Introduction
Mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, are common among adults worldwide. Depression, which is characterized by a consistently low mood, is a complex mental illness influenced by genetics, brain chemical abnormalities, psychosocial stressors, and traumatic experiences (Bistas and Tabet, 2023). An increasing number of studies have shown the relationship between gut microbiota and mental health through the brain-gut axis communication (Clapp et al., 2017; Xiong et al., 2023). Gut microbiota dysbiosis negatively impacts the maintenance of mental health and promotes the progression of mental illness. A healthy and balanced gut microbiota composition is influenced by several factors, including diet, age, and stress levels (Abdul-Aziz et al., 2016).
Probiotics are widely recognized for their influence on the gut microbiota, playing a role in regulating the composition and structure of the gut microbiota. Moreover, an extensive number of studies have shown that probiotics supplementation significantly improves psychological symptoms of mental illness (Amirani et al., 2020). However, despite their benefits, probiotics have certain risks, for example, antibiotic resistance and potential infections in individuals with immunocompromised conditions (Nataraj et al., 2020). Postbiotics, which have emerged as alternatives to probiotics, are soluble substances secreted or released by bacteria during lysis and include enzymes, peptides, cell wall components, polysaccharides, and cell surface proteins, as well as metabolites produced by bacterial growth (Nataraj et al., 2020). In addition, recent evidence suggests that extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from bacteria may also be classified as postbiotics because of their protective abilities against the development and progression of diseases (Yang et al., 2022). In this review, we mainly focus on EVs from probiotics as potential therapeutic agents for mental illnesses. Additionally, we discuss evidence suggesting that probiotics-derived EVs (PEVs) alleviate the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
Probiotics
An aging population and the global increase in chronic health conditions are steering consumers toward adopting healthier lifestyles. This has led to increased awareness and interest in functional foods (Baker et al., 2022; Lillo-Pérez et al., 2021; Palanivelu et al., 2022). In particular, probiotics represent the primary focus in functional food production because of their significant health potential (Begum et al., 2017). The global probiotics market, focusing solely on the human end-use segment, is projected to exceed an anticipated value of approximately USD 5.5 billion by 2032 (Lee et al., 2024). Probiotics are defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) as “Live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host.” Probiotics are live microorganisms that differ from prebiotics, which are selectively used to confer health benefits, and from postbiotics, which are non-living microbial products or substances that provide advantageous effects to the host (Ji et al., 2023). Probiotics primarily include lactic acid bacteria (LAB), with notable representatives, such as Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, and Pediococcus (Son et al., 2018). LAB are generally recognized as safe owing to their inherent presence in fermented foods, such as kimchi, cheese, and jeotgal (Castellano et al., 2017). Every genus encompasses numerous species, and within each species, there exist a multitude of strains. The health benefits associated with probiotics are typically regarded as being specific to each strain (Ji et al., 2023). Probiotics have the potential to modify the composition of the gut microbiota, vie with pathogens for nutrients and attachment sites on the intestinal lining, fortify the integrity of the intestinal barrier, and regulate the immune system (Wang et al., 2021; Wieёrs et al., 2020). In particular, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG, isolated from the human intestine, is one of the most effective probiotics due to its ability to survive in the acidic stomach and colonize the intestine, and it is still widely used as a commercial strain (Capurso, 2019). In addition to providing gut-related health benefits, probiotics may also affect brain function, cognition, and behavior through interactions between gut microbes and the central nervous system (CNS; Gambaro et al., 2020). The bidirectional connection between the microbiota gut brain axis is based on metabolic, neural, and immunological pathways that include the vagal nerve, the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis, and the production of bacterial metabolites (Góralczyk-Bińkowska et al., 2022; Zagórska et al., 2020). Because probiotics positively alter the gut microbiota and produce neuroactive and neuroendocrine molecules that act on the CNS based on the microbiota gut brain axis, they can serve as a foundation for the treatment of psychiatric disorders (Gambaro et al., 2020; Tong et al., 2020). Although probiotics offer health benefits as a medicine for mental disorders, the WHO and the FAO have noted that the use of living microbial cells in probiotics may raise safety concerns and potential side effects (Yeşilyurt et al., 2021). Probiotics side effects include systemic infections and harmful metabolic activities, and common issues are gastrointestinal disorders (diarrhea, nausea, gas, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain; Zielińska et al., 2018). There is research indicating that using derivatives or byproducts of viable microorganisms inactivated through diverse techniques can mitigate safety concerns and lower the infection risk in individuals with increased intestinal permeability and a compromised immune system (Collado et al., 2019).
Postbiotics
Postbiotics are considered a promising alternative supplement to address potential risks associated with probiotics (Chaudhari and Dwivedi, 2022; Żółkiewicz et al., 2020). In 2021, the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) defined postbiotics as “a preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the host” (Salminen et al., 2021). Possible pathways for the transmission of health benefits through postbiotics are similar to those of probiotics (Hernández-Granados and Franco-Robles, 2020; Yeşilyurt et al., 2021). Postbiotics refer to metabolic byproducts, including organic acids, short-chain fatty acids, and polysaccharides or bioactive compounds such as lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan, as well as DNA generated by living microorganisms during growth or fermentation (Balthazar et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023; Yan et al., 2024). Although the precise mechanisms by which postbiotics exert their beneficial effects on the host have not been well understood, one of the most well-documented effects is their immunomodulatory potential. For instance, several postbiotic molecules, such as lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan in the cell wall structure, can directly interact with Toll-like receptors or nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, modulating immune functions by regulating intracellular signaling pathways, including the nuclear factor-κB, mitogen-activated kinase pathways and PI3K/Akt-mediated pathways. Moreover, postbiotics not only interact with host cells, but may also affect microbial communities, which may represent indirect mechanisms of action (Jastrząb et al., 2021). Furthermore, as non-living substances and because they do not replicate in the gut, postbiotics offer a safer option than probiotics for individuals with a compromised immune system or critical illness (Ailioaie and Litscher, 2021). Postbiotics offer the advantage of being stored at room temperature, simplifying transportation and ensuring cell counts remain constant (Piqué et al., 2019; Yan et al., 2024). Their functional attributes result in improved stability, texture, and taste compared to probiotics, enhancing the physicochemical and sensory qualities of the product. As a result, they can be incorporated as functional additives to enhance product quality (Barros et al., 2020). The increasing research on the physiological benefits of PEVs suggests that EVs could serve as potential novel postbiotics (Krzyżek et al., 2023; Liang and Xing, 2023; Xie et al., 2023).
Characteristics of Extracellular Vesicles
Current research indicates that the health-beneficial activity of probiotics is mainly regulated by the production of EVs (Krzyżek et al., 2023). Recent studies propose that EVs could emerge as the postbiotics of the future, carrying potential health advantages (Xie et al., 2023). EVs are nano-scaled lipid-bilayer particles secreted by virtually every type of living cell, including plant cells, mammalian cells, bacteria, and probiotics (Kameli et al., 2021; Krzyżek et al., 2023; Morishita et al., 2021). EVs are classified into various types based on their sizes, origins, and function, for example, exosomes, ectosomes, apoptotic bodies, and oncosomes (Kong et al., 2023). Among these, exosomes are particularly well studied and typically fall within the nano-size range of 20–300 nm (Kong et al., 2023; Mandelbaum et al., 2023).
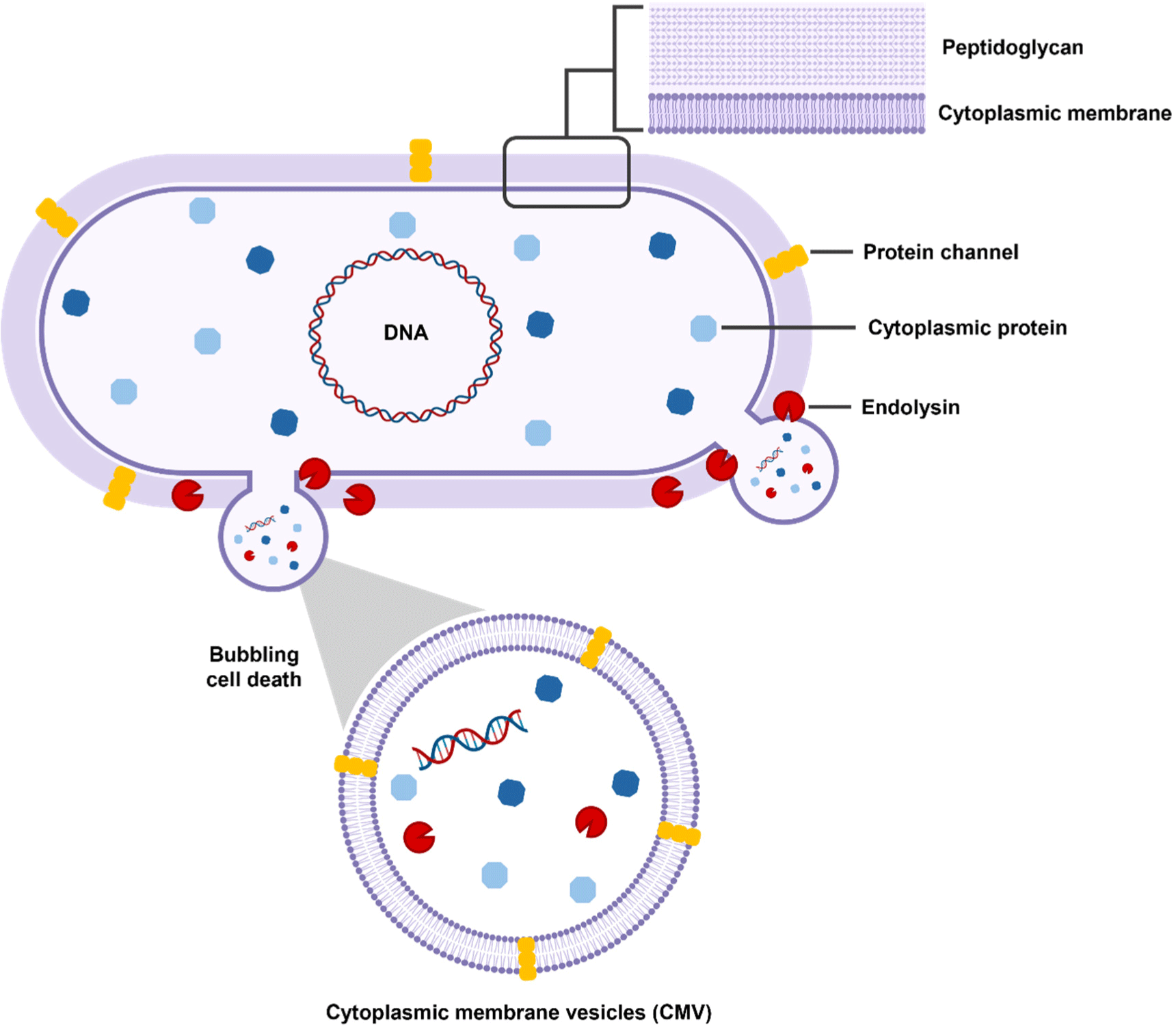
Probiotics, which are mostly Gram-positive bacteria, have a complex process for the biogenesis of EVs because of the presence of a thick peptidoglycan layer (Fig. 1; Liu et al., 2022). Previously, some non-mutually-exclusive hypotheses have been proposed about the mechanism by which EVs are released from the thick cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria. First, the release of the EVs from the cytoplasm membrane generates turgor pressure, prompting the extrusion of EVs through the cell wall. Additionally, specialized protein channels in the peptidoglycan layer may help guide EVs out of the cell (Brown et al., 2015). Finally, endolysin degrades the peptidoglycan layer, causing bubbling cell death and leading to the formation of cytoplasmic membrane vesicles (CMVs). These CMVs refer to EVs produced by Gram-positive bacteria. CMVs can carry various cargo, including cytoplasmic membrane proteins, RNA, chromosomal DNA, endolysins, and virulence factors (Bose et al., 2020; Muñoz-Echeverri et al., 2024; Suri et al., 2023).
EVs contain various molecules, such as microRNAs (miRNA), proteins, lipids, and metabolites, that can be functionally delivered between cell types and across species (Gandham et al., 2020). Genetic information carried by EVs, like mRNA and miRNA, can be safely transferred from outside the cell into the cell, where it can regulate gene expression or send signals within the cell (Mulcahy et al., 2014). Because miRNAs have complex regulatory networks, they can commute between different cells to control the rate of translation and transcription (O’Brien et al., 2018). As a result, EVs can act as signal molecules to mediate intercellular communication, transfer cargo from donor cells to recipient cells (Lee et al., 2023; Li et al., 2023), and impact physiological and pathological responses. In addition, EVs participate in antigen presentation, neuronal communication, immune modulation, metastasis, interspecies/intraspecies/interkingdom communication, stress tolerance, and horizontal gene transfer (Hosseini-Giv et al., 2022; Lee et al., 2023). According to recent research, PEVs can serve as a new communication pathway between the host and microbe (Morishita et al., 2021). PEVs can permeate the blood brain barrier (BBB) and other tissue barriers (Guo et al., 2024). For example, fluorescent-labeled exosomes administered intranasally to mice were located in the brain (Zhuang et al., 2011). Furthermore, it has been observed that CMVs derived from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum have the capability to traverse the BBB and undergo internalization by neurons (Xie et al., 2023). Another mechanism by which EVs can penetrate the brain is through the vagus nerve (Bleibel et al., 2023). In mice administered with EVs via oral gavage, the absorption of EVs increased, whereas in mice that underwent vagotomy, EVs’ absorption was inhibited (Lee et al., 2020). This ability demonstrates that EVs may be useful for drug delivery. Research findings suggest that PEVs promote gut health by modulating gut microbiota and regulating inflammatory responses in the intestine (Tong et al., 2021; Table 1). Moreover, PEVs offer a broader range of health benefits beyond promoting gut health (Fig. 2). For instance, PEVs have been shown to inhibit the growth of liver cancer cells and induce apoptosis (Behzadi et al., 2017), as well as alleviate conditions such as food allergies and atopic dermatitis (Kim et al., 2016; Kim et al., 2018). Another feature of PEVs is that they interact with immunological receptors on glial cells, leading to changes in brain function (Guo et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2021). As such, PEVs have various effects on the health of not only the intestine but also the whole body, and we have noted the effects of these various effects, especially on mental health.
| Species | Models | Biological effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Q7 | C57BL/6J mice | Regulation of intestinal microbiota | Hao et al. (2021) |
| Lacticaseibacillus paracasei PC-H1 | HCR116 cells SW1116 cells SW620 cells |
Inhibition of colorectal cancer cell | Shi et al. (2022) |
| L. paracasei | RAW 264.7 cells HT-29 cells Male C57BL/6J mice |
Anti-inflammatory effect | Choi et al. (2020) |
| Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG | HepG2 cells | Anti-proliferative effect | Behzadi et al. (2017) |
| L. rhamnosus JB-1 | HT-29 cells MODE-K cells |
Immunoregulatory activity | Champagne-Jorgensen et al. (2021) |
| Limosilactobacillus reuteri BBC3 | HT11 cells | Anti-inflammatory properties Immunomodulatory effect |
Hu et al. (2021) |
| Latilactobacillus sakei NBRC 15893 | PP and BMDCs from Balb/c mice | Immunomodulatory effect | Miyoshi et al. (2021) |
| Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563 | LP cells, T cells, B cells Balb/c wild-type mice |
Novel treatment option for allergic diseases | Kim et al. (2016) |
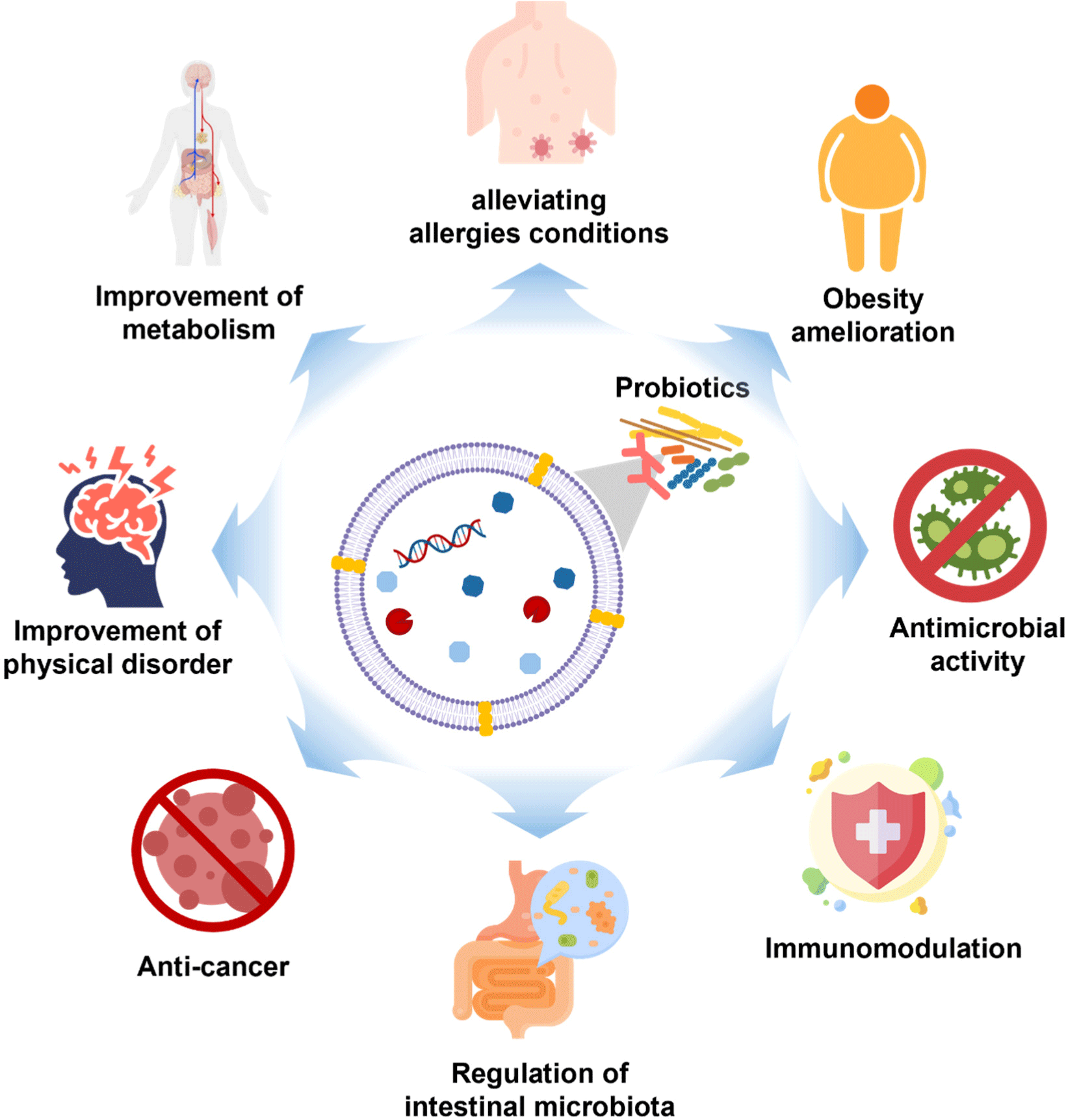
Mental health is critically important to everyone, everywhere. Mental disorders are health conditions that are defined by dysfunctional thinking, mood, or behavior, which are associated with many problems that can include disability, pain, or death (Gamm et al., 2010). The recent rapid population aging and tremendous economic and political changes have contributed to and will continue to contribute to the prevalence and impacts of mental disorders (Hossain et al., 2020; Park and Kim, 2011). Additionally, the need for mental health care is on the rise due to the widespread confusion caused by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic across the population in recent years (Hossain et al., 2020; Roy et al., 2020). However, according to the WHO, current mental health responses are insufficient and inadequate (WHO, 2022). Moreover, the mental health treatment field has its limitations and is prone to adverse effects, highlighting the need for novel, customized treatments (Johnson et al., 2023). Recent progress in research on PEVs has confirmed the potential for applying PEVs to enhance the treatment of mental disorders, and we would like to introduce this.
Potential as an Antidepressant
Several studies have shown that the Lactobacillus-derived EVs reverse the expression of neurotrophic factors increased by glucocorticoids (GC), a class of stress hormones, in HT-22 cells. Corticosterone is the primary stress hormone in mammals and a key GC in rodents (Silva et al., 2022). Furthermore, the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) belongs to a family of neurotrophins that play an important role in the survival and differentiation of neuronal populations (Miranda et al., 2019). EVs derived from L. plantarum (Lp-EV) reversed GC-induced reduced expression of total Bdnf (tBdnf) and the BDNF splicing variants Bdnf1, Bdnf4, and Ngf. Moreover, Lp-EV treatment blocked GC-induced reduced expression of proBDNF (Choi et al., 2019). The siRNA-mediated knockdown of Sirt1 in HT-22 cells suggested that Sirt1 played an important role in Lp-EV-induced upregulation of Bdnf4 and cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 (Creb1). This ultimately demonstrates that Lp-EV treatment increases Sirt1, which in turn induces the upregulation of Bdnf and Creb1. The same effect was seen in the hippocampus of mice. Lp-EV treatment in mice during the stress treatment (chronic restraint stress, CRST) phase increased expression of Bdnf1, Bdnf4, and Nt4/5. Also, Lp-EV injection at each stress session blocked the stress-induced decreased expression of proBDNF. Behavioral tests showed that mice treated with Lp-EV blocked stress-induced increased immobility and increased sociability.
Similar results were also observed in the study by Kwon et al. (2023a). Lacticaseibacillusparacasei-derived EVs (Lpc-EV) treatment counteracted GC-induced decreased expression of Bdnf, Nt3, Ngf, and TrkB. Knockdown of Mecp2 by siRNA inhibited the Lpc-EV-induced recovery of Bdnf, Nt4/5, TrkB, p53, Mkp1, and Fkbp5 expression induced by GC. Microarray data comparing gene expression in GC-treated HT-22 cells versus GC+Lpc-EV-treated cells showed that GC decreased stress-related MAPK pathways and neuronal cell death regulation, but Lpc-EV treatment reversed these alterations. These results demonstrate that Lpc-EV modulates GC-induced neurotrophic factor expression changes through Mecp2 regulation and affects stress response and epigenetic modification pathways via specific gene clusters. Similar trends of genetic changes were seen in CRST mice. In the results of the social interaction test, CRST mice exhibited reduced social interaction, in addition to increased immobility in the tail suspension test and the forced swim test. However, Lpc-EV treatment after stress partially reversed these changes. In conclusion, these findings demonstrate that Lp-EV and Lpc-EV directly act on neuronal cells and mediate the antidepressant effects. Additionally, Lp-EV and Lpc-EV cargo components can effectively mitigate stress-induced changes in gene expression and depressive behaviors, highlighting their potential as therapeutic agents for stress-related disorders (Table 2).
| Species | Models | Biological effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | HT-22 cells Male C57BL/6J mice (7-weeks old) |
Increase the expression of BDNF Antidepressant-like effect |
Choi et al. (2019) |
| Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | HT-22 cells Male C57BL6 mice (7-weeks old) |
Restored stress-induced changes of those factors Alleviated stress induced depressive-like behavior |
Kwon et al. (2023a) |
Possibility as a Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease
Amyloid-beta (Aβ) appears to play an important role in Alzheimer’s disease. An imbalance of Aβ production and clearance induces Aβ accumulation, which can be continued to Alzheimer’s disease. Treatment with Aβ42 in HT-22 cells downregulated the expression of Bdnf, Nt3, Nt4/5, Ngf, TrkB, and Mecp2, but Lpc-EV blocked these effects (Kwon et al., 2023b). Through siRNA-mediated knockdown, it was demonstrated that the upregulation of Bdnf, Nt3, Nt4/5, and TrkB by Lpc-EV was mediated by MeCP2 and Sirt1. These tendencies were analogous to those observed in Tg-APP/PS1 mice. In the hippocampus of these mice, the expression of Bdnf, Nt4/5, TrkB, Mecp2, Creb1, Sirt1, Sirt5, and Sirt7 was downregulated, whereas the expression of Hdac2, G9a, Setdb1, and Suv39h1 was upregulated. In contrast, when treated with Lpc-EV, the expression of Bdnf, Nt4/5, TrkB, Mecp2, Creb1, Sirt1, Sirt5, and Sirt7 was upregulated, whereas the expression of Hdac2, G9a, Setdb1, and Suv39h1 was downregulated. Furthermore, Lpc-EV treatment restored the downregulated expression of MeCP2 and Sirt1 proteins in the hippocampal neurons of Tg-APP/PS1 mice. Lpc-EV suppressed gliosis in the brains of Tg-APP/PS1 mice. In several behavioral tests, including the novel object recognition (NOR) test, water maze test, and passive avoidance (PA) test, the results revealed that Tg-APP/PS1 mice treated with Lpc-EV exhibited improved performance in object recognition and retention memory in NOR, as well as enhanced retention memory for shock-associated stimuli in the PA test. In conclusion, Lpc-EV induces MeCP2- and Sirt1-dependent upregulation of Bdnf, Nt3, Nt4/5, TrkB, Mmp-2, and Mmp-9, and epigenetic modification is a critical mechanism by which Lpc-EV alleviates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in Tg-APP/PS1 mice (Table 3).
| Species | Models | Biological effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | HT-22 cells Tg-APPswe/PS1dE9 (Tg-APP/PS1) mice |
Beneficial for treating Alzheimer’s disease |
Kwon et al. (2023b) |
Conclusion and Prospect
EVs can be used as a potential treatment in health and disease because they can interact with host cells and deliver long-distance molecules to neighboring bacteria and host cells (Mandelbaum et al., 2023). Over the past few years, awareness of PEVs as promising therapeutic sources has been growing rapidly (Krzyżek et al., 2023). The evidence collated in this review suggests that PEVs might improve cognitive functioning in depression and Alzheimer’s disease via several mechanisms. Although PEVs can improve mental health and psychological function, they can be offered as new medicines for common mental disorders, some challenges and limitations should be addressed.
First, considering that bacterial EVs contain proteins, peptides, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and bacterial metabolites (Yang et al., 2018), the bioactive components in PEVs should include some of these components. Therefore, the characterization of which substances will be included in PEVs and cause a transcriptional reaction must be made. Second, in some papers, PEVs regulate the expression of epigenetic factors. Considering that epigenetic factors can serve as the basic regulators of chromosome structures and the transcription of numerous genes, PEVs-induced changes in the epigenetic regulation of genes likely have genome-wide effects (Kwon et al., 2023a). Given the massive genome-wide effects of PEVs, bioactive components in PEVs might drive multiple arrays of signaling events to restore a homeostatic ability. Third is the lack of uniform standards for the separation, purification, characterization, storage, and quality control of PEVs. Due to the unique properties of PEVs, their separation and purification methods may not completely imitate the manufacturing process. Finally, although the safety of orally administered PEVs has been verified through animal experiments, their safety and biocompatibility with other nasogastric pathways must be comprehensively evaluated. The importance and potential application of PEVs in human health are not yet widely recognized. More clinical studies are necessary to determine the clinical significance of the effects and their bioequivalence or superiority against current treatments (Ansari et al., 2020).
In recent years, immunotherapy has emerged as an effective treatment strategy, and nanoparticle-mediated biotherapy has been reported to synergize with immunotherapy to improve response rates, resulting in better clinical outcomes (Zhang and Zhang, 2020). PEVs are attractive due to their unique advantages and therapeutic potential, especially in regulating immune responses to fight diseases. Therefore, future in-depth investigation needs to be undertaken to solve the above problems and apply them to biotherapeutics.













