Introduction
Protecting the body against bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances in the immune system is a vital in maintaining physiological homeostasis (Lee et al., 2022a; Peters et al., 2019). Immune system disorders can cause autoimmunity, inflammation, and cancer. Thus, it is important for immunodeficiency patients to maintain their system (Lee et al., 2021). Innate immunity is a non-specific immune response that involves immune cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, and natural killer cells (Andrés et al., 2022; Baek et al., 2023). Immune cells associated with innate immunity can identify foreign invaders like bacteria and control the activation of other cells through various receptors and signaling pathways (Vijay, 2018). The macrophages stimulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway secrete pro-inflammatory factors such as nitrite oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and interleukin (IL)-6 (Cho et al., 2023a; Gautier and Yvan-Charvet, 2014; Sun et al., 2020). These pro-inflammatory factors regulate the immune system to protect the body from external infection (Abdulkhaleq et al., 2018). Several immunostimulants, which stimulate the immune system non-specifically, are highly toxic, side-effective, and expensive (Gasmi et al., 2023). Therefore, it is important to develop immune stimulants from natural materials with high stability (Gasmi et al., 2023; Nooraei et al., 2023).
Ovomucin (OM), a glycoprotein found in egg whites, has gelling property and contributes to foam stability (Sun et al., 2018; Tu et al., 2020). OM comprises two subunits, α-OM and β-OM, of which β-OM is more heavily glycosylated (Hiidenhovi, 2015). The insoluble OM contains approximately 2.5 times more β-OM than the soluble OM (Hiidenhovi, 2015), and is difficult to dissolve OM in water without sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and beta-mercaptoethanol (Abeyrathne et al., 2016). However, the process of chemically transforming proteins is complicated, and the reactions during the process leave toxic substances behind that lead to potential safety issues (Wang and Arntfield, 2016).
Enzymatic hydrolysis releases the encoded peptide by cleaving the peptide bond established in the protein (Cruz-Casas et al., 2021), and can enhance the functional properties of OM due to small peptide molocules (Moreau et al., 1997). Peptides hydrolyzed using various enzymes have different structural characteristics, such as amino acid lengths and sequences, and exhibit various functional activities (Cho et al., 2022). Previous studies reported that hydrolysates of ovalbumin, ovotransferrin, and ovomucoid have various functional properties (Abeyrathne et al., 2013; Abeyrathne et al., 2015; Rathnapala et al., 2021).
The functional properties of OM and OM hydrolysates (OMHs) have also been investigated; however, their specific immunomodulatory activities are not well understood. Therefore, in this study, we evaluated the immunostimulatory properties of enzymatically hydrolyzed OM by quantifying the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) in RAW 264.7 macrophages. In addition, we determined the activation of the immunostimulatory mechanism via the MAPK signaling pathway and investigated the immune-stimulating activity of OMHs.
Materials and Methods
Alcalase, Neutrase, and Protamax were sourced from Novozymes (Basvaerd, Denmark), whereas bromelain and papain were purchased from Daejong (Seoul, Korea). α-Chymotrypsin (from bovine pancreas), pancreatin (from porcine pancreas), trypsin (from porcine pancreas), and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM), penicillin-streptomycin, fetal bovine serum (FBS), and phosphate-buffered saline were provided by HyClone (Logan, UT, USA). Thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and Griess reagent were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Ethyl alcohol and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were purchased from Samchun (Seoul, Korea). Mouse TNF-α and IL-6 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits were obtained from AbFrontier (Seoul, Korea).
OM was isolated from chicken egg whites, as described method (Abeyrathne et al., 2013). To produce the OMHs, various proteolytic enzymes, including Alcalase, bromelain, α-chymotrypsin, Neutrase, pancreatin, papain, Protamax, and trypsin were utilized as per the procedure outlined the method (Cho et al., 2022). Freeze-dried OM was solubilized in distilled water (20 mg/mL) and adjusted to pH 7.0. Prior to use, the enzymes were diluted in distilled water (20 mg/mL), with the exception of Alcalase in aqueous form. Each enzyme was added to the OM mixture at an enzyme to substrate ratio of 1:100 (w/w) and incubated at 37°C for 3 h. After the incubation period, the enzymes were deactivated by heating at 100°C for 15 min. The resulting hydrolysates were centrifuged at 10,000×g for 15 min, and the supernatant was lyophilized.
Peptides derived from OM were analyzed to assess their molecular weight using 20% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) gels and a Mini-Protein II cell (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 (Sigma-Aldrich) was used to stain the gels and visualize the protein bands.
The protein solubility of the OM and OMHs were determined using the Lowry assay, as the described previously (Lowry et al., 1951). The sample concentrations were maintained at low levels to ensure complete dissolution of all proteins in DC protein assay reagents A and B (Bio-Rad Laboratories). OM and OMHs were centrifuged at 5,000×g for 10 min at 4°C. Then, 25 μL of DC protein assay reagent A and 200 μL of DC protein assay reagent B were loaded to a 96-well plate. Each well was seeded with 5 μL of sample supernatant. The 96 well-plate was incubated at 37°C for 15 min in the dark, and absorbance was measured at 750 nm using a microplate reader (Emax, Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Bovine serum albumin was used to construct a standard curve for protein solubility. The solubility (%) of proteins was calculated using the following Eq. (1):
The RAW 264.7 cell line (Korean Cell Line Bank, Seoul, Korea) was cultured DMEM with 10% FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. The RAW 264.7 cell line was incubated in an MCO-18AIC incubator (Sanyo, Osaka, Japan) at 37°C and 5% CO2.
The viability of OMH treated RAW 264.7 cells in response to OMH was evaluated using the MTT assay as the described method (Lee et al., 2021). RAW 264.7 cells (2×105 cells/100μL) were seeded in 96-well plates and incubated for 4 h. Subsequently, OMH was added to the wells at concentrations of 125, 250, and 500 μg/mL. After incubation for 24 h, MTT solution (2 mg/mL) was added to each well. The cells were cultured for an additional 2 h. The supernatant was discarded, and formazan crystals were solubilized in DMSO. DMEM was used as a control. Absorbance at 570 nm was measured by using a microplate reader. Cell viability was calculated as a percentage using the following Eq. (2):
NO production was assessed using the Griess assay (Lee et al., 2022b). RAW 264.7 cells were loaded into a 96-well plate at a concentration of 2×105 cells/well and precultured for 2 h. Different concentrations of OMHs (62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL) were added to each well and incubated for 24 h. Cells treated with LPS (10 ng/mL) was used as positive controls. The amount of NO generated was quantified by adding the Griess reagent, a 1:1 mixture of 0.1% N-(1-naphthyl)-ethylenediamine dihydrochloride in distilled water, and 1% sulfanilamide in 5% phosphoric acid. The absorbance of the plates was measured at 540 nm using a microplate reader (Emax, Molecular Devices). A standard curve for NO production was constructed using sodium nitrate. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to measure the impact of OMHs prepared with pancreatin (OMPA) on the mRNA expression of iNOS. RAW 264.7 cells were added to a 6-well plate (1×106 cells/well) and incubated for 24 h. Following treatment with various concentrations of OMPA (62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL), the cells were incubated for an additional 24 h. RNeasy mini kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) was used to extract the total RNA from RAW 264.7 cells. Total RNA was transformed into cDNA using a Revert Aid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). iNOS mRNA expression levels were quantified using SYBR green reagent (PhileKorea, Daejeon, Korea) and a PikoReal Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The delta-delta Ct method was used to analyze the amplified mRNA levels, with β-actin serving as a reference gene. The primer sequences used in this study are listed in Table 1.
In the presence of LPS (10 ng/mL) or OMPA (62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL), RAW 264.7 cells (4×105 cells/mL) were cultured for 24 h in 6-well plate. Morphological differences between RAW 264.7 cells were examined by capturing images using a light microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). The cell number of RAW 264.7 treated with OMPA was confirmed using the trypan blue assay (Felice et al., 2009).
The impact of OMPA on the expression and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) was evaluated using qRT-PCR and ELISA. qRT-PCR analysis was conducted to assess the mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-6 using a previously described method. ELISA was performed to measure TNF-α and IL-6 protein levels. RAW 264.7 cells (4×105 cells/well) were plated in a 12-well plate and incubated for 24 h. Following treatment with various concentrations of OMH (62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL), the cells were incubated for an additional 24 h. The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the cell culture supernatant were analyzed using an ELISA kit (AbFrontier, Seoul, Korea) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
To detect MAPK phosphorylation, RAW 264.7 cells (3×106 cells/well) were cultured in a 6-well plate for 24 h. Subsequently, the cells were incubated for 30 min with LPS (10 ng/mL) and OMPA (62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL). Total protein was isolated from the cells using radioimmunoprecipitation buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with a protease/phosphatase inhibitor cocktail. Protein from each sample (25 μg) was separated using 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. After blocking with 5% skim milk in Tris-buffered saline containing 1% Tween 20 (TBST), the membranes were incubated with specific primary antibodies against the total or phosphorylated forms of p38, JNK, and ERK. After washing with TBST, the membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody for 2 h. After washing, the protein bands were identified using a reagent designed for enhanced chemiluminescence and visualized by exposing the PVDF membrane to an X-ray film. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The protein bands were quantified using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Statistical data are presented as the average value±SD. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Duncan’s multiple range test was performed to evaluate the comparison of means, and a p-value less than 0.05 was deemed statistically significant. Statistical evaluation was conducted using the SPSS software version 18 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results and Discussion
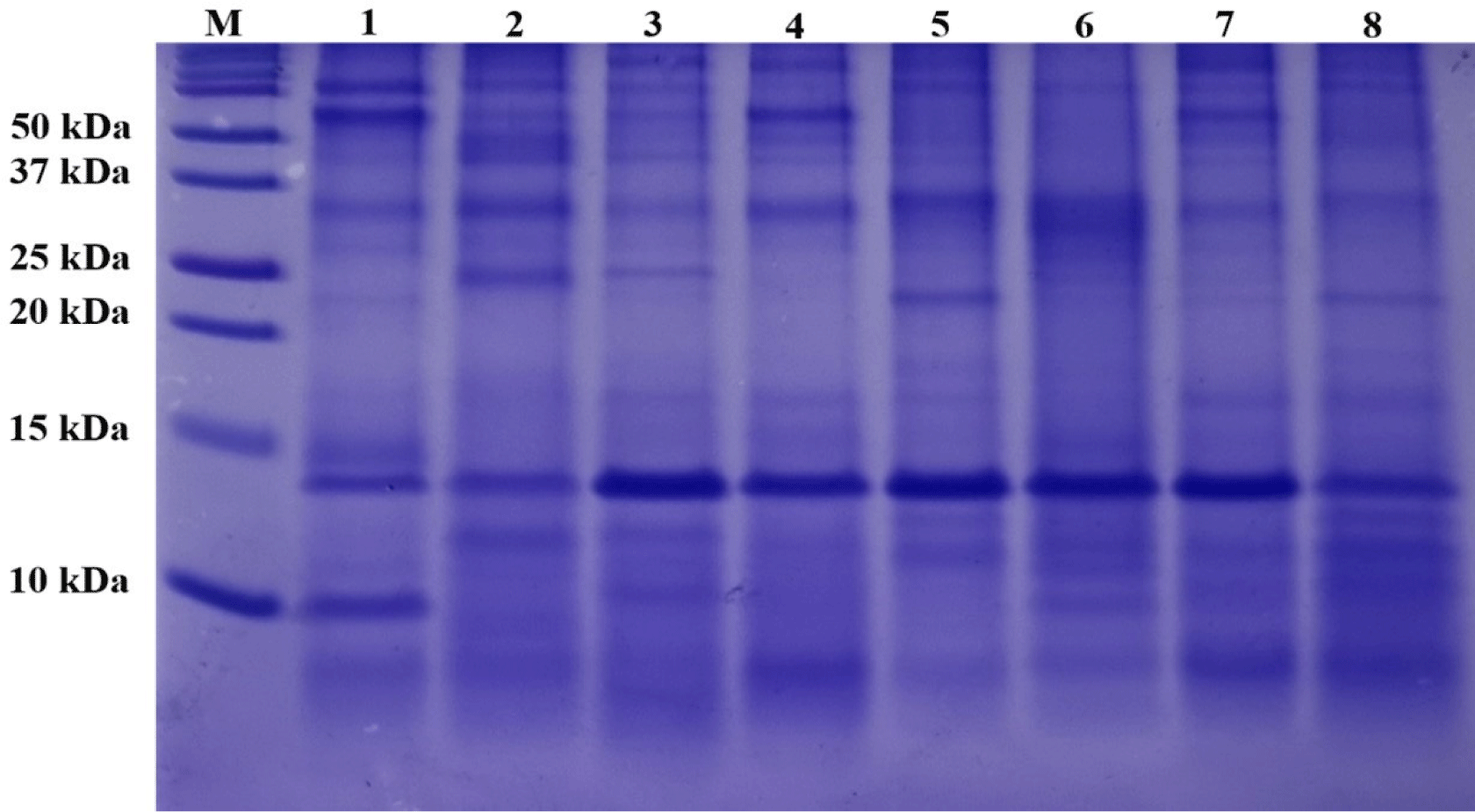
The SDS-PAGE patterns of the OMHs are shown in Fig. 1. Because OM is insoluble, it was not included in this experiment. Despite loading the same concentration (10 mg/mL) of OMHs into lanes 1 to 8, each OMH sample exhibited diverse band profiles and varying band thicknesses. These distinct band profiles suggest that the eight enzymes generated various peptides from OM. Additionally, the OMHs showed many low-molecular weight peptides, 10 kDa or less. Biologically functional peptides are generally short, consisted of 2 to 9 amino acids, with a low-molecular weight (Khiari et al., 2014). Consequently, these hydrolysates are likely to exhibit various functional activities.
The effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on protein solubility are summarized in Table 2. The protein solubility of the OM was 3.68%, which was barely soluble. In contrast, the solubility of all OMHs was over 90%. Protein solubility can be enhanced through hydrolysis by reducing the size of protein molecules and increasing the repulsive forces between them (Gravel and Doyen, 2020; Sathe et al., 2018). Low-solubility proteins can accumulate intra- and intermolecularly to form large insoluble aggregates (Vihinen, 2020). Therefore, only OMHs were used in the subsequent studies.
| Sample | Solubility (%) |
|---|---|
| OM | 3.68±1.14c |
| OMAC | 91.92±3.27b |
| OMBM | 95.32±2.12ab |
| OMCT | 97.56±1.60a |
| OMNT | 98.56±0.94a |
| OMPA | 91.56±2.88b |
| OMPP | 90.64±3.91b |
| OMPT | 94.37±1.36ab |
| OMTP | 97.93±1.19a |
OM, ovomucin; OMAC, ovomucin hydrolysate prepared with Alcalase; OMBM, ovomucin hydrolysate prepared with bromelanin; OMCT, ovomucin hydrolysate prepared with α-chymotrypsin; OMNT, ovomucin hydrolysate prepared with Neutrase; OMPA, ovomucin hydrolysates prepared with pancreatin; OMPP, ovomucin hydrolysate prepared with papain; OMPT, ovomucin hydrolysate prepared with Protamax; OMTP, ovomucin hydrolysate prepared with trypsin.
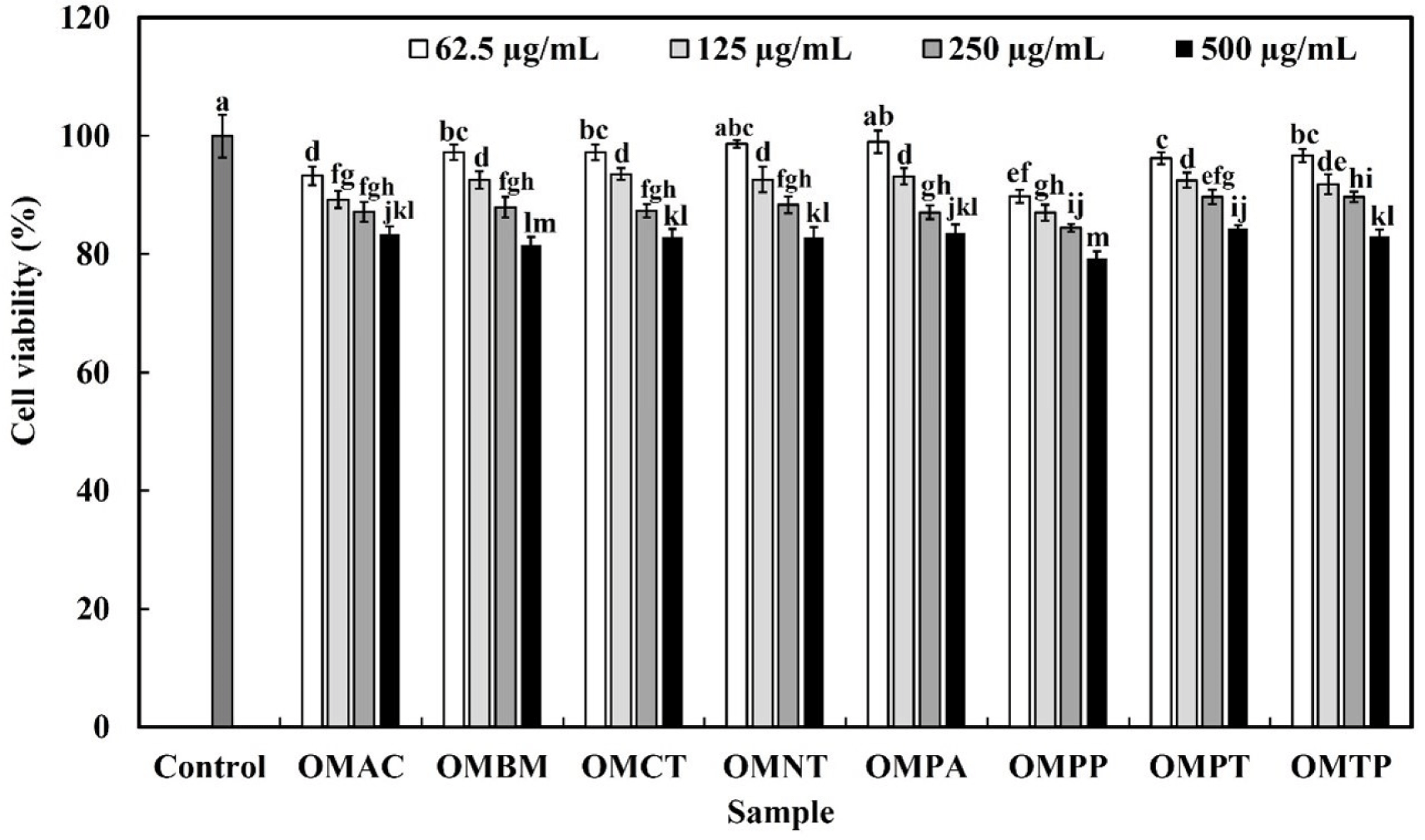
The effects of the hydrolysates on the viability of RAW 264.7 macrophages were evaluated using the MTT assay after treating the cells with OMHs for 24 h. For the concentrations of OMHs (62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL), excluding OMPP, the cell viability was over 85% (Fig. 2). Subsequent experiments were conducted at concentrations that did not induce cytotoxicity, because it was determined that cell growth affected at concentrations below 85%.
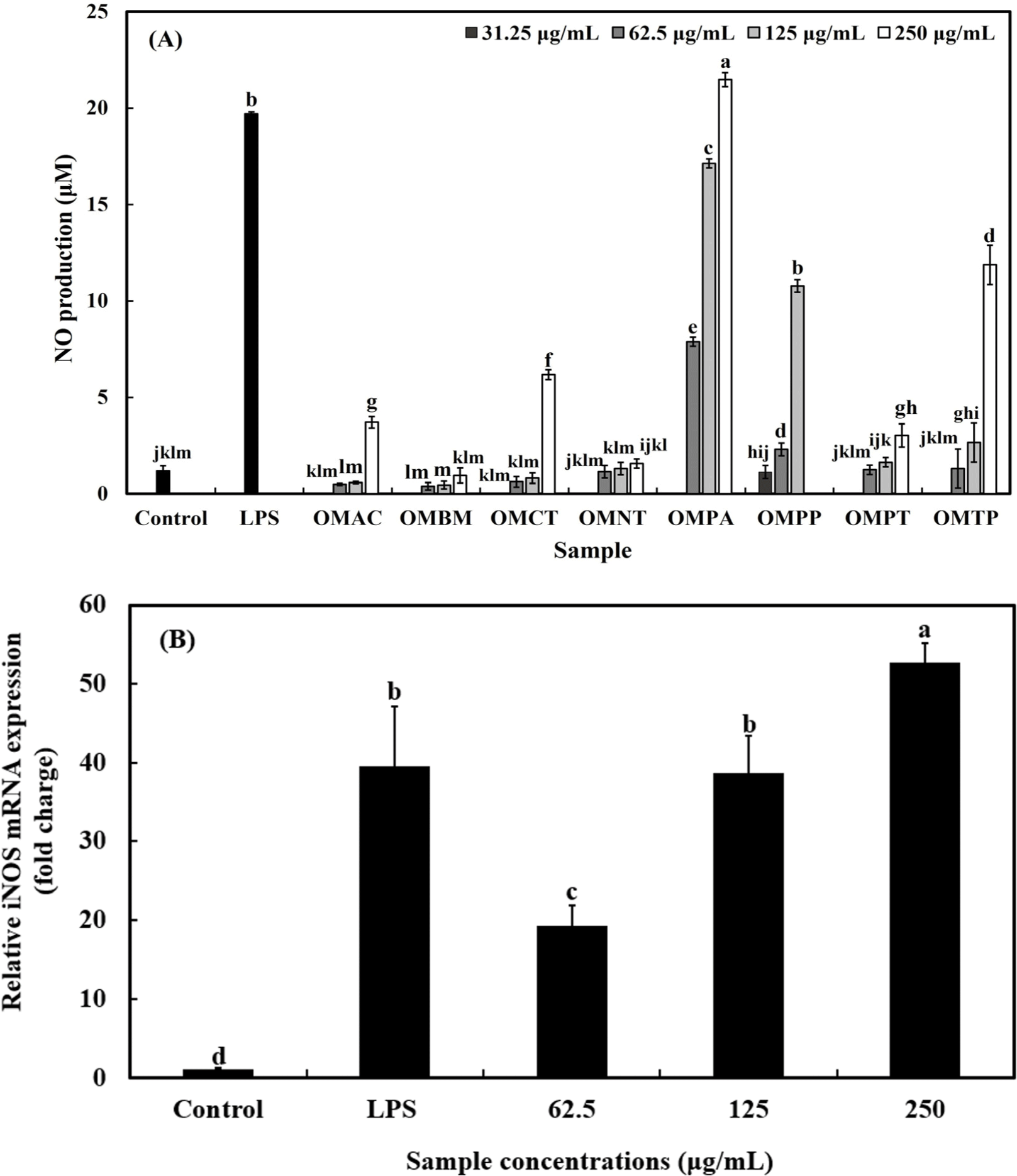
As shown in Fig. 3A, NO production after treatment with LPS (10 ng/mL) was 18.86 μM, and all OMHs-treated samples increased NO production in a concentration-dependent manner (p<0.05). Among the OMHs, OMPA produced the highest amount of NO by 7.89 μM, 17.13 μM, and 21.47 μM at 62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL, respectively. At a concentration of 250 μg/mL, OMPA produced the highest NO production of 21.47 μM compared to the NO amount induced by LPS treatment (10 ng/mL). Therefore, OMPA was selected for further study.
iNOS catalyzes the conversion of L-arginine to NO and L-citulline via an oxidative deamination. NO is synthesized by iNOS, which is involved in the immune response to external stimuli such as bacterial LPS and cytokines (Jang et al., 2020). NO is a critical mediator of the inflammatory response and, plays a vital role in maintaining health by combating pathogenic microorganisms, eliminating tumor cells, and performing various essential biological functions (Cho et al., 2023b). Therefore, the effect of OMPA treatment on iNOS of that expression in macrophages was verified.
The effects of OMPA on iNOS expression are shown in Fig. 3B. LPS treatment significantly upregulated iNOS expression by 39.2-fold compared to the control group (p<0.05). Treatment with OMPA at concentrations of 62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL also led to a significant increase in iNOS mRNA expression by 19.2-, 38.3-, and 52.2-folds, respectively, compared to the control (p<0.05). The results of our study determined that OMPA induced iNOS expression and NO production (Figs. 3A and B).
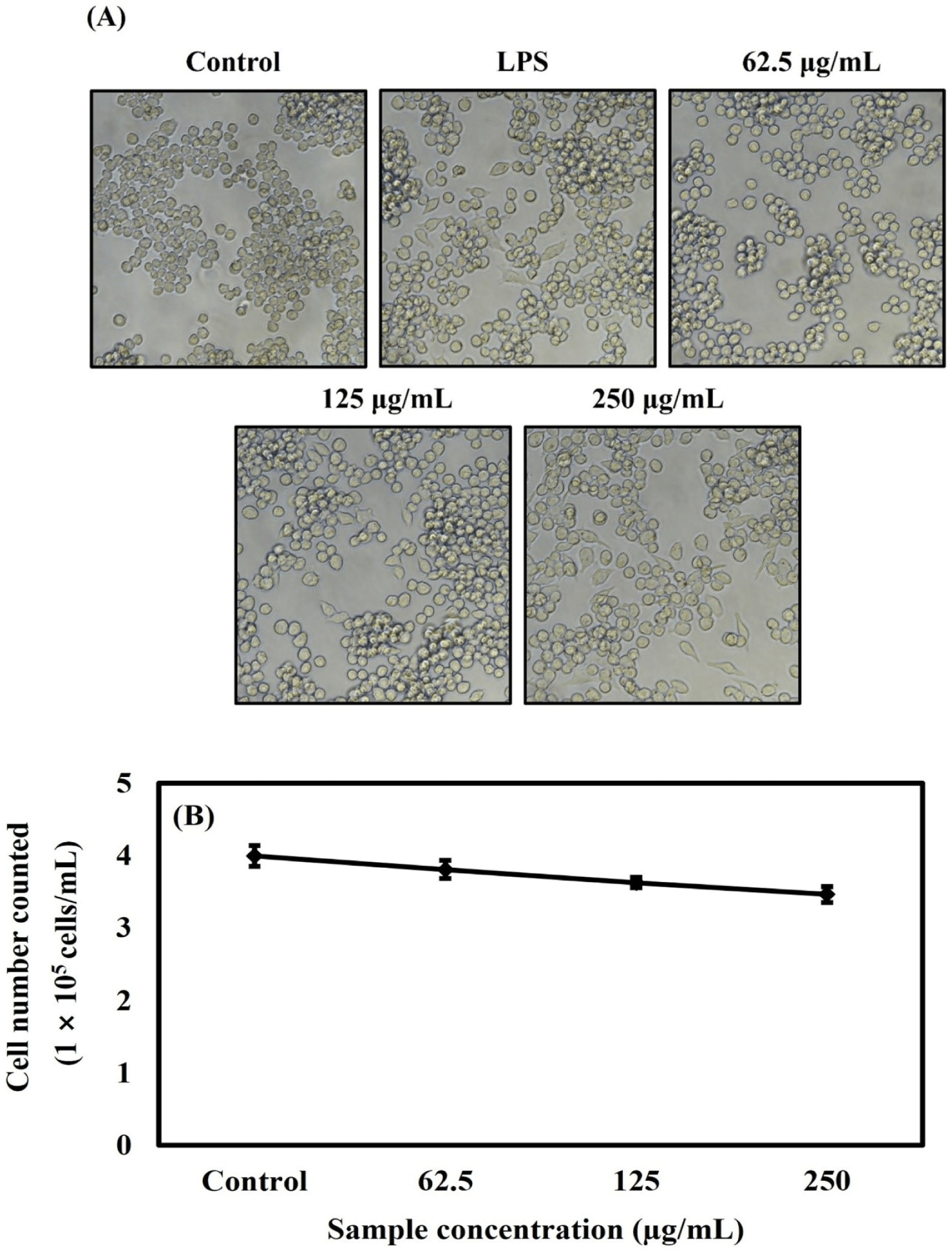
The cells were treated with OMPA concentrations of 62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL to investigate the morphology and number of the RAW 264.7 cells under OMPA or LPS (10 ng/mL) treatment. As shown in Fig. 4A, it showed that the normal morphology of RAW 264.7 cells in the control group was round. After treatment with 250 μg/mL OMPA, the cells increased in size and showed a dendritic-like morphology, similar to the morphological changes observed in the LPS-treated group. As shown in Fig. 4B, the number of RAW cells was deceased by OMPA to 3.8×105 cells/mL, 3.6×105 cells/mL, and 3.4×105 cells/mL at 62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL, respectively. These results from the trypan blue assay showed a similar tendency to the effect of OMPA on the cell viability of Fig. 2.
Cytokines are humoral factors responsible for transducing signals between cells to maintain homeostasis and play a central role in the pathophysiology of various diseases (Narazaki and Kishimoto, 2022). Pro-inflammatory cytokines regulate host defense against pathogens by initiating inflammatory responses and mediating innate immune responses (Xiao et al., 2020).
TNF-α is a crucial component of the innate immune system, offering initial protection against foreign invaders prior to the activation of the adaptive immune response (Medzhitov and Janeway, 2000). It is primarily synthesized by macrophages upon the activation of membrane-bound pattern-recognition receptors, which recognize typical bacterial cell surface components, such as polysaccharides, carbohydrates, and LPSs (Berry et al., 2007).
IL-6 is an important signaling molecule in the transition from the innate immune response to the adaptive immune response (Wu et al., 2018). IL-6 stimulates the production of macrophages and neutrophils in innate immunity, and plays an important role in B cell maturation in adaptive immunity (Lee et al., 2022c). Therefore, the effects of OMPA treatment on the production and mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) were evaluated using ELISA and qRT-PCR.
As shown in Figs. 5A and B, OMPA treatment increased the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) in a dose-dependent manner (p<0.05). Compared with LPS, which was used as a positive control, when the concentration of OMPA was 250 μg/mL, the production of TNF-α and IL-6 increased 2.3-fold and 15.4-fold, respectively.
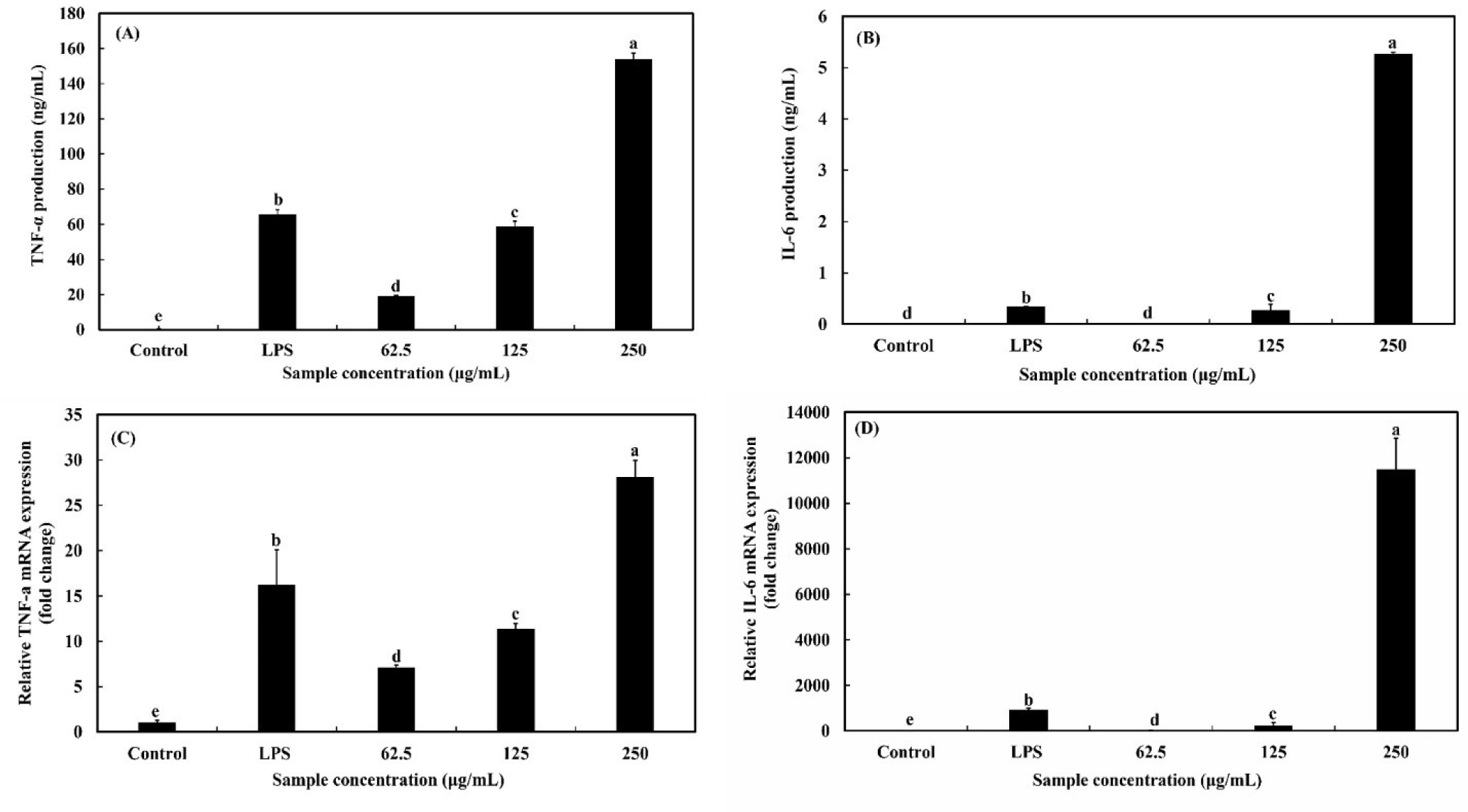
Moreover, as presented in Figs. 5C and D, the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) was dose-dependently enhanced in RAW 264.7 macrophages (p<0.05) by treatment with OMPA. After the treatment OMPA at a concentration of 250 μg/mL, the level of mRNA expression (TNF-α and IL-6) in RAW 264.7 macrophages increased to by 1.7 times and 12.3 times, respectively. These results show that immune-modulating effects can be exerted by upregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines in macrophages at both mRNA and protein levels and that OMPA stimulates macrophages to upregulate pro-inflammatory cytokine and mRNA expression.
MAPK is a protein kinase capable of self-phosphorylation, specifically at its dual serine and threonine residues (Peti and Page, 2013). The MAPK signaling pathway is activated when ERK, JNK, and p38 are phosphorylated. Growth factors, hormones, and pro-inflammatory stimuli trigger ERK activation, whereas cellular and environmental stressors, along with pro-inflammatory stimuli, induce the activation of JNK and p38 (Kyriakis and Avruch, 2012; Mercedes et al., 2016). The MAPK signaling pathway contributes significantly to the regulation of various cellular physiological activities, including cell growth, maturation, proliferation, and apoptosis (Guo et al., 2020). Therefore, Western blotting was performed to determine whether OMPA treatment induces the phosphorylation of MAPKs (ERK, JNK, and p38) to activate RAW 264.7 cells.
As shown in Figs. 6A, B, C, and D, treatment with OMPA at 62.5, 125, and 250 μg/mL induced the phosphorylation of p38, JNK and ERK, respectively, compared with the control. In contrast, no differences were observed in the total protein levels of p38, JNK, or ERK. LPS, a component of the cell wall in gram-negative bacteria, induces MAPK phosphorylation and contributes to macrophage activation. Treatment with OMPA (250 μg/mL) triggered the phosphorylation of ERK, JNK, and p38 to a level similar to that observed with LPS treatment.
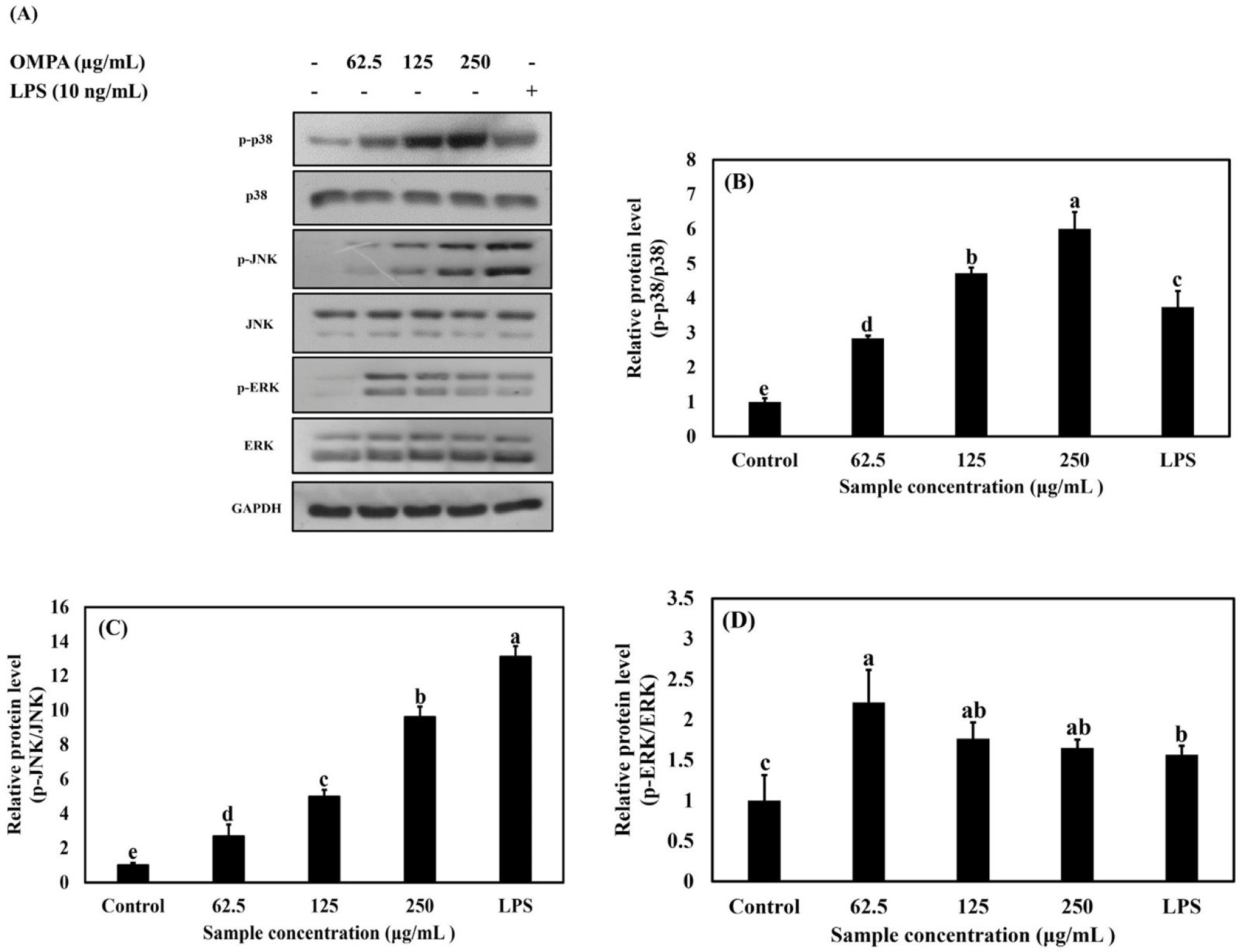
These results indicate that OMPA triggers the activation of RAW 264.7 macrophages via the p38, JNK, and ERK signaling pathways.
Conclusion
In the present study, investigated the immunostimulatory effects of OMHs on RAW 264.7 cells. In conclusion, OMPA enhanced iNOS mRNA expression and NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. In addition, the treatment OMPA increased the production of TNF-α and IL-6 and gene expression mRNA expression by stimulating RAW 264.7 cells. OMPA triggered the phosphorylation of p38, JNK, and ERK, which are involved in the MAPK signaling pathway. Therefore, OMPA has been demonstrated to be a potential immune-stimulating agent in the pharmaceutical and or functional food industries. Furthermore, the poultry industry development can be improved by making high-valued functional poultry products, but further in vivo studies should be carried out to confirm the activity and safety of OMPA.













