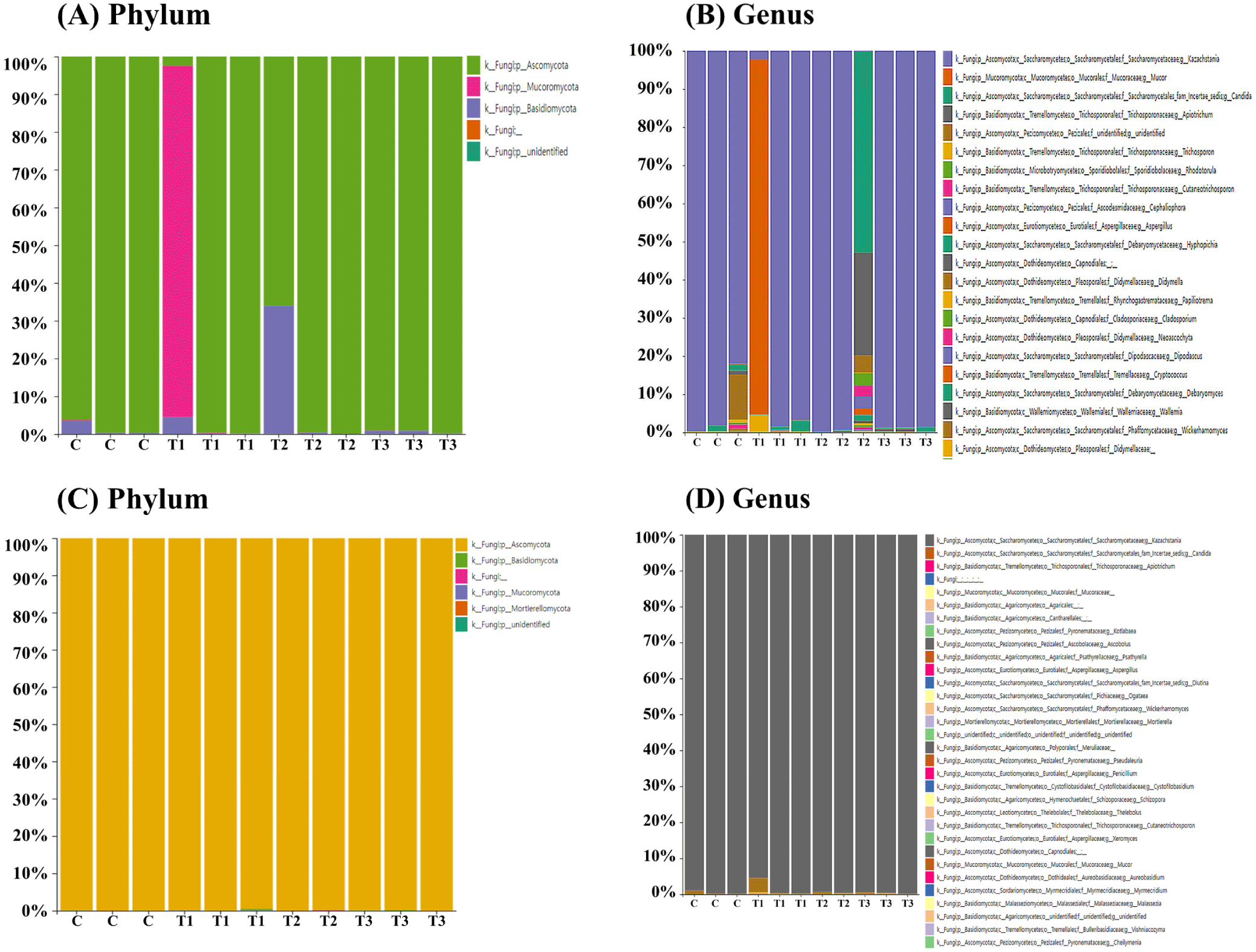
To determine the fungal composition of the rectum (n=12) and cecum (n=11), samples were collected from weaned piglets for ITS metagenomic sequencing. Ascomycota (80.7%) was the predominant phylum in the rectum (Fig. 3A), followed by Mucoromycota (15.1%) and Basidiomycota (4.2%). However, one piglet in the T1 group exhibited disparate results, with Mucoromycota (93.1%) as the dominant phylum in the rectum. At the genus level, Kazachstania (73.2%) was the dominant genus in the rectum (Fig. 3B), followed by Mucor (15.1%), Candida (5.2%), and Apiotrichum (2.6%). However, one piglet in the T1 group showed Mucor (93.0%) as the most dominant genus in the rectum, and another in the T2 group had Candida (52.7%) as the most dominant genus in the rectum (Fig. 3B). In the cecum, across all four groups, Ascomycota (99.9%) was the dominant phylum (Fig. 3C), and Kazachstania (99.1%) was the dominant genus (Fig. 3D).
Untargeted metabolomics was performed on the blood, liver, cecum, urine, and fecal samples collected after 28 days from the control group and DON-treated groups (Fig. 4). Metabolomic profiling by LC-MS analysis revealed a clear separation between the control and DON-contaminated groups in piglets. A total of 1,242 compounds were identified in the blood (153), liver (261), cecum (268), urine (264), and feces (296). To test the ability of the metabolome to separate the groups, principal component analysis (PCA) was performed. All the samples with DON exposure showed an overlap. To further highlight the differences in metabolomic profiles, the PLS-DA score plot showed good clustering for DON exposure based on qualitative and quantitative data (Fig. 4, left panels). Contribution of the metabolite groups to the separation in PCA is shown in the biplot (Fig. 4, middle panels). Characteristics of the OPLS model parameters (R2X, R2Y, and Q2) were predominantly favorable, except for the blood parameter, which exhibited a relatively low Q2 value of 0.075. The R2X, R2Y, and Q2 values for the liver tissue were 0.754, 0.979, and 0.745, respectively, for the cecum were 0.406, 0.463, and 0.358, respectively, for urine were 0.899, 0.980, and 0.898, respectively, and for the feces were 0.761, 0.900, and 0.733, respectively. To determine the effect of the metabolites induced by DON in the blood, liver, cecum, urine, and feces, a series of metabolites were screened. The metabolites were randomly divided into distinct categories. The effect of DON treatment was evident in the heatmap generated for 73 metabolites that were frequently observed in DON-exposed samples. These clusters showed distinct patterns of altered metabolite abundance (Fig. 4, right panel). The variable importance of projection (VIP) value was set to >1.0.
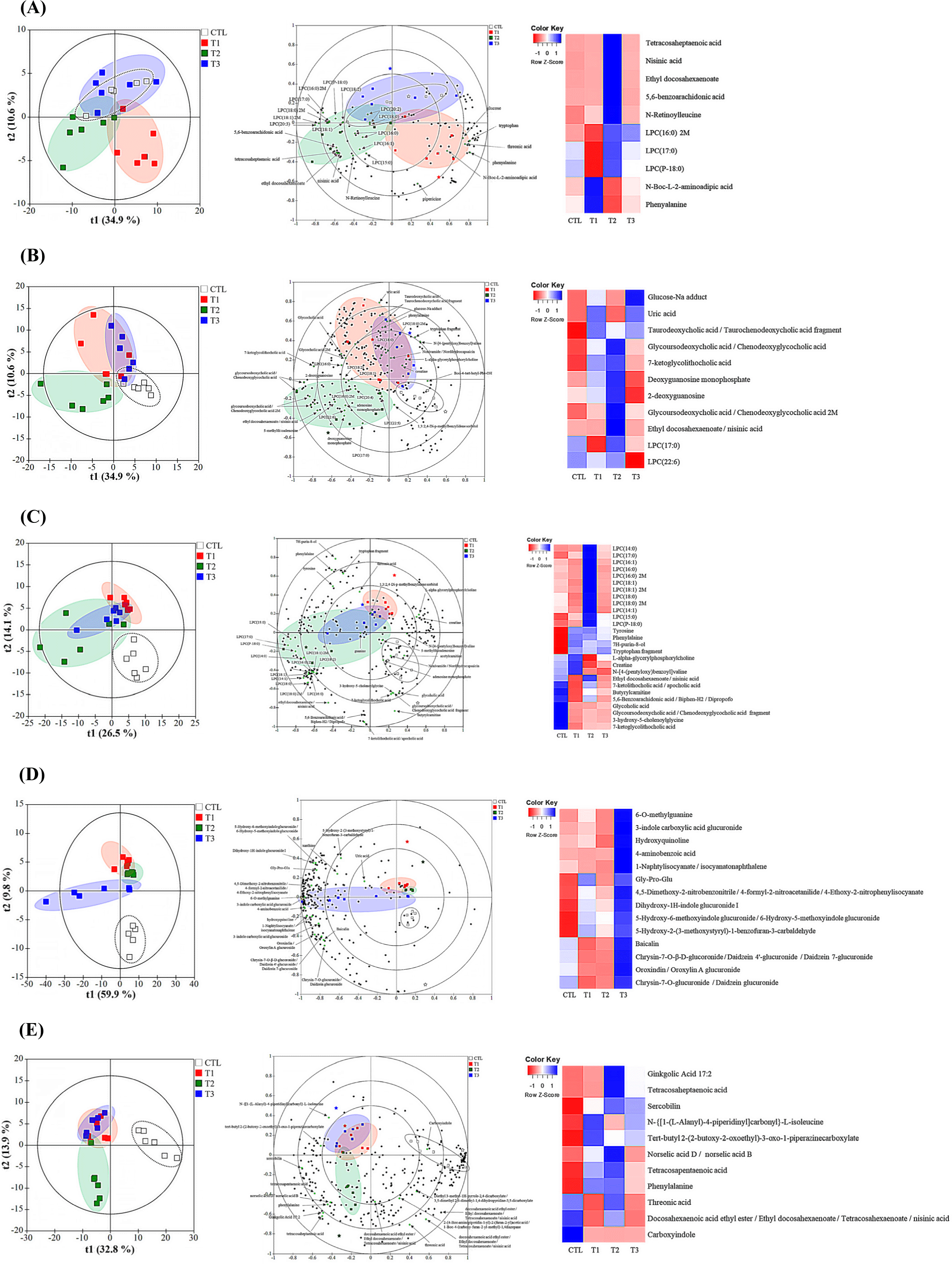
Among the metabolites, the most significant differentiating compounds between the control and DON groups were as follows: blood [N-Boc-L-2-aminoadipic acid, phenylalanine, N-retinoylleucine, tetracosaheptaenoic acid, nisinic acid, 5,6-benzoarachidonic acid, ethyl docosahexaenoate, LPC (P-18:0), LPC (16:0) 2M, and LPC (17:0)]; liver [GLU-Na adduct, deoxyguanosine monophosphate, uric acid, 2-deoxyguanosine, taurodeoxycholic acid/taurochenodeoxycholic acid fragment, glycoursodeoxycholic acid/chenodeoxyglycocholic acid 2M, glycoursodeoxycholic acid/chenodeoxyglycocholic acid, 7-ketoglycolithocholic acid, ethyl docosahexaenoate/nisinic acid, LPC (22:6), and LPC (17:0)]; cecum (L-alpha-glycerylphosphorylcholine, CREA, 7H-purin-8-ol, tyrosine, phenylalaine, butyrylcarnitine, tryptophan fragment, glycoholic acid, glycoursodeoxycholic acid /chenodeoxyglycocholic acid fragment, 3-hydroxy-5-cholenoylglycine, 7-ketoglycolithocholic acid, N-[4-(pentyloxy)benzoyl]valine, 5,6-Benzoarachidonic acid/Biphen-H2/Dipropofo, ethyl docosahexaenoate/nisinic acid, 7-ketolithocholic acid/apocholic acid, LPC (14:0), LPC (16:1), LPC (16:0), LPC (18:1), LPC (15:0), LPC (18:0), LPC (14:1), and LPC (17:0); urine (4-aminobenzoic acid, Gly-Pro-Glu, 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzonitrile/4-formyl-2-nitroacetanilide, 4-Ethoxy-2-nitrophenylisocyanate, 6-O-methylguanine, Dihydroxy-1H-indole glucuronide I, 3-indole carboxylic acid glucuronide, 5-Hydroxy-6-methoxyindole glucuronide, 6-Hydroxy-5-methoxyindole glucuronide, Chrysin-7-O-β-D-glucoronide/Daidzein 4’-glucuronide, Daidzein 7-glucuronide, Oroxindin/Oroxylin A glucuronide, Chrysin-7-O-glucuronide/Daidzein glucuronide, hydroxyquinoline, Baicalin, 1-Naphtylisocyanate/isocyanatonaphthalene, 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-methoxystyryl)-1-benzofuran-3-carbaldehyde); and feces (threonic acid, phenylalanine, N-{[1-(L-Alanyl)-4-piperidinyl]carbonyl}-L-isoleucine, tert-butyl 2-(2-butoxy-2-oxoethyl)-3-oxo-1-piperazinecarboxylate, Carboxyindole, sercobilin, Ginkgolic Acid 17:2, tetracosaheptaenoic acid, norselic acid D/norselic acid B, and tetracosapentaenoic acid).
Discussion
This study examined the impact of three different concentrations of DON on growth characteristics, histology, gut fungi, and metabolomic profiles of weaned piglets over a four-week period. The results demonstrated that weaned piglets exhibited growth retardation with increasing DON concentrations (Table 1). The study revealed that DON contamination leads to fibrosis and apoptosis in specific organs of weaned piglets. Consequently, these findings emphasized the risks associated with high DON concentrations in piglets, including histological changes and adverse effects on growth performance. Furthermore, alterations in the gut fungal community and tissue-specific metabolites have been observed in response to DON contamination. These results indicated the possibility of identifying potential biomarkers of DON contamination.
The impact of DON on growth performance and nutrient utilization varies across species, contingent on the duration of exposure, dosage, and the source of contamination (natural or commercial). The administration of low dosages of naturally DON-contaminated feed at 0.28, 0.54, 0.84, and 1 mg/kg to piglets did not result in any observable effects on their feed consumption or ADG during the 4 weeks (Jia et al., 2020). The greatest reduction in weight was observed in pigs fed 5 mg/kg of DON, in comparison to pigs fed 1 and 3 mg/kg of DON, as evidenced by the results of a six-week trial (Wellington et al., 2020). The administration of a low dosage of DON via artificial inoculation over a short period of time did not result in any adverse effects on animal performance, when compared to the effects observed in animals exposed to natural contamination and high dosages of DON (Dersjant-Li et al., 2003). In growing pigs, a reduction in ADG and growth performances were observed during the initial week of DON treatment (Li et al., 2018). A separate study demonstrated that dietary supplementation with DON had no impact on initial body weight. However, growth performance was affected after four weeks of the experiment (Liu et al., 2020). The findings suggest that DON contamination (natural vs. commercial) may demonstrate differential adaptation in pigs. It would appear that there is a paucity of literature examining the direct effects of ingestion of high concentrations of commercially purified DON on gut and fecal microbiota composition in piglets. Also, natural mycotoxins did not contain only DON; it is difficult to obtain a single mycotoxin from nature to know its effectiveness against a single mold because residue levels are set based on a single mycotoxin. In light of the potential impact of DON, a commercially purified Fusarium mycotoxin, on piglets, this study was conducted to gain a deeper understanding of its effects.
Studies have shown that DON affects the growth characteristics of weaned piglets negatively (Wang et al., 2018; Xiao et al., 2013). DON can cause severe anorexigenic effects and vomiting, which can reduce the feed intake in pigs (Holanda and Kim, 2021). This can lead to intestinal damage, which can reduce the absorption and utilization of nutrients (Ghareeb et al., 2015). Body weight loss in pigs can be primarily determined by DON concentration (Recharla et al., 2022). In this study, growth performance was not significantly affected by DON intake below 3 mg/kg. Similarly, several other studies have reported that dietary DON levels below 3 mg/kg have no effect on growth performance in pigs (Wellington et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2015). However, we found that the ADG of the T3 group was reduced by approximately 13.5% than that of the control group over the course of 28 days, resulting in the lowest final body weight. Previous studies had reported that high concentrations of DON, at above 8 mg/kg, decreased the ADG and body weight of pigs, which was in agreement with our results (Reddy et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2015). Additionally, the ADFI tended to decrease across the groups depending on DON concentrations, particularly in the T3 group, in which it decreased by approximately 11% compared to that in the control group. These results were consistent with those of Wang et al. (2018), which suggested a 15.7% decrease in feed intake and 17.7% decrease in weight gain in weaned piglets that ingested DON for 28 days. Consequently, the results indicated that the growth retardation was primarily due to decreased feed intake.
Liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying and metabolizing DON. Therefore, it is considered to be the organ most affected by DON (Ruan et al., 2022). In this study, we observed apoptosis in the different tissue of weaned piglets at high-DON concentrations. Similarly, Ji et al. (2023) had reported apoptosis in the liver cells of weaned piglets that ingested feed contaminated with DON. Apoptosis is closely associated with oxidative stress caused by DON (Kang et al., 2019). Excessive generation of ROS by DON can lead to cellular oxidative stress and reduction of antioxidant enzyme activity (Hou et al., 2023). This can damage the structure and function of mitochondrial membranes, causing mitochondrial apoptosis in liver tissue (Hou et al., 2023). Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in liver cells can activate hepatic stellate cells, leading to fibrosis (Lan et al., 2015). Previous studies had demonstrated that ingestion of DON for 3–6 weeks induces liver fibrosis in pigs (Skiepko et al., 2020). Similar to previous studies, we found that liver fibrosis in weaned piglets increased with DON ingestion.
Furthermore, our findings indicated that DON causes fibrosis in intestinal tissues, including the duodenum and rectum. After ingestion of DON-contaminated feed, the intestinal tract of pigs is the primary target organ, since it serves as the initial physical barrier against feed contaminants, chemicals, and enteric pathogens (Pasternak et al., 2018; Pierron et al., 2016). To our knowledge, no previous study had reported intestinal fibrosis due to DON ingestion in pigs. However, DON is known to cause various histological changes in the intestine. Several studies have demonstrated that DON ingestion can induce histological damage in the intestine, including multifocal atrophy, villous apical necrosis, enterocyte cytoplasmic vacuolization, lamina propria edema, and villi fusion (Gerez et al., 2015). Such histological changes in the intestine caused by mycotoxins result in the loss of the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier and persistent tissue damage, leading to inflammation due to an excessive immune reaction (Jacobs et al., 2021). This can contribute to the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix, which can lead to intestinal fibrosis (Jacobs et al., 2021).
To our knowledge, only few studies have investigated the effects of DON on intestinal fungi in pigs. Nevertheless, studies have shown that gut fungi play important roles in various physiological processes, such as immunity, digestion, and metabolism (Wang et al., 2023). In the rectum and appendix, no significant variation was observed at the phylum or genus level between the dietary treatment groups. This can be explained by the observation that fungi account for only 0.1% of the gut microbiome (Luo et al., 2021). The dominant fungal taxa found at the phylum level in both rectum and the cecum were Ascomycota, Mucromycota, and Basidiomycota. This taxonomic composition is similar to that observed in previous studies that analyzed intestinal fungi in pigs (Kong et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Furthermore, the dominant genera in the rectum were Kazachstania, Mucor, Candida, and Apiotrichum. In the cecum, Kazachstania was the predominant genus. Kong et al. (2021) identified Derxomyces, Lecanicillium, Aspergillus, and Simplicillium as the predominant genera in pigs. These discrepancies in taxonomic composition may be attributed to regional variations in the gut microbial composition, which are influenced by the functional diversity of the fecal matter and the different segments of the gastrointestinal tract (Wang et al., 2023). Furthermore, the environment, breed, host genotype, and host phenotype can influence the composition of the gut microbiota (Benson et al., 2010; Li et al., 2018; Pajarillo et al., 2014). In summary, the results of this study indicated that DON ingestion has no significant effect on the intestinal fungi in piglets.
Previous studies had reported that DON exposure can disrupt a number of biological processes, including inflammation, immune response, oxidative stress, nutritional regulation, and programmed cell death (Hao et al., 2021; Lessard et al., 2015; Tang et al., 2021). To further understand the biological changes observed in the DON-treated groups, metabolomic analyses were performed. Thus, they reflect an organ or biological system’s integrated response to pathophysiological stimuli (Wishart, 2019). In this study, a variety of metabolites were identified in blood, liver, cecum, urine, and feces of the DON-treated groups compared to that in the control. The relative concentrations of most metabolites were lower in the DON group than in the control, with the exception of those in urine. In other words, the metabolites in blood, liver, cecum, and feces were either upregulated or downregulated, whereas those in urine were elevated in the high-DON group (10 mg/kg). Based on these results, we tentatively suggested an association with urea cycle disorders.
Serum CHOL levels are affected by both feed intake and the rate of fatty acid production in the liver (Hodson et al., 2020). ALKP is a group of enzymes that facilitate PHOS hydrolysis (Sharma et al., 2014). ALT is a cytosolic enzyme that is predominantly expressed in the hepatocytes (Kim et al., 2008). The synthesis of urea from ammonia occurs in the liver, where it is subsequently excreted by the kidneys (Wang et al., 2014). Various biological changes are indicated by blood biochemical parameters. In this study, despite the observation of significant differences in biochemical parameters according to age or DON concentration, PHOS (p value for interaction=0.002) and ALT (p=0.03) were one of the strongest biochemical markers that changed significantly with DON exposure. DON decreases blood PHOS concentration in male piglets (Sauvé et al., 2023). To enhance the accuracy of the blood parameters, future studies would require an increase in the number of animals studied.
Urea cycle disorders are a group of rare inherited metabolic disorders caused by a partial or complete lack of one of the enzymes involved in the urea cycle or the transport proteins that mediate the urea cycle. These deficiencies result in the accumulation of ammonia and other nitrogenous compounds (Nagamani et al., 2021). Liver diseases caused by urea cycle disorders may be characterized by increased serum level of ALT or AST, hepatomegaly, steatosis, fibrosis, cirrhosis with portal hypertension, and hepatic impairment (Burrage et al., 2020; Ranucci et al., 2019). A reduction in the level of N-acetyl amino acids may result from a lack of N-acetyl amino acid synthase or, alternatively, from an inherited mutation in the coding region of the gene for the enzyme. In either case, this could lead to the development of metabolic abnormalities and/or diseases. Deficiency in NAcGlu results in urea cycle fails, causing ammonia to accumulated in the blood without being converted to urea, leading to Type I Hyperammonemia (Jenkins et al., 2000; Winsberg et al., 2000).
The intake of DON has the potential to disrupt the normal functioning of cells by inhibiting protein synthesis, as well as through the activation of critical cellular kinases, associated with cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis (Xiao et al., 2013). For more information on the effects of DON contamination, metabolic LC-MS fingerprints were generated for the blood, liver, cecum, urine, and fecal samples of piglets. Although the LC/MS platform was not able to provide complete coverage of the metabolome, piglets exposed to high-dose DON showed a significant difference in metabolic profile. Metabolic profiling in mice kidneys and spleens exposed to 2 mg/kg of DON were identified its impact on immunity function and nucleotide metabolism (Ji et al., 2023).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the purpose of this study was the investigation of the impact of DON contamination in piglet feed. Anorexia and reduced growth performance in piglets were induced by a 28-day acute repeated exposure to DON (10 mg/kg). Although the fungal microbiome was not significantly affected, alterations were observed in blood biochemistry and metabolite concentrations.
The histological alterations were observed in the liver, muscle, and other tissues of piglets exposed to DON for 28 days suggest that this toxin induces dysfunction of these organs. The method used to assess hepatic dysfunction, which involves the analysis of plasma ALT transaminase, was found to be influential. Although these findings did not provide a definitive explanation for DON contamination in pigs, additional studies might provide more accurate indicators. To our knowledge, this was the first report on the beneficial properties of mycotoxin-induced alterations in gut fungal compositions. However, whether DON exposure accurately reflects tissue fibrosis in urea cycle disorders is still unclear. Consequently, additional studies would be required to investigate with more animals and to reveal the correlation between various biomarkers to assess the presence of mycotoxins.













